用Java实现二叉查找树
Posted q964024886
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了用Java实现二叉查找树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 原理
二叉查找树,又称为二叉排序树、二叉搜索树。对于树中每一个节点X,它的左子树中所有项的值小于X中的项,而它的右子树中所有项的值大于X中的项。二叉查找树的平均深度为O(log N),搜索元素的时间复杂度也是O(log N)。是两种库集合类TreeSet、TreeMap实现的基础。
2. public API
void makeEmpty( ) --> 置空
boolean isEmpty( ) --> 判空
AnyType findMin( ) --> 寻找最小值
AnyType findMax( ) --> 寻找最大值
boolean contains( x ) --> 是否存在元素x
void insert( x ) --> 插入元素x
void remove( x ) --> 删除元素x
void printTree( ) --> 遍历二叉树
3. 核心思想图解:递归
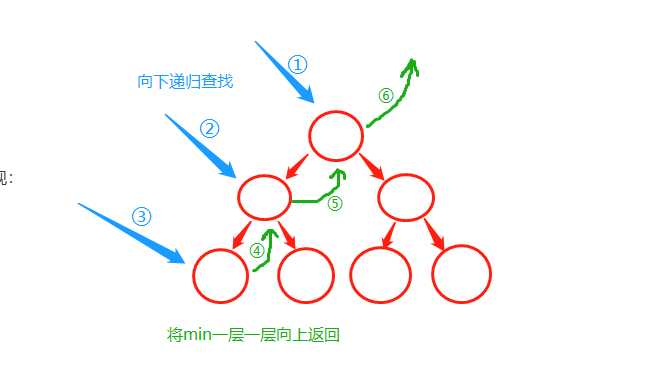
!寻找最小值
此处用递归实现:
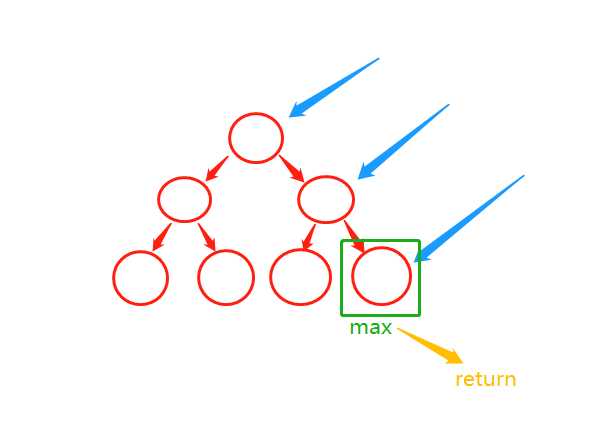
!寻找最大值
此处用非递归实现,也可以用递归实现:
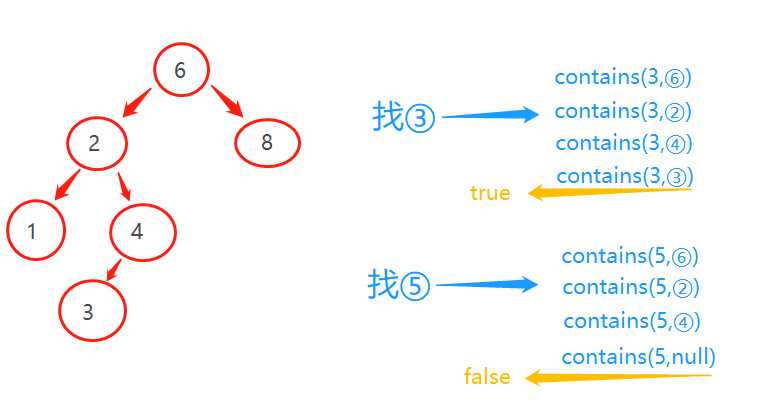
!是否存在元素x
从root开始往下找,找到含有项X的节点,则此操作返回true,没有找到则返回false。
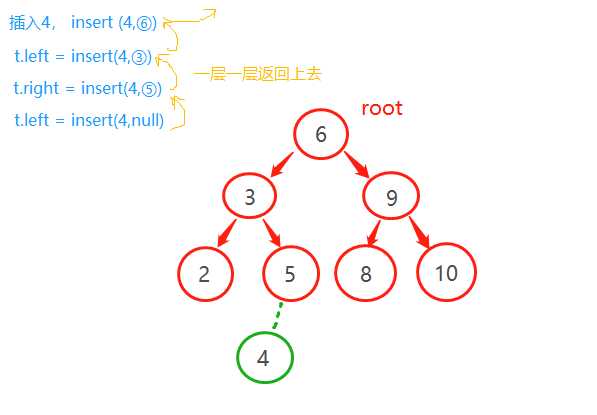
!插入元素x
从root开始往下找到合适的插入位置,然后插入。
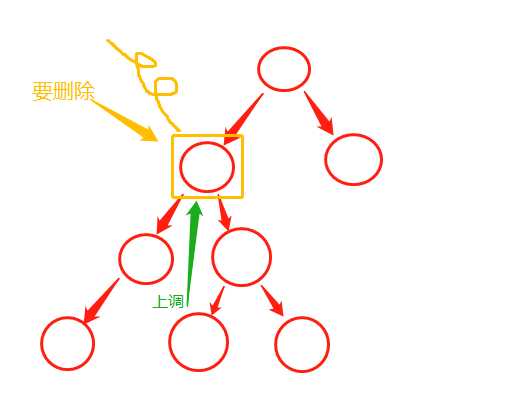
!删除元素x
从root开始往下找到元素x,找到则删除,并且处理好后续工作。
4. BinarySearchTree代码实现
类中,大量使用方法来调用递归方法的技巧,很好地体现了面向对象的封装性。
1 /** 2 * @author: wenhx 3 * @date: Created in 2019/10/8 19:41 (之前) 4 * @description: 二叉查找树的实现 5 */ 6 public class BinarySearchTree<AnyType extends Comparable<? super AnyType>> { 7 ? 8 /** 9 * 树的根节点 10 */ 11 private BinaryNode<AnyType> root; 12 ? 13 /** 14 * 定义树的节点(内部类) 15 */ 16 private static class BinaryNode<AnyType> { 17 ? 18 AnyType element; // 元素值 19 BinaryNode<AnyType> left; // 左孩子 20 BinaryNode<AnyType> right; // 右孩子 21 ? 22 // 节点的构造器:初始化一个树的节点 23 BinaryNode(AnyType theElement) { 24 this(theElement, null, null); 25 } 26 ? 27 BinaryNode(AnyType theElement, BinaryNode<AnyType> lt, BinaryNode<AnyType> rt) { 28 element = theElement; 29 left = lt; 30 right = rt; 31 } 32 } 33 ? 34 /** 35 * 二叉排序树的构造器:初始化根节点 36 */ 37 public BinarySearchTree() { 38 root = null; 39 } 40 ? 41 /** 42 * 置空 43 */ 44 public void makeEmpty() { 45 root = null; 46 } 47 ? 48 /** 49 * 判空 50 */ 51 public boolean isEmpty() { 52 return root == null; 53 } 54 ? 55 /** 56 * 寻找最小值 57 */ 58 public AnyType findMin() { 59 if (isEmpty()) { 60 throw new RuntimeException(); 61 } 62 return findMin(root).element; 63 } 64 ? 65 /** 66 * 寻找最大值 67 */ 68 public AnyType findMax() { 69 if (isEmpty()) { 70 throw new RuntimeException(); 71 } 72 return findMax(root).element; 73 } 74 ? 75 ? 76 /** 77 * 是否存在元素x 78 */ 79 public boolean contains(AnyType x) { 80 return contains(x, root); 81 } 82 ? 83 /** 84 * 插入元素x 85 */ 86 public void insert(AnyType x) { 87 root = insert(x, root); 88 } 89 ? 90 /** 91 * 删除元素x 92 */ 93 public void remove(AnyType x) { 94 root = remove(x, root); 95 } 96 ? 97 /** 98 * 遍历此二叉树 99 */ 100 public void printTree() { 101 if (isEmpty()) { 102 System.out.println("Empty tree"); 103 } else { 104 printTree(root); 105 } 106 } 107 ? 108 /** 109 * 寻找最小值(内部方法):此处用递归实现 110 */ 111 private BinaryNode<AnyType> findMin(BinaryNode<AnyType> t) { 112 if (t == null) { 113 return null; 114 } else if (t.left == null) { 115 return t; 116 } 117 return findMin(t.left); 118 } 119 ? 120 /** 121 * 寻找最大值(内部方法):此处用非递归实现 122 */ 123 private BinaryNode<AnyType> findMax(BinaryNode<AnyType> t) { 124 if (t != null) { 125 while (t.right != null) { 126 t = t.right; 127 } 128 } 129 return t; 130 } 131 ? 132 /** 133 * 是否存在元素x(内部方法) 134 */ 135 private boolean contains(AnyType x, BinaryNode<AnyType> t) { 136 /** 137 * 跳出递归的条件 138 */ 139 if (t == null) { 140 return false; 141 } 142 ? 143 /** 144 * 如果x小于节点值,则递归到左孩子; 145 * 如果x大于节点值,则递归到右孩子; 146 * 如果x等于节点值,则找到。 147 */ 148 int compareResult = x.compareTo(t.element); 149 ? 150 if (compareResult < 0) { 151 return contains(x, t.left); 152 } else if (compareResult > 0) { 153 return contains(x, t.right); 154 } else { 155 return true; 156 } 157 ? 158 } 159 ? 160 /** 161 * 插入元素x(内部方法) 162 */ 163 private BinaryNode<AnyType> insert(AnyType x, BinaryNode<AnyType> t) { 164 /** 165 * 跳出递归的条件 166 */ 167 if (t == null) { 168 return new BinaryNode<>(x, null, null); 169 } 170 ? 171 /** 172 * 如果x小于节点值,则递归到左孩子; 173 * 如果x大于节点值,则递归到右孩子; 174 * 如果x等于节点值,则说明已有元素x,无需操作。 175 */ 176 int compareResult = x.compareTo(t.element); 177 ? 178 if (compareResult < 0) { 179 t.left = insert(x, t.left); 180 } else if (compareResult > 0) { 181 t.right = insert(x, t.right); 182 } else { 183 } 184 return t; 185 ? 186 } 187 ? 188 /** 189 * 删除元素x(内部方法) 190 */ 191 private BinaryNode<AnyType> remove(AnyType x, BinaryNode<AnyType> t) { 192 /** 193 * 跳出递归的条件 194 */ 195 if (t == null) { 196 return t; // Item not found; do nothing 197 } 198 ? 199 /** 200 * 如果x小于节点值,则递归到左孩子; 201 * 如果x大于节点值,则递归到右孩子; 202 * 如果x等于节点值,则要删除此节点。 203 */ 204 int compareResult = x.compareTo(t.element); 205 ? 206 if (compareResult < 0) { 207 t.left = remove(x, t.left); 208 } else if (compareResult > 0) { 209 t.right = remove(x, t.right); 210 } else if (t.left != null && t.right != null) { 211 // 要删除的节点有两个孩子(可选用右孩子最小元素/左孩子最大元素上调) 212 t.element = findMin(t.right).element; 213 t.right = remove(t.element, t.right); 214 } else { 215 // 要删除的节点有一个孩子或者没有孩子 216 t = (t.left != null) ? t.left : t.right; 217 } 218 return t; 219 } 220 ? 221 /** 222 * 遍历此二叉树(内部方法) 223 */ 224 private void printTree(BinaryNode<AnyType> t) { 225 // 中序遍历-->即递增顺序 226 if (t != null) { 227 printTree(t.left); 228 System.out.println(t.element); 229 printTree(t.right); 230 } 231 } 232 ? 233 /** 234 * 求树的深度(内部方法) 235 */ 236 private int height(BinaryNode<AnyType> t) { 237 if (t == null) { 238 return -1; 239 } else { 240 return 1 + Math.max(height(t.left), height(t.right)); 241 } 242 } 243 ? 244 /** 245 * 主方法用来测试 246 */ 247 public static void main(String[] args) { 248 BinarySearchTree<Integer> t = new BinarySearchTree<>(); 249 t.insert(6); 250 t.insert(3); 251 t.insert(9); 252 t.insert(2); 253 t.insert(5); 254 t.insert(8); 255 t.insert(10); 256 t.printTree(); 257 t.insert(4); 258 } 259 }
以上是关于用Java实现二叉查找树的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章