Spring Boot入门系列六( SpringBoot 整合thymeleaf)
Posted 乾源
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring Boot入门系列六( SpringBoot 整合thymeleaf)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
SpringBoot 整合thymeleaf
一、什么是Thymeleaf模板
Thymeleaf是一款用于渲染XML/Xhtml/HTML5内容的模板引擎。类似JSP,Velocity,FreeMaker等,它也可以轻易的与Spring MVC等Web框架进行集成作为Web应用的模板引擎。与其它模板引擎相比,Thymeleaf最大的特点是能够直接在浏览器中打开并正确显示模板页面,而不需要启动整个Web应用。它的功能特性如下:
-
@Controller中的方法可以直接返回模板名称,接下来Thymeleaf模板引擎会自动进行渲染
-
模板中的表达式支持Spring表达式语言(Spring EL)
-
表单支持,并兼容Spring MVC的数据绑定与验证机制
-
国际化支持
Spring官方也推荐使用Thymeleaf,所以本篇代码整合就使用Thymeleaf来整合。
二、开发步骤
1、在maven中引入依赖
<!--热部署-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
2、在配置文件application.properties配置thymeleaf模板
Spring-Boot配置文件thymeleaf模板配置项(常用配置项为红色)
|
################################ ## thymeleaf模板 ################################ #应用于模板的模板模式。另请参见StandardTemplateModeHandlers spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5 #模板编码 spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8 #Content-Type值 spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html #开发时关闭缓存,不然没法看到实时页面 spring.thymeleaf.cache=false #在构建URL时预先查看名称的前缀 spring.thymeleaf.prefix = classpath:/templates/ #构建URL时附加查看名称的后缀 spring.thymeleaf.suffix = .html
3、创建Thymeleaf模板文件,在template中新增文件夹thymeleaf,并在新建的文件夹中新增index.html用于显示controller返回的数据
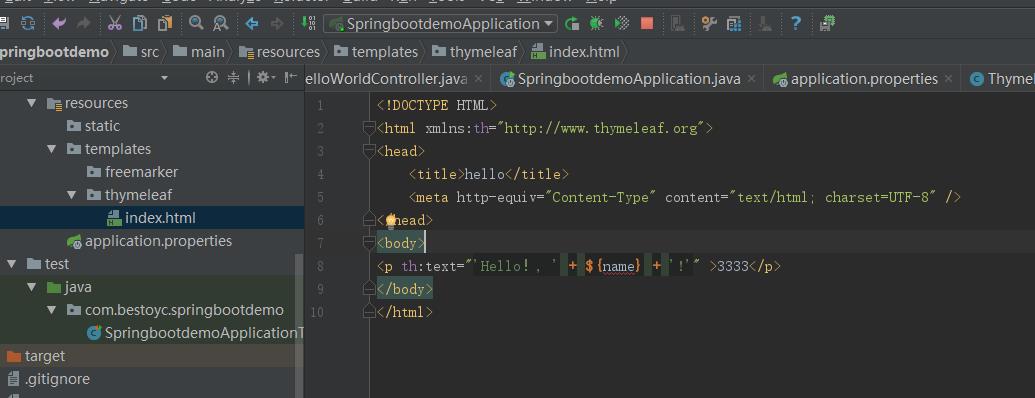
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <title>hello</title> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /> </head> <body> <p th:text="\'Hello!, \' + ${name} + \'!\'" >3333</p> </body> </html>
4、在controller中新增ThymeleafController.java,用于向前端返回数据
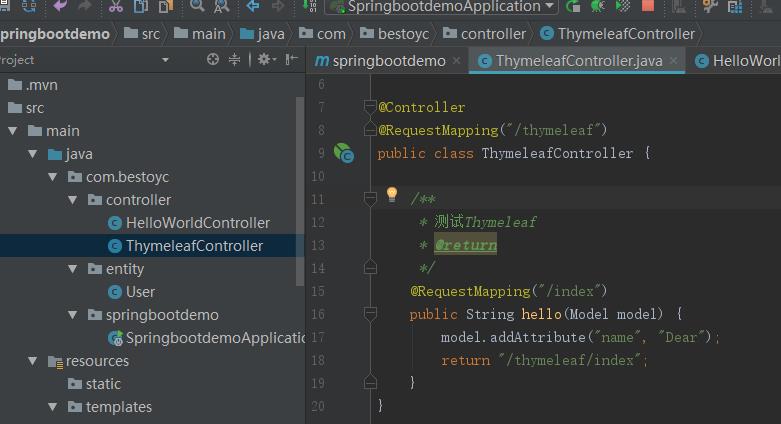
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/thymeleaf")
public class ThymeleafController {
/**
* 测试Thymeleaf
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String hello(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", "Dear");
return "/thymeleaf/index";
}
}
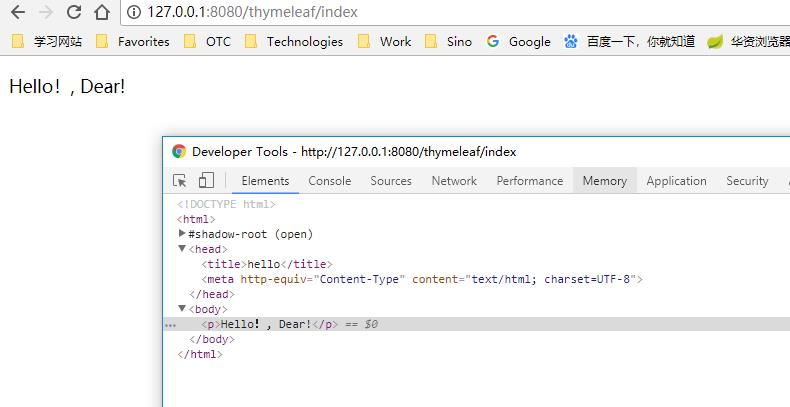
5、测试
三、Thymeleaf的基础语法
回味上面的DEMO,可以看出来首先要在改写html标签
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
这样的话才可以在其他标签里面使用th:*这样的语法.这是下面语法的前提.
1.获取变量值
<p th:text="\'Hello!, \' + ${name} + \'!\'" >3333</p>
可以看出获取变量值用$符号,对于javaBean的话使用变量名.属性名方式获取,这点和EL表达式一样.
另外$表达式只能写在th标签内部,不然不会生效,上面例子就是使用th:text标签的值替换p标签里面的值,至于p里面的原有的值只是为了给前端开发时做展示用的.这样的话很好的做到了前后端分离.
2.引入URL
Thymeleaf对于URL的处理是通过语法@{…}来处理的
<a th:href="@{http://blog.csdn.net/u012706811}">绝对路径</a>
<a th:href="@{/}">相对路径</a>
<a th:href="@{css/bootstrap.min.css}">Content路径,默认访问static下的css文件夹</a>
类似的标签有:th:href和th:src
3.字符串替换
很多时候可能我们只需要对一大段文字中的某一处地方进行替换,可以通过字符串拼接操作完成:
<span th:text="\'Welcome to our application, \' + ${user.name} + \'!\'">
一种更简洁的方式是:
<span th:text="|Welcome to our application, ${user.name}!|">
当然这种形式限制比较多,|…|中只能包含变量表达式${…},不能包含其他常量、条件表达式等。
4.运算符
在表达式中可以使用各类算术运算符,例如+, -, *, /, %
th:with="isEven=(${prodStat.count} % 2 == 0)"
逻辑运算符>, <, <=,>=,==,!=都可以使用,唯一需要注意的是使用<,>时需要用它的HTML转义符:
th:if="${prodStat.count} > 1"
th:text="\'Execution mode is \' + ( (${execMode} == \'dev\')? \'Development\' : \'Production\')"
5.条件
if/unless
Thymeleaf中使用th:if和th:unless属性进行条件判断,下面的例子中,标签只有在th:if中条件成立时才显示:
<a th:href="@{/login}" th:unless=${session.user != null}>Login</a>
th:unless于th:if恰好相反,只有表达式中的条件不成立,才会显示其内容。
Switch
Thymeleaf同样支持多路选择Switch结构:
<div th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case="\'admin\'">User is an administrator</p>
<p th:case="#{roles.manager}">User is a manager</p>
</div>
默认属性default可以用*表示:
<div th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case="\'admin\'">User is an administrator</p>
<p th:case="#{roles.manager}">User is a manager</p>
<p th:case="*">User is some other thing</p>
</div>
6.循环
渲染列表数据是一种非常常见的场景,例如现在有n条记录需要渲染成一个表格,该数据集合必须是可以遍历的,使用th:each标签:
<body>
<h1>Product list</h1>
<table>
<tr>
<th>NAME</th>
<th>PRICE</th>
<th>IN STOCK</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="prod : ${prods}">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onions</td>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41</td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yes</td>
</tr>
</table>
<p>
<a href="../home.html" th:href="@{/}">Return to home</a>
</p>
</body>
可以看到,需要在被循环渲染的元素(这里是)中加入th:each标签,其中th:each=”prod : ${prods}”意味着对集合变量prods进行遍历,循环变量是prod在循环体中可以通过表达式访问。
7.Utilities
为了模板更加易用,Thymeleaf还提供了一系列Utility对象(内置于Context中),可以通过#直接访问:
- #dates
- #calendars
- #numbers
- #strings
- arrays
- lists
- sets
- maps
- …
下面用一段代码来举例一些常用的方法:
date
/*
* Format date with the specified pattern
* Also works with arrays, lists or sets
*/
${#dates.format(date, \'dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm\')}
${#dates.arrayFormat(datesArray, \'dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm\')}
${#dates.listFormat(datesList, \'dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm\')}
${#dates.setFormat(datesSet, \'dd/MMM/yyyy HH:mm\')}
/*
* Create a date (java.util.Date) object for the current date and time
*/
${#dates.createNow()}
/*
* Create a date (java.util.Date) object for the current date (time set to 00:00)
*/
${#dates.createToday()}
string
/*
* Check whether a String is empty (or null). Performs a trim() operation before check
* Also works with arrays, lists or sets
*/
${#strings.isEmpty(name)}
${#strings.arrayIsEmpty(nameArr)}
${#strings.listIsEmpty(nameList)}
${#strings.setIsEmpty(nameSet)}
/*
* Check whether a String starts or ends with a fragment
* Also works with arrays, lists or sets
*/
${#strings.startsWith(name,\'Don\')} // also array*, list* and set*
${#strings.endsWith(name,endingFragment)} // also array*, list* and set*
/*
* Compute length
* Also works with arrays, lists or sets
*/
${#strings.length(str)}
/*
* Null-safe comparison and concatenation
*/
${#strings.equals(str)}
${#strings.equalsIgnoreCase(str)}
${#strings.concat(str)}
${#strings.concatReplaceNulls(str)}
/*
* Random
*/
${#strings.randomAlphanumeric(count)}
补充
在spring-boot1.4之后,支持thymeleaf3,可以更改版本号来进行修改支持.
3相比2极大的提高了效率,并且不需要标签闭合,类似的link,img等都有了很好的支持,按照如下配置即可
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<!-- set thymeleaf version -->
<thymeleaf.version>3.0.0.RELEASE</thymeleaf.version>
<thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.0.0</thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>
<!--set java version-->
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
以上是关于Spring Boot入门系列六( SpringBoot 整合thymeleaf)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章