springboot学习(二十二)_ 使用@Constraint注解自定义验证注解
Posted Kevin-养码青年
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了springboot学习(二十二)_ 使用@Constraint注解自定义验证注解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
最近项目在使用如@NotNull @Max 等配合@vaild 注解进行验证传过来的参数校验,然后通过统一异常处理,直接返回给前端,不用在业务代码中对这些参数进行校验。但是官方提供的并不能全部满足项目的需求,我经过查找发现了@Constraint这个注解。
Constraint 详细信息
@Null 被注释的元素必须为 null
@NotNull 被注释的元素必须不为 null
@AssertTrue 被注释的元素必须为 true
@AssertFalse 被注释的元素必须为 false
@Min(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
@Max(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
@DecimalMin(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
@DecimalMax(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
@Size(max, min) 被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内
@Digits (integer, fraction) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内
@Past 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期
@Future 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期
@Pattern(value) 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式
需求
现在有的列表查询,根据查询条件进行查询,当然这些查询条件可以为null,如果存在值,就必须进行验证。这里就对长度就行验证,不为nul的时候 输入字符不能为空串,且长度必须大于等于1且小于等于10
代码实现
1、定义自定义注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
//代表处理逻辑是MyConstraintValidator类
@Constraint(validatedBy = MyConstraintValidator.class)
public @interface MyConstraint {
String message() default "参数校验不通过,请重新输入";;
long min();
long max();
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}
2.处理类,需要实现ConstraintValidator接口
public class MyConstraintValidator implements ConstraintValidator<MyConstraint, Object> {
private long max = 1;
private long min = 1;
@Override
public void initialize(MyConstraint constraintAnnotation) {
max = constraintAnnotation.max();
min = constraintAnnotation.min();
System.out.println("my validator init");
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(Object o, ConstraintValidatorContext constraintValidatorContext) {
if(o == null){
return true;
}
if(o.toString().trim().length()>=min && o.toString().trim().length()<=max){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
3.进行验证
3.1 定义一个实体类User
@Data
public class User {
@MyConstraint( min = 1, max =10 )
private String name;
private String address;
}
3.2 全局异常中进行处理,这里只是看下效果,返回String字符串
@RestControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class KevinExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public String handleException(Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
if (e instanceof BindException) {
BindException ex = (BindException) e;
List<ObjectError> allErrors = ex.getAllErrors();
ObjectError error = allErrors.get(0);
String defaultMessage = error.getDefaultMessage();
return defaultMessage;
} else {
return "error";
}
}
}
3.3controller测试方法
@RestController
public class Hello {
@RequestMapping(value = "hello")
public User hello(@Valid User user){
return user;
}
}
3.4 通过swagger 进行验证
-
不输入值,为null时
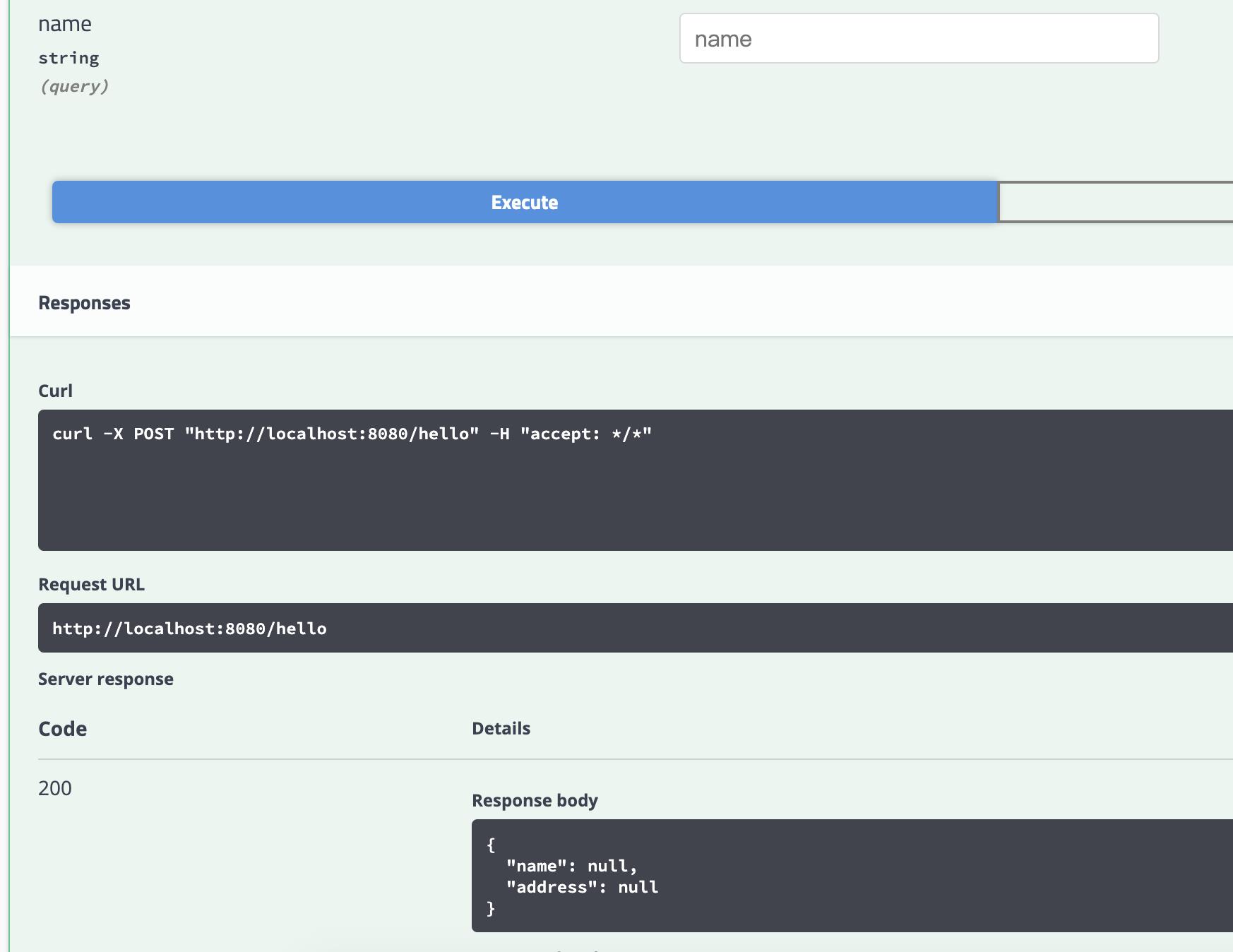
-
输入空格
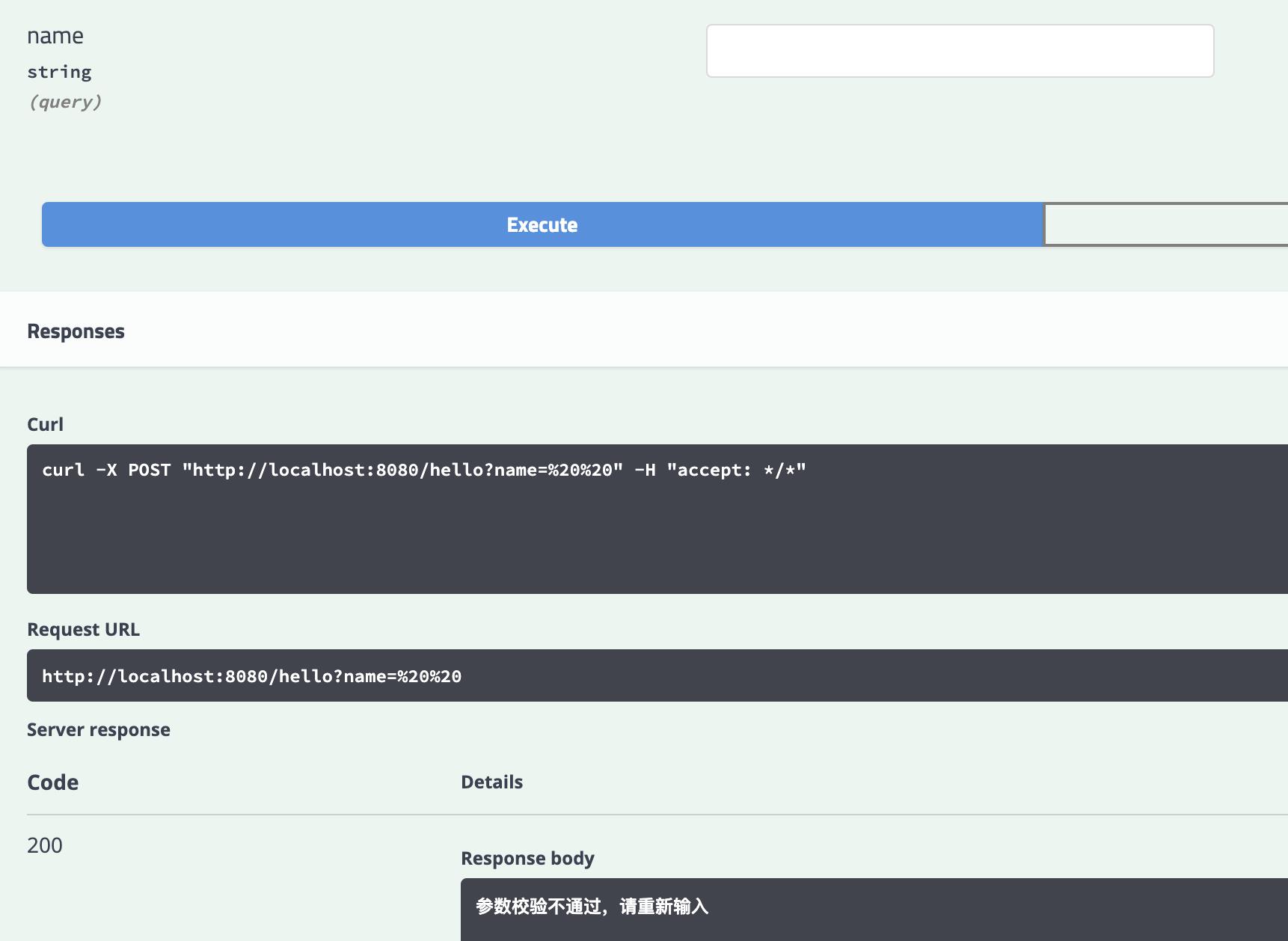
-
输入超过长度
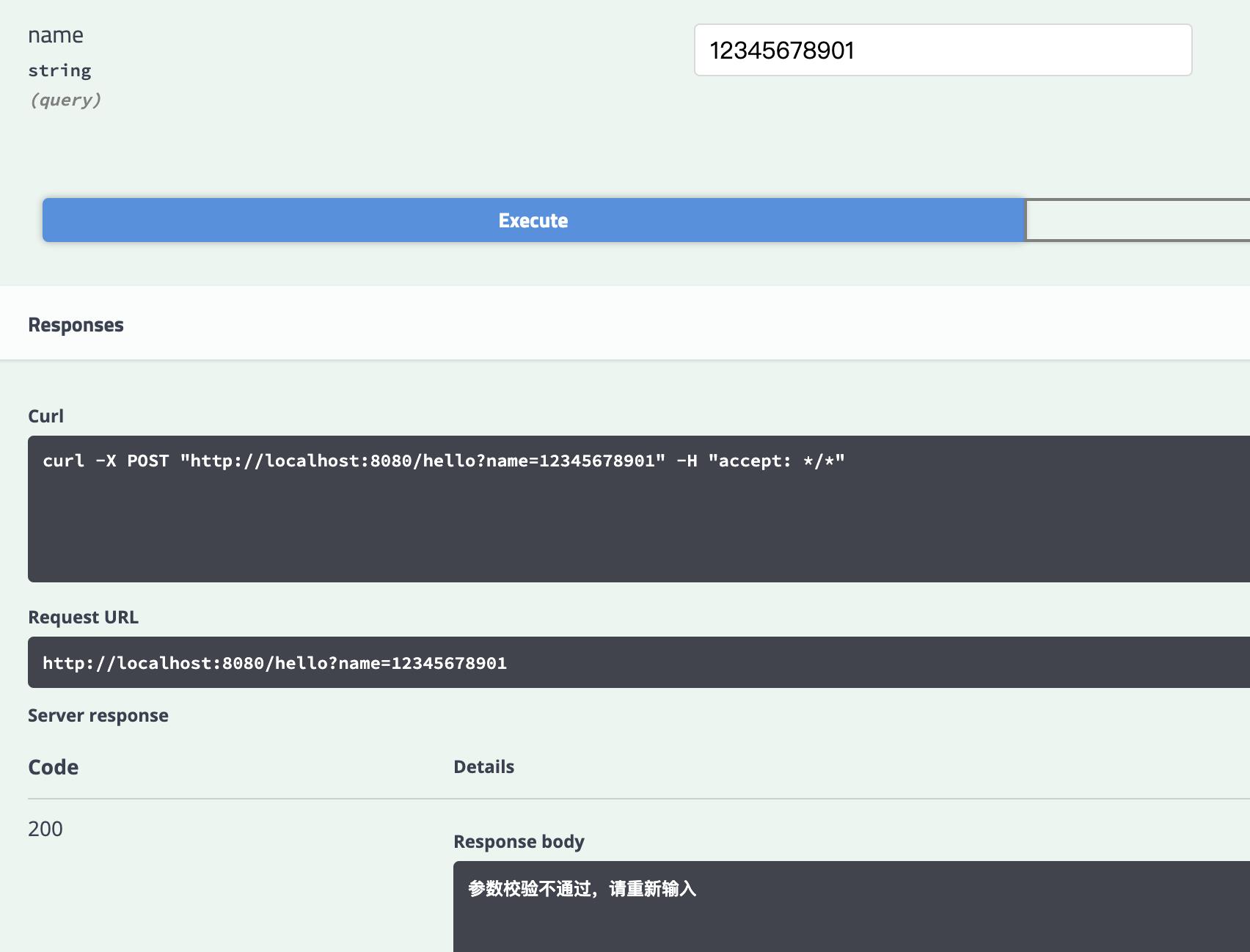
-
输入正常值
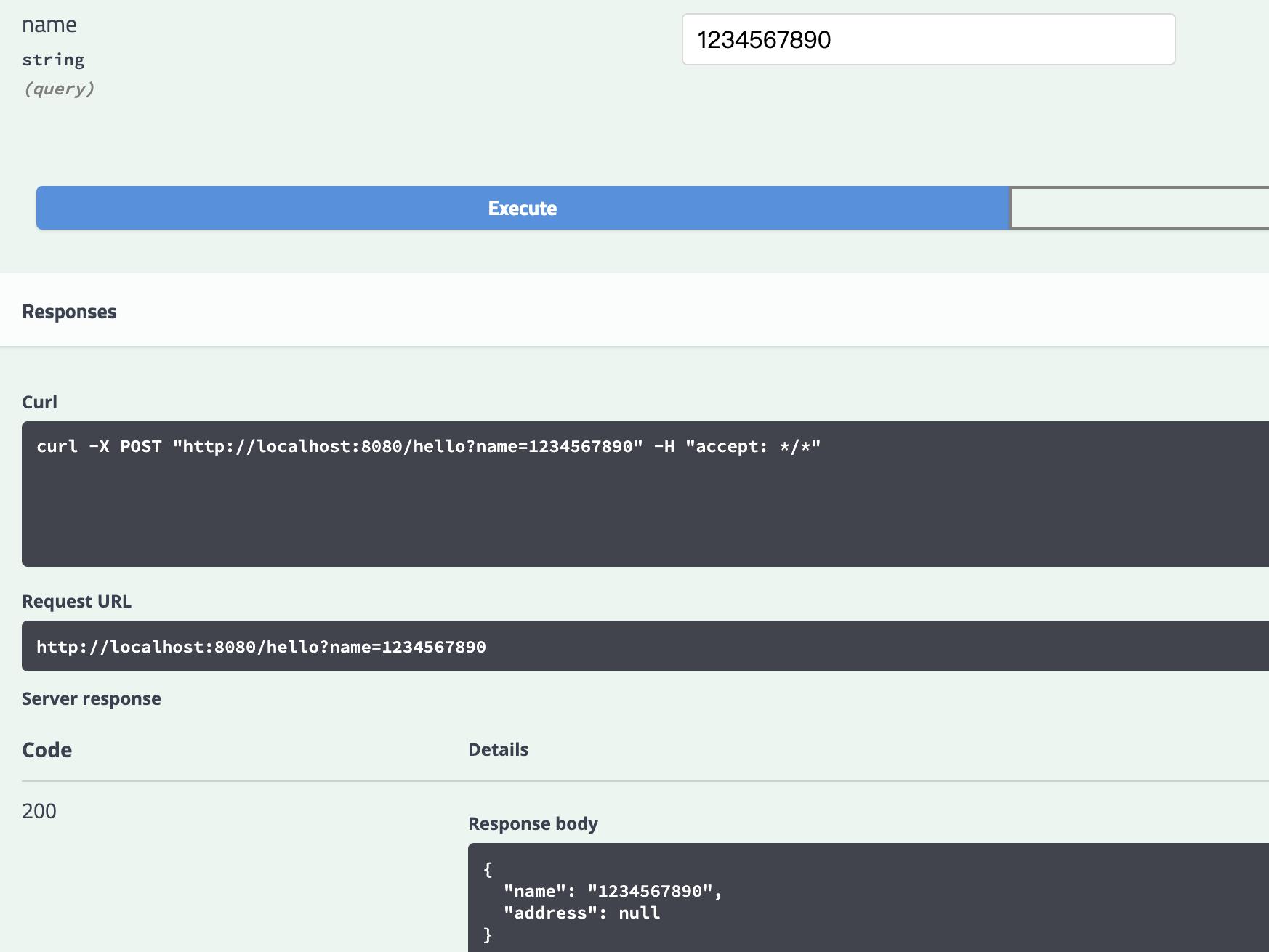
总结
使用注解验证参数配合异常处理,很方便且减少了很多业务代码,各种if判断肯定让人看的头痛。好了,玩的开心!
以上是关于springboot学习(二十二)_ 使用@Constraint注解自定义验证注解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章