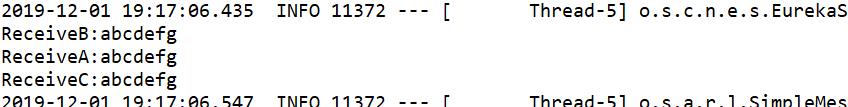springboot-rabbitmq的使用
Posted 哎哟我去a
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了springboot-rabbitmq的使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一.RabbitMQ的介绍
RabbitMQ是消息中间件的一种,消息中间件即分布式系统中完成消息的发送和接收的基础软件.这些软件有很多,包括ActiveMQ(apache公司的),RocketMQ(阿里巴巴公司的,现已经转让给apache).
消息中间件的工作过程可以用生产者消费者模型来表示.即,生产者不断的向消息队列发送信息,而消费者从消息队列中消费信息.具体过程如下:
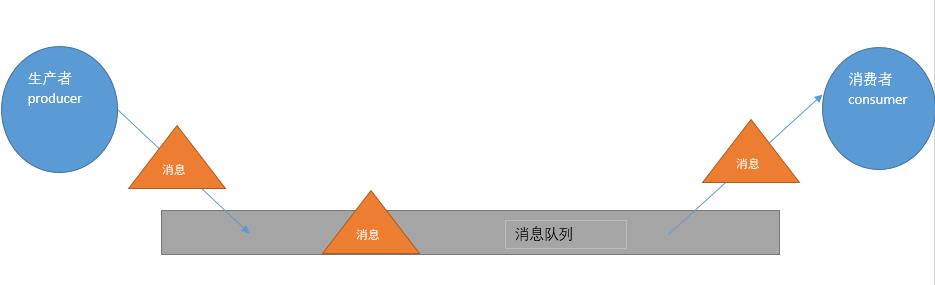
从上图可看出,对于消息队列来说,生产者,消息队列,消费者是最重要的三个概念,生产者发消息到消息队列中去,消费者监听指定的消息队列,并且当消息队列收到消息之后,接收消息队列传来的消息,并且给予相应的处理.消息队列常用于分布式系统之间互相信息的传递.
对于RabbitMQ来说,除了这三个基本模块以外,还添加了一个模块,即交换机(Exchange).它使得生产者和消息队列之间产生了隔离,生产者将消息发送给交换机,而交换机则根据调度策略把相应的消息转发给对应的消息队列.那么RabitMQ的工作流程如下所示:
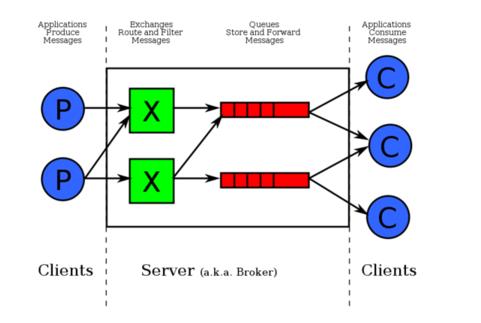
紧接着说一下交换机.交换机的主要作用是接收相应的消息并且绑定到指定的队列.交换机有四种类型,分别为Direct,topic,headers,Fanout.
Direct是RabbitMQ默认的交换机模式,也是最简单的模式.即创建消息队列的时候,指定一个BindingKey.当发送者发送消息的时候,指定对应的Key.当Key和消息队列的BindingKey一致的时候,消息将会被发送到该消息队列中.
topic转发信息主要是依据通配符,队列和交换机的绑定主要是依据一种模式(通配符+字符串),而当发送消息的时候,只有指定的Key和该模式相匹配的时候,消息才会被发送到该消息队列中.
headers也是根据一个规则进行匹配,在消息队列和交换机绑定的时候会指定一组键值对规则,而发送消息的时候也会指定一组键值对规则,当两组键值对规则相匹配的时候,消息会被发送到匹配的消息队列中.
Fanout是路由广播的形式,将会把消息发给绑定它的全部队列,即便设置了key,也会被忽略.
二.项目工程的依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.7.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>1.7</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
<scope>true</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加springboot对amqp的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
三、配置文件
spring: rabbitmq: host: 115.29.140.222 port: 5672 username: guest password: guest virtualHost: / publisher-returns: true #开启发送失败退回 publisher-confirms: true #开启发送确认 listener: direct: prefetch: 1000 concurrency: 2000 max-concurrency: 5000
四、依次写rabbitmq的 Direct模式、top、Fanout的模式
(1)Direct模式:此模式是点对点模式,即:发送消息的队列名称和接收队列的名称一致,否则接收方接收不到消息;例: 发送者队列A 接收者只能接收A
Direct的配置:
@Configuration public class DirectConfig { @Bean public Queue queueA() { return new Queue("queueA"); } @Bean public Queue queueB() { return new Queue("queueB"); } @Bean public Queue queueC() { return new Queue("queueC"); } }
(2) Direct 发送消息端
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class DirectSend { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate; public void send() { for(int i=0;i<3;i++) { if(i==0) { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("queueA","a"); }else if(i==1) { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("queueB","b"); } if(i==2) { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("queueC","c"); } } } }
(2) Direct 接收消息端
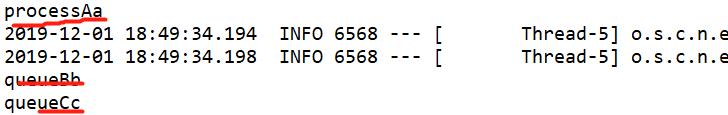
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class DirectReceiver { @RabbitListener(queues="queueA") public void processA(String str) { System.out.println("processA"+str); } @RabbitListener(queues="queueB") public void processB(String str) { System.out.println("queueB"+str); } @RabbitListener(queues="queueC") public void processC(String str) { System.out.println("queueC"+str); } }
(3)测试
import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; import com.supers.system.SystemApp; import com.supers.system.rabbitmq.DirectSend; import com.supers.system.rabbitmq.FanoutSender; import com.supers.system.rabbitmq.TopSend; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = SystemApp.class) //自己的启动类 public class RabbitMqHelloTest { @Autowired private DirectSend directSend; @Test public void directSend() throws Exception { directSend.send(); } }
(2)Fanout Exchange形式 : 需要配置队列Queue,再配置交换机(Exchange),再把队列按照相应的规则绑定到交换机上:
@Configuration public class TopConfig { @Bean(name="message") public Queue queueMessage() { return new Queue("topic.message"); } @Bean(name="messages") public Queue queueMessages() { //队列绑定的路由键规则 return new Queue("topic.messages"); } //交换机 @Bean public TopicExchange exchange() { return new TopicExchange("exchange"); } @Bean //将队列绑定此交换机上,路由的键是topic Binding bindingExchangeMessage(@Qualifier("message") Queue queueMessage, TopicExchange exchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessage).to(exchange).with("topic.message"); //topic.message 路由键 } @Bean Binding bindingExchangeMessages(@Qualifier("messages") Queue queueMessages, TopicExchange exchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(queueMessages).to(exchange).with("topic.#");//*表示一个词,#表示零个或多个词 } }
发送端的配置:
@Component public class TopSend { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate; public void send() { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange","topic.message","hello,topic.message"); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange","topic.messages","hello,topic.messages"); } }
接收端的:
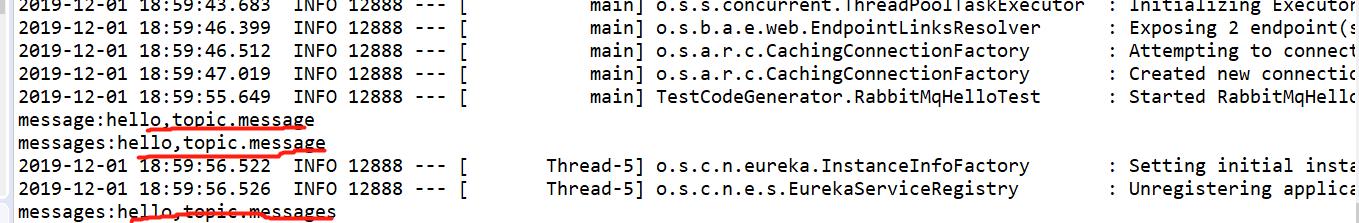
@Component public class TopReceiver { @RabbitListener(queues="topic.message") public void process1(String str) { System.out.println("message:"+str); } @RabbitListener(queues="topic.messages") public void process2(String str) { System.out.println("messages:"+str); } }
测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = SystemApp.class) public class RabbitMqHelloTest { @Autowired private DirectSend directSend; @Autowired private TopSend topSend; @Test public void directSend() throws Exception { directSend.send(); } @Test public void TopSend() throws Exception { topSend.send(); } }
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange","topic.message","hello,topic.message");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("exchange","topic.messages","hello,topic.messages");
方法的第一个参数是交换机名称,第二个参数是发送的key,第三个参数是发送的消息;由于messages的路由键的规则为topic.# ,所以messages队列可以接收到message的消息,#的意思匹配零个或多个;
Fanout Exchange: 广播式,们发送到路由器的消息会使得绑定到该路由器的每一个Queue接收到消息,发送端配置如下:
@Configuration public class FanoutConfig { @Bean(name="debugMessage") public Queue debugMessage() { return new Queue("fanout.debug"); } @Bean(name="infoMessage") public Queue infoMessage() { return new Queue("fanout.info"); } @Bean(name="WarnMessage") public Queue WarnMessage() { return new Queue("fanout.warn"); } @Bean FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() { return new FanoutExchange("fanoutExchange");//配置广播路由器 } @Bean Binding bindingExchangeDebug(@Qualifier("debugMessage") Queue debugMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(debugMessage).to(fanoutExchange()); } @Bean Binding bindingExchangeInfo(@Qualifier("infoMessage") Queue infoMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(infoMessage).to(fanoutExchange()); } @Bean Binding bindingExchangeWarn(@Qualifier("WarnMessage") Queue WarnMessage, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(WarnMessage).to(fanoutExchange()); } }
发送端的代码
@Component public class FanoutSender { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate; public void send() { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange","","abcdefg"); } }
接收端的代码
@Component public class FanoutReceiver { @RabbitListener(queues="fanout.debug") public void processA(String str1) { System.out.println("ReceiveA:"+str1); } @RabbitListener(queues="fanout.info") public void processB(String str) { System.out.println("ReceiveB:"+str); } @RabbitListener(queues="fanout.warn") public void processC(String str) { System.out.println("ReceiveC:"+str); } }
测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = SystemApp.class) public class RabbitMqHelloTest { @Autowired private DirectSend directSend; @Autowired private TopSend topSend; @Autowired FanoutSender fanoutSender; @Test public void directSend() throws Exception { directSend.send(); } @Test public void TopSend() throws Exception { topSend.send(); } @Test public void fanoutSend() throws Exception { fanoutSender.send(); } }
以上三种模式:top模式最为灵活
以上是关于springboot-rabbitmq的使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章