剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
Posted 徐同学呀
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题干
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制:
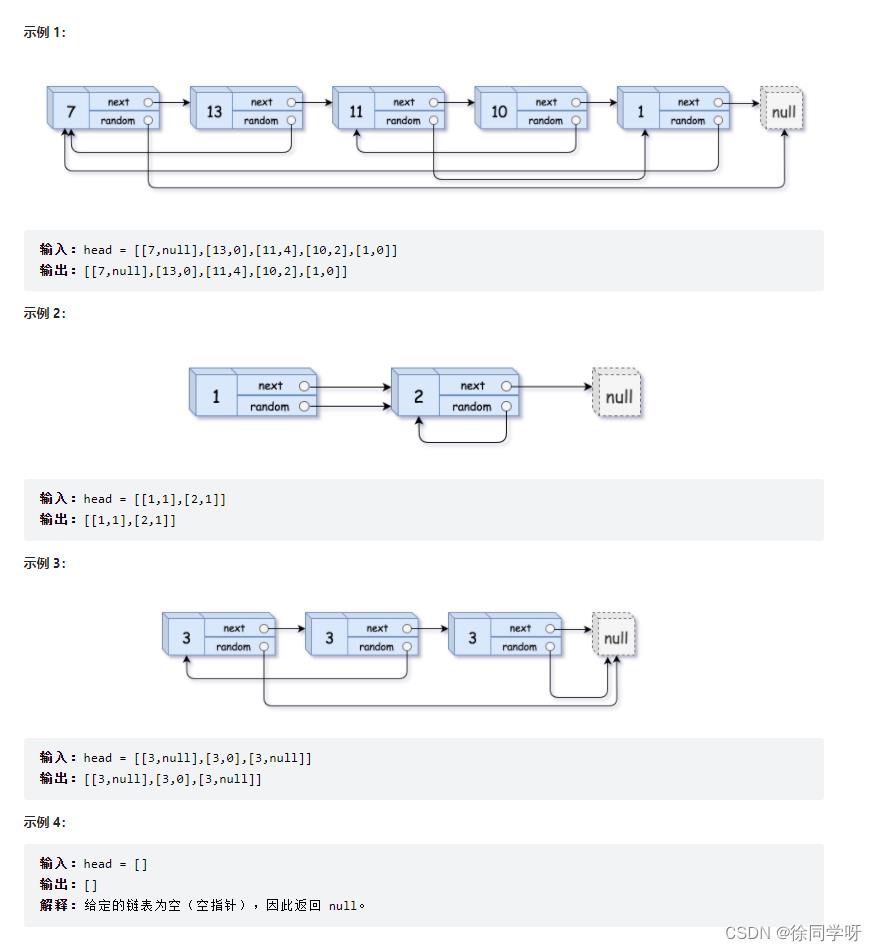
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val)
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
*/
class Solution
public Node copyRandomList(Node head)
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9p0yy1/
思路解析
普通链表复制很简单,可以从一个节点遍历完所有节点,但是复杂链表的复制难点就在random指针的不确定性。
在通过next指针顺序遍历并构建新链表时,random指针指向的节点对应到的新节点可能还没创建,所以无法单纯通过遍历构建新节点的random指针。
方法一:哈希表存储新旧节点关系
既然在构建新节点的random指针时,random指针指向的新节点可能还没有创建,那么一次性把新节点都创建出来不就行了?
利用哈希表 map,key为 旧节点,value 为新节点:
- 顺序遍历原链表,将旧新节点键值对关系存储到哈希表
map中。 - 再次从头遍历原链表,从
map中通过旧节点取出新节点,构建新链表: map.get(旧节点).next = map.get(旧节点.next);map.get(旧节点).random= map.get(旧节点.random);
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度 O(N): 两轮遍历链表,使用 O(N) 时间。
空间复杂度 O(N): 哈希表 map 使用线性大小的额外空间。
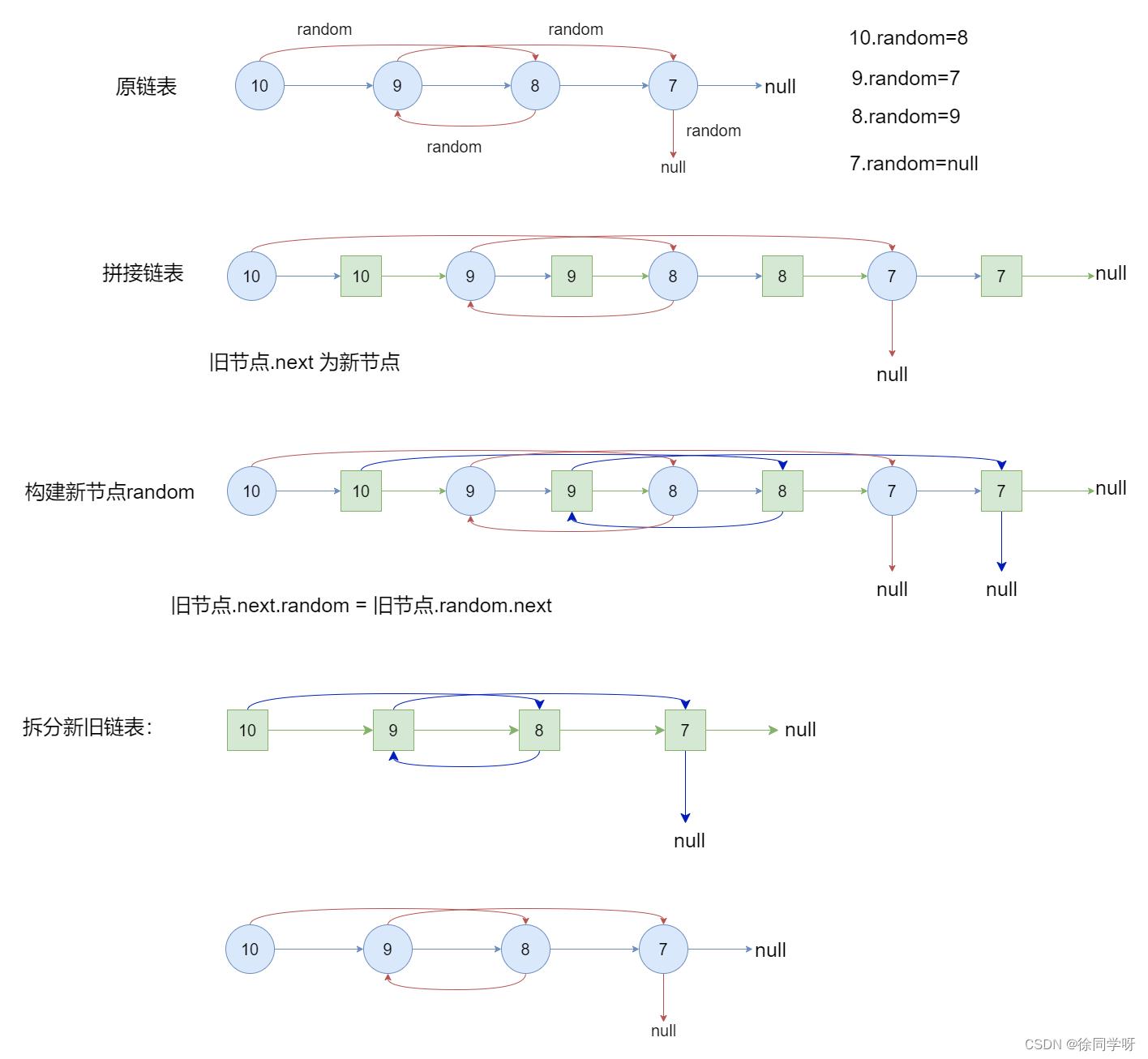
方法二:拼接+拆分
- 新旧节点构建成一条链表:旧节点1–>新节点1–>旧节点2–>新节点2,如此就有:旧节点.next为新节点
- 构建新节点的random:
旧节点.next.random = 旧节点.random.next; - 拆分新旧链表:设置
pre / cur分别指向旧 / 新链表头节点,遍历执行pre.next = pre.next.next和cur.next = cur.next.next将两链表拆分开。
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度 O(N): 三轮遍历链表,使用 O(N)时间。
空间复杂度 O(1): 节点引用变量使用常数大小的额外空间。
说实在的,还是借助哈希表的方式容易理解,方法二有三次遍历,虽然也可以算是O(n),但毕竟多了一次遍历,而且代码相对复杂。
如果对内存没什么要求,个人推荐方法一。
代码实现
方法一:哈希表存储新旧节点关系
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val)
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
*/
class Solution
public Node copyRandomList(Node head)
if (head == null)
return null;
Node cur = head;
// 构建一个map
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
while (cur != null)
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
cur = head;
// 遍历构建原节点对应的新节点的next、random
while (cur != null)
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
return map.get(head);
方法二:拼接+拆分
public Node copyRandomList(Node head)
if (head == null)
return null;
//合成一个长链表
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null)
Node tmp = new Node(cur.val);
tmp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = tmp;
cur = tmp.next;
// 构建新节点的random
cur = head;
while (cur != null)
if (cur.random != null)
// 前提是 cur.random != null
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
// 拆分出两个链表,使用双指针
Node res = head.next;
Node pre = head;
cur = res;
// while 终止条件是cur向右移动到最后一个新节点,
// cur.next 为 null 时终止
while (cur.next != null)
// 必须先拆分pre,如果先拆cur,会使链表断开,影响拆分pre
pre.next = pre.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
// 遍历结束,cur.next 为 null,
// 但是 旧链表的尾节点的next还指向新链表的尾节点
// 所以 单独处理旧链表尾节点
pre.next = null;
return res;
参考致谢:https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/illustration-of-algorithm/9plk45/
以上是关于剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章