java集合系列之LinkedList源码分析
Posted sowhat1943
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java集合系列之LinkedList源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
java集合系列之LinkedList源码分析
- LinkedList数据结构简介
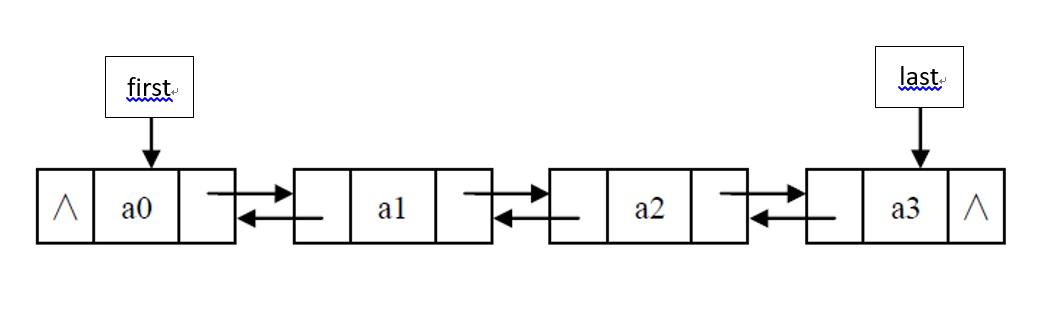
LinkedList底层是通过双端双向链表实现的,其基本数据结构如下,每一个节点类为Node对象,每个Node节点包含该节点的数据和分别指向前一个前一个和后一个节点的引用。LinkedList内部维护两个成员变量first和last,分别指向链表的头节点和尾节点(接下来的成员变量介绍中会提到)。由于LinkedList基于链表,因此查询速度慢,增删速度快,又因为链表为双端双向,因此可进行双向遍历。
其实对LinkedList的各种操作其实是对链表的各种操作!!!
/** *节点类 * */ private static class Node<E> { E item;//节点数据 Node<E> next;//指向前一个节点的引用 Node<E> prev;//指向后一个节点的引用 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
- LinkedList成员变量
//链表节点数量,即集合包含的元素数量 transient int size = 0; //链表的头节点 transient Node<E> first; //链表的尾节点 transient Node<E> last;
另外还有一个从父类继承的modCount成员变量,关于modCount的介绍已经在本人的ArrayList源码分析一文中进行过介绍(https://www.cnblogs.com/gdy1993/p/9246250.html),因此此文简单带过,不再详述。
protected transient int modCount = 0;
- LinkedList构造方法
LinkedList有两个构造方法,一个空参,一个传入一个Collection集合,然后调用addAll(c)方法
/** * 空参构造:并未对链表进行初始化 */ public LinkedList() { } /** * 传入一个Collection集合 */ public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); }
/** * 往链表尾部添加元素,内部调用了addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c),传入的是索引为size,即一个元素添加的索引 */ public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(size, c); } /** * 往指定索引处添加元素 * 1. 首先判断该索引是否越界,必须保证index >= 0 && index <= size * 2. 将Collection集合转变成为数组 * 3. 如果数组长度为 0 ,直接返回false * 4. 根据index是否为最后,对下一个元素的前节点(pred)和后节点(succ)进行设置 * 5. 把数组中的元素依次从index位置向后插入 * 6. 设置last节点 * 7. 修改size和modCount */ public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { checkPositionIndex(index);//1 Object[] a = c.toArray();//2 int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0)//3 return false; Node<E> pred, succ;//4 if (index == size) {//如果要添加元素至链表最后 succ = null;//下一个节点为null pred = last;//上一个节点为当前链表的last节点 } else {//如果添加元素不在链表最后 succ = node(index);//获得第index个节点,并赋值给succ pred = succ.prev;// } for (Object o : a) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); if (pred == null)//如果之前链表为空 first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; pred = newNode;//将新添加的节点置为下一个要添加元素的前一个节点 } //6 if (succ == null) {//如果index == size last = pred;//最后添加的节点就是last节点 } else {//如果不是,双向关联Collection集合中的最后一个节点和原来链表的第index个节点 pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } //7. size += numNew; modCount++; return true; } //检查索引是否越界 private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index <= size; } private void checkPositionIndex(int index) { if (!isPositionIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); }
- LinkedList添加元素
/** * 从集合头部添加元素 */ public void addFirst(E e) { linkFirst(e); } /** *从集合尾部添加元素 */ public void addLast(E e) { linkLast(e); } /** * 往链表头部添加元素 * 1. 保存原来的first节点 * 2. 创建新节点,并将first指向该新节点 * 3. 如果原链表为空,将最后一个节点指向新节点 * 4. 若不为空,将原来的first节点(以保存)的前一个节点设置为新节点 * 5. 修改size和modCount */ private void linkFirst(E e) { final Node<E> f = first;//1 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);//2 first = newNode;//2 if (f == null)//3 last = newNode; else//4 f.prev = newNode; size++; modCount++; } /** * 往链表尾部添加元素:其原理与linkFirst()基本相同,不再介绍 */ void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
/** * 从指定位置处添加元素: * 1. 检查索引是否越界 index >= 0 && index <= size * 2. 如果要添加的索引为链表最后一个节点的下一个节点,即往链表末端追加节点 * 3. 如果不是往链表末端添加节点.将该节点插入到原链表的第index个节点前边 */ public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index);//1. if (index == size) linkLast(element);//2. else linkBefore(element, node(index));//3. } /** * 将节点插入到succ节点前边 */ void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;//保留succ的前一个节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);//创建新节点,并将新节点的前一个节点指向pred,后一个节点指向succ succ.prev = newNode;//将succ的前一个节点指向新节点 if (pred == null)//判断新节点是否在链表顶端 first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
addAll()方法已经在构造方法中介绍过。
- LinkedList删除方法
/** * 删除头结点 * 如果头结点为空,即集合为空,抛出NoSuchElementException * 否则调用unlinkFirst()删除 */ public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkFirst(f); } /** * 删除头结点,并将其数据设为null,以help GC */ private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { final E element = f.item;//获取头结点数据 final Node<E> next = f.next;//获得头结点的下一个节点 f.item = null;//help GC f.next = null; // help GC first = next;//将头结点的下一个节点设为新的头结点 if (next == null)//如果原来链表只有一个节点,删除后现在链表为空,则将last指向null last = null; else//否则,将现在头节点的前一个节点指向null next.prev = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
/** * 删除尾节点,如果集合为空,则抛出NoSuchElementException * 否则调用unlinkLast()方法删除 */ public E removeLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkLast(l); } /** * 基本原理与unlinkedFirst相同,不再介绍 */ private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) { final E element = l.item; final Node<E> prev = l.prev; l.item = null; l.prev = null; // help GC last = prev; if (prev == null) first = null; else prev.next = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
/** *删除指定索引处的元素: * 首先检查索引是否越界 * 调用unlink()删除 */ public E remove(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); } /** * 删除指定节点 */ E unlink(Node<E> x) { final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) {//如果删除的是头结点 first = next;//将next设置为新的头结点 } else {//否则 prev.next = next;//将删除节点的前一个节点指向其后一个节点 x.prev = null;//将删除节点的前一个节点置为null,help GC } if (next == null) {//如果删除节点的后一个节点为null,表明删除节点为last节点 last = prev;//将删除节点的前一个节点设为last节点 } else {//否则 next.prev = prev;//将删除节点的后一个节点的前一个节点设为删除节点的前一个节点(有点绕) x.next = null;//help GC } x.item = null;//help GC size--; modCount++; return element;//返回删除元素 }
- LinkedList查询
/** * 获取头结点的数据 */ public E getFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return f.item; } /** * 获取尾节点的数据 */ public E getLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return l.item; }
/** * 获取指定索引处的元素,首先检查索引是否越界,然后调用node()方法 */ public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; } /** * 其实链表是不能通过索引进行访问的,正式这个方法使得LinkedList可通过索引访问 */ Node<E> node(int index) { //如果索引小于链表长度的一半,则从first节点从前往后找 if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else {//如果索引大于链表长度的一半,则从后往前找 Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
/** * 从前向后遍历查找指定元素,如果o==null,则用==判断,否则,使用equals判断 */ public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } return -1; } /** * 从后向前遍历查找指定元素,如果o==null,则用==判断,否则,使用equals判断 */ public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { int index = size; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (x.item == null) return index; } } else { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; } } return -1; }
- 补充
1. LinkedList实现类Deque<E>接口,Deque<E>继承自Queue,因此它具备一些队列的特有方法,而且是双端队列,不过这些方法都是基于以上增删查方法实现的,不再做详细解释;另外也可以实现栈的相关方法
/** * 返回first的数据,如果链表为空,返回null */ public E peek() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; } /** * 返回first的数据,如果链表为空抛出NoSuchElementException */ public E element() { return getFirst(); } /** *删除并返回头节点的数据,如果头结点为null,返回null */ public E poll() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); } /** * 删除头结点的元素,如果链表为空,抛出NoSuchElementException */ public E remove() { return removeFirst(); } /** * 添加元素,添加到链表最后 */ public boolean offer(E e) { return add(e); } // Deque operations /** * 添加头结点 */ public boolean offerFirst(E e) { addFirst(e); return true; } /** * 添加尾节点 */ public boolean offerLast(E e) { addLast(e); return true; } /** * 返回头结点 */ public E peekFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; } /** * 返回尾节点 */ public E peekLast() { final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : l.item; } /** * 返回并删除头结点 */ public E pollFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); } /** * 返回并删除尾节点 */ public E pollLast() { final Node<E> l = last; return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l); } /** * 压栈 */ public void push(E e) { addFirst(e); } /** *弹栈 */ public E pop() { return removeFirst(); }
- LinkedList集合的遍历
关于对LinkedList的迭代遍历的并发修改问题的实现与ArrayList的原理基本相同,可参见(https://www.cnblogs.com/gdy1993/p/9246250.html),不再这里介绍了。
以上是关于java集合系列之LinkedList源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章