JAVA 图形开发中组件对齐方法及界面开发
Posted ITryagain
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JAVA 图形开发中组件对齐方法及界面开发相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
/*文章中用到的代码只是一部分,需要源码的可通过邮箱联系我 1978702969@qq.com*/
在上篇博客中提到了JAVA图形界面开发时的两种布局,流式布局和边框布局。
在实际使用中可能会发现,往容器中添加组件往往并不能得到想要的结果。比如想上下对齐两个组件,而流式布局是从左到右的,此时就很难实现上下对齐,此篇文章将介绍两个方法。
1.直接使用坐标贴图
如下面这个计算器的制作
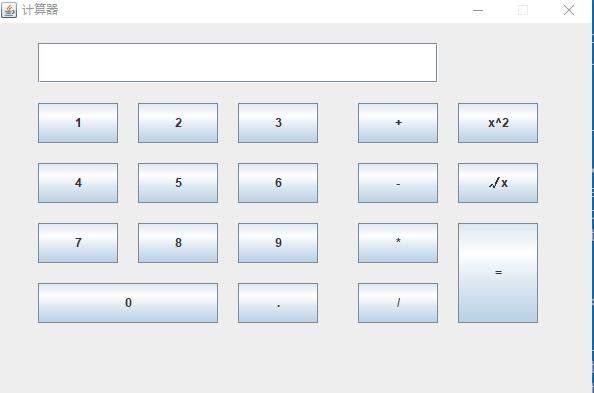

1 package Graphic; 2 3 import java.awt.BorderLayout; 4 import java.awt.Dimension; 5 import java.awt.FlowLayout; 6 7 import javax.swing.JButton; 8 import javax.swing.JFrame; 9 import javax.swing.JLabel; 10 import javax.swing.JPanel; 11 import javax.swing.JTextField; 12 13 public class Calculator { 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 Calculator login = new Calculator(); 17 login.Init(); 18 } 19 20 public void Init() 21 { 22 String arr[] = {"1","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9","0","+","-","*","/","="}; 23 24 JFrame frame = new JFrame(); 25 frame.setTitle("计算器"); 26 frame.setSize(600,400); 27 frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null); 28 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(3); 29 frame.setResizable(false); 30 31 frame.setLayout(null); 32 33 JTextField text1 = new JTextField(); 34 text1.setBounds(40, 20, 400, 40); 35 frame.add(text1); 36 37 38 for(int i=0;i<9;i++) 39 { 40 JButton button = new JButton(); 41 button.setText(arr[i]); 42 button.setBounds((i%3)*100+40, (i/3)*60+80, 80, 40); 43 frame.add(button); 44 } 45 46 JButton button = new JButton(); 47 button.setText("0"); 48 button.setBounds(40, 260, 180, 40); 49 frame.add(button); 50 51 JButton button1 = new JButton(); 52 button1.setText("."); 53 button1.setBounds(240, 260, 80, 40); 54 frame.add(button1); 55 56 for(int i=10;i<arr.length - 1;i++) 57 { 58 JButton button2 = new JButton(); 59 button2.setText(arr[i]); 60 button2.setBounds(360, (i-10)*60+80, 80, 40); 61 frame.add(button2); 62 } 63 64 65 JButton button2 = new JButton(); 66 button2.setText("x^2"); 67 button2.setBounds(460, 80, 80, 40); 68 frame.add(button2); 69 70 JButton button3 = new JButton(); 71 button3.setText("√x"); 72 button3.setBounds(460, 140, 80, 40); 73 frame.add(button3); 74 75 JButton button4 = new JButton(); 76 button4.setText("="); 77 button4.setBounds(460, 200, 80, 100); 78 frame.add(button4); 79 80 frame.setVisible(true); 81 } 82 }
2.设置组件大小
下面这个界面的制作
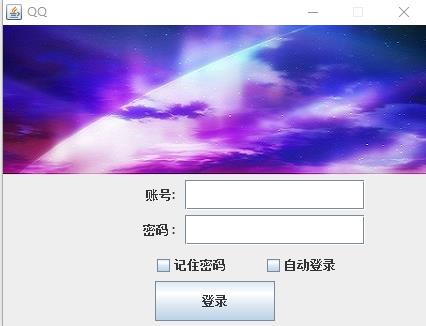

1 package Graphic; 2 3 import java.awt.BorderLayout; 4 import java.awt.Dimension; 5 import java.awt.FlowLayout; 6 7 import javax.swing.ImageIcon; 8 import javax.swing.JButton; 9 import javax.swing.JCheckBox; 10 import javax.swing.JFrame; 11 import javax.swing.JLabel; 12 import javax.swing.JPanel; 13 import javax.swing.JPasswordField; 14 import javax.swing.JTextField; 15 16 public class Login1 { 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 20 Login1 login = new Login1(); 21 login.Init(); 22 } 23 24 public void Init() 25 { 26 JFrame frame = new JFrame(); 27 frame.setTitle("QQ"); 28 frame.setSize(430,330); 29 frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null); 30 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(3); 31 frame.setResizable(false); 32 33 BorderLayout b1 = new BorderLayout(); 34 frame.setLayout(b1); 35 //添加图片 北 36 ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon("C:\\\\Users\\\\long452a\\\\Desktop\\\\a1.jpg"); 37 JLabel labIcon = new JLabel(icon); 38 frame.add(labIcon,BorderLayout.NORTH); 39 40 //添加面板容器:账号、密码 41 JPanel centerPanel = new JPanel(); 42 centerPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER,10,5)); 43 44 JLabel labName = new JLabel("账号:"); 45 labName.setHorizontalAlignment(JLabel.RIGHT);//这步很关键,通过设置右对齐的方式在前面补空 46 labName.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(110,30)); 47 centerPanel.add(labName); 48 49 JTextField textName = new JTextField(); 50 textName.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(180,30)); 51 centerPanel.add(textName); 52 53 54 JLabel labPassowrd = new JLabel("密码 :"); 55 labPassowrd.setHorizontalAlignment(JLabel.RIGHT); 56 labPassowrd.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(110,30)); 57 centerPanel.add(labPassowrd); 58 59 JPasswordField textPassword = new JPasswordField(); 60 textPassword.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(180,30)); 61 centerPanel.add(textPassword,labPassowrd); 62 63 64 JPanel centerPanel1 = new JPanel(); 65 centerPanel1.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER,5,5)); 66 JCheckBox rememberBox = new JCheckBox(); 67 rememberBox.setText("记住密码"); 68 rememberBox.setHorizontalAlignment(JLabel.RIGHT); 69 rememberBox.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(140,30)); 70 centerPanel.add(rememberBox); 71 72 JCheckBox rememberBox2 = new JCheckBox(); 73 rememberBox2.setText("自动登录"); 74 rememberBox2.setHorizontalAlignment(JLabel.RIGHT); 75 rememberBox2.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(100,30)); 76 centerPanel.add(rememberBox2); 77 78 JButton southButton = new JButton(); 79 southButton.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(120,40)); 80 southButton.setText("登录"); 81 centerPanel1.add(southButton); 82 83 frame.add(centerPanel1, BorderLayout.SOUTH); 84 frame.add(centerPanel,BorderLayout.CENTER); 85 frame.setVisible(true); 86 } 87 }
以上是关于JAVA 图形开发中组件对齐方法及界面开发的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
