Spring IOC分析
Posted xmz_java
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring IOC分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
关于Spring,我想无需做太多的解释了。每个Java程序猿应该都使用过他。Spring的ioc和aop极大的方便了我们的开发,但是Spring又有着不好的一面,为了符合开闭原则,Spring的一个方法可以涉及到好几十个类,从设计上来说,这样的设计易于宽展,职责明确。但从开发角度而言,Spring就像一个迷宫,经常会在里面迷失方向。最近,在git上发现tiny-spring。几千行代码就实现了IOC和AOP,看了下很有借鉴意义,对spring的结构清楚了很多。本文开始对IOC做出分析。
对于IOC,我希望从两个问题来讨论
1.什么是IOC容器,它是如何实现的。
2.IOC是如何解决循环依赖的
1.容器的创建与初始化
抛开Spring,假如要求我们自己实现一个容器。应该是如下几步
1.定义一个对象储存bean的信息
public class BeanDefinition { private Object bean; private Class beanClass; private String beanClassName; }
2.定义一个Map,map的key就是这个bean的名称,value就是bean的BeanDefination
private Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>();
3.每次项目启动的时候把这些bean保存到map里面,需要用到的时候通过bean的name来获得bean的BeanDefination
public Object getBean(String name) { return beanDefinitionMap.get(name).getBean(); }
ioc容器就是上述这个思路。但是干的事情可比上面那3步复杂多了。
举个例子
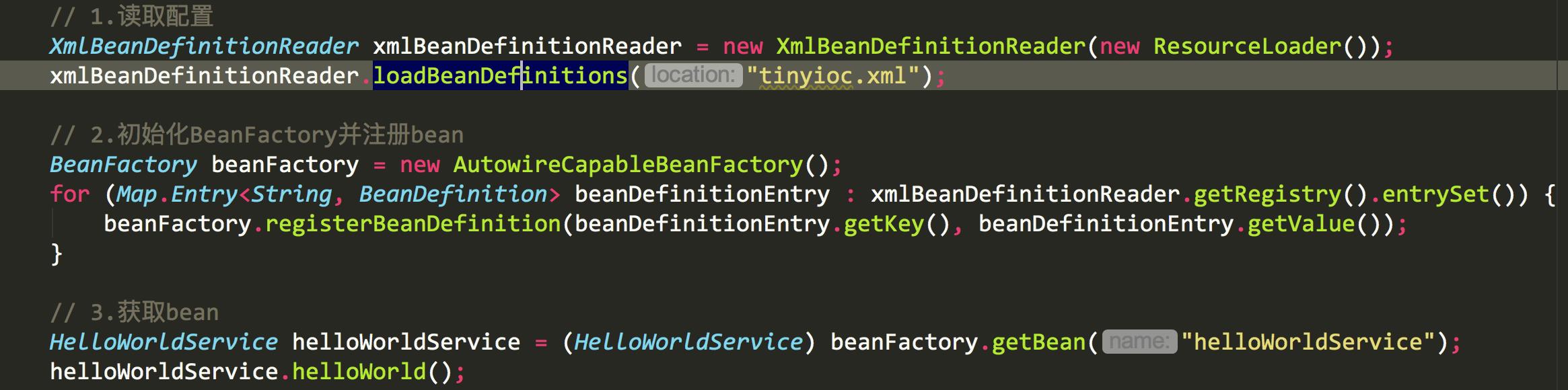
XML配置

第一步:读取配置
配置的方式有很多种,xml,注解,代码等都能实现。spring选用的xml作为配置文件,所以第一步就需要读取配置文件。将配置文件的配置信息读到内存中。
下面的代码就是将XML的配置信息填充到Beandefnition。此外还要保存住这些beandefination,所以就需要一个map来保存这些。
private void processProperty(Element ele,BeanDefinition beanDefinition) { NodeList propertyNode = ele.getElementsByTagName("property"); for (int i = 0; i < propertyNode.getLength(); i++) { Node node = propertyNode.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element propertyEle = (Element) node; String name = propertyEle.getAttribute("name"); String value = propertyEle.getAttribute("value"); beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(name,value)); } } }
第二步:生产bean
配置信息都已经读取到了,接下来就可以开始创建bean了。创建bean这个工作我们交给BeanFactory来完成。这个时候的创建bean总共可以分作两步
1.根据类的全限定名反射生成javaBean
2.将从xml中的读取道德配置信息设置到javaBean中
protected Object doCreateBean(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception { Object bean = createBeanInstance(beanDefinition); applyPropertyValues(bean, beanDefinition); return bean; } protected Object createBeanInstance(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception { return beanDefinition.getBeanClass().newInstance(); } protected void applyPropertyValues(Object bean, BeanDefinition mbd) throws Exception { for (PropertyValue propertyValue : mbd.getPropertyValues().getPropertyValues()) { Field declaredField = bean.getClass().getDeclaredField(propertyValue.getName()); declaredField.setAccessible(true); declaredField.set(bean, propertyValue.getValue()); } }
第三步:
这一步其实就是从map中获取bean,没什么好多的,但值得注意的是,但spring设置成懒加载的时候,这一步就会像第二步一样去创建javaBean。
2.循环依赖的解决
看以下代码
public class A { private B b; public B getB() { return b; } public void setB(B b) { this.b = b; } } public class B { private A a; public A getA() { return a; } public void setA(A a) { this.a = a; } }
两个类互相持有对方的引用,A在设置自己属性的时候发现B还没有被实例化,这时候就去要去实例化B,然后b在设置自己属性的时候发现A还没有实例化完成,就去实例化A,这就会导致循环依赖问题。
spring新增BeanReference对象,来表示这个属性是对另一个bean的引用。这个在读取xml的时候初始化,并在初始化bean的时候,进行解析和真实bean的注入。
举个例子,下面两个bean互相持有对方引用

读取xml的时候初始化
String ref = propertyEle.getAttribute("ref");
if (ref == null || ref.length() == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Configuration problem: <property> element for property \'"
+ name + "\' must specify a ref or value");
}
BeanReference beanReference = new BeanReference(ref);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(name, beanReference));
解析获取bean
protected void applyPropertyValues(Object bean, BeanDefinition mbd) throws Exception { for (PropertyValue propertyValue : mbd.getPropertyValues().getPropertyValues()) { Field declaredField = bean.getClass().getDeclaredField(propertyValue.getName()); declaredField.setAccessible(true); Object value = propertyValue.getValue(); if (value instanceof BeanReference) { BeanReference beanReference = (BeanReference) value; value = getBean(beanReference.getName()); } declaredField.set(bean, value); } }
我们再看下getBean的方法
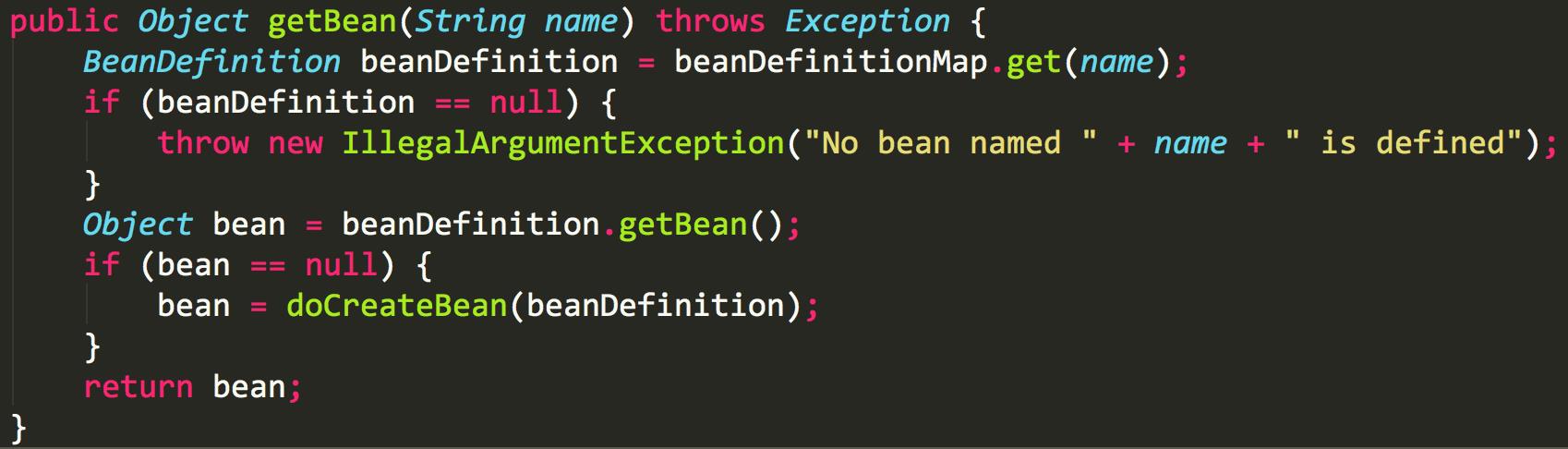
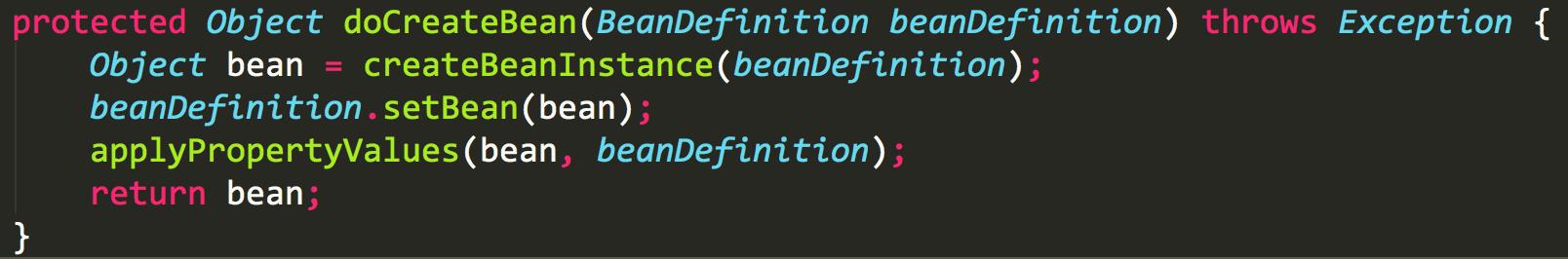
在注入bean的时候,如果bean不存在,则创建bean。创建完成之后,再去注入。这样就解决了循环依赖问题。
3.IOC流程简述
以上通过两个问题去探索IOC,这样的介绍会有点不够体系化。接下来跟着代码从头到尾运行一遍。
测试代码如下
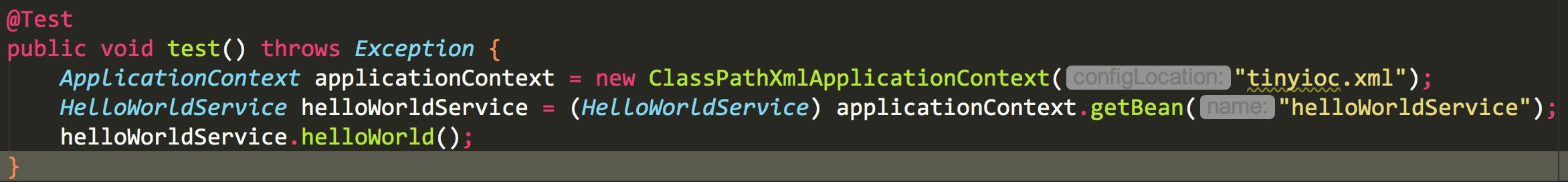
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext继承ApplicationContext,而ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子集。相比而言,ApplicationContext对bean的一些操作做了封装 使用起来更加方便 下面的代码是不用ApplicationContext时我们获取bean需要的步骤。对于开发者而言,ApplicationContext无疑更加友好
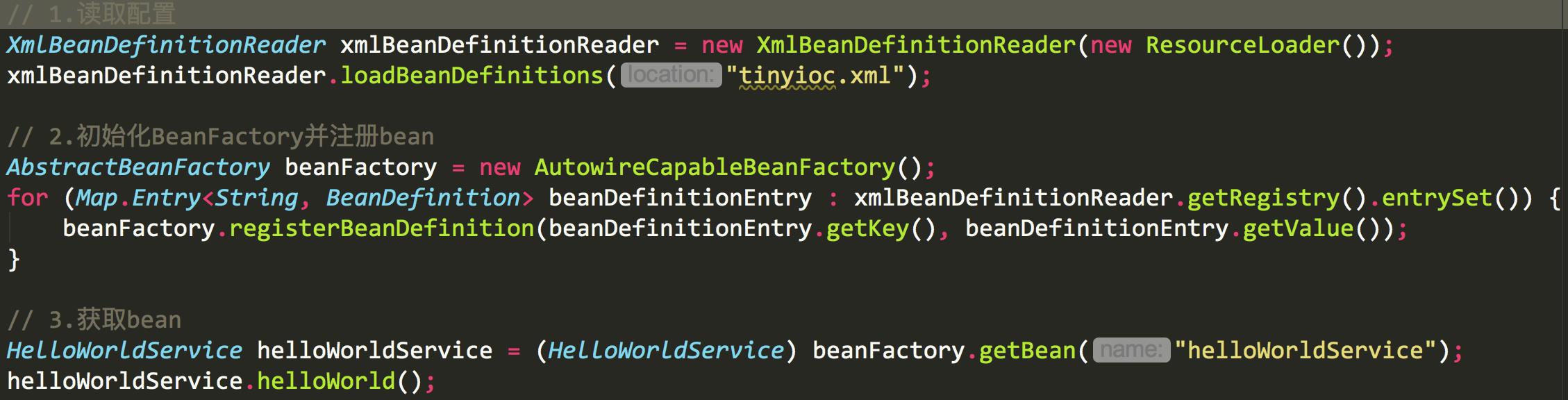
现在点进ClassPathXmlApplicationContext


这里主要看refresh

现在![]() 已经执行完毕了。容器的大致框架已经建立,但这个时候bean还没生成。我们接着看下一行。
已经执行完毕了。容器的大致框架已经建立,但这个时候bean还没生成。我们接着看下一行。![]()
getBean的方法点进去
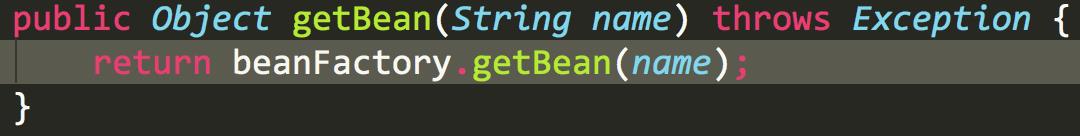
真正获取bean操作的还是beanFactory,这也说明了ApplicationContext是对beanFactory的封装

再看doCreateBean
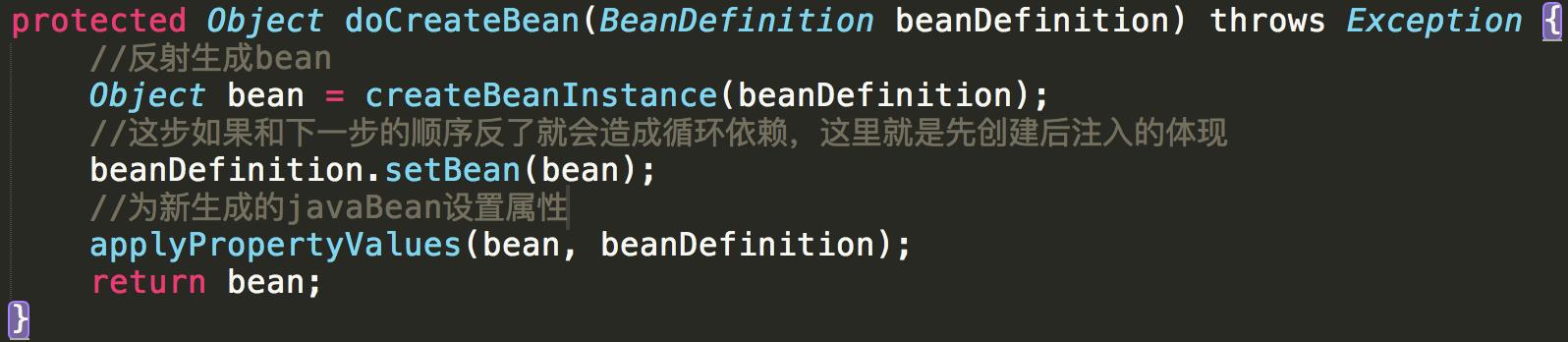
设置属性
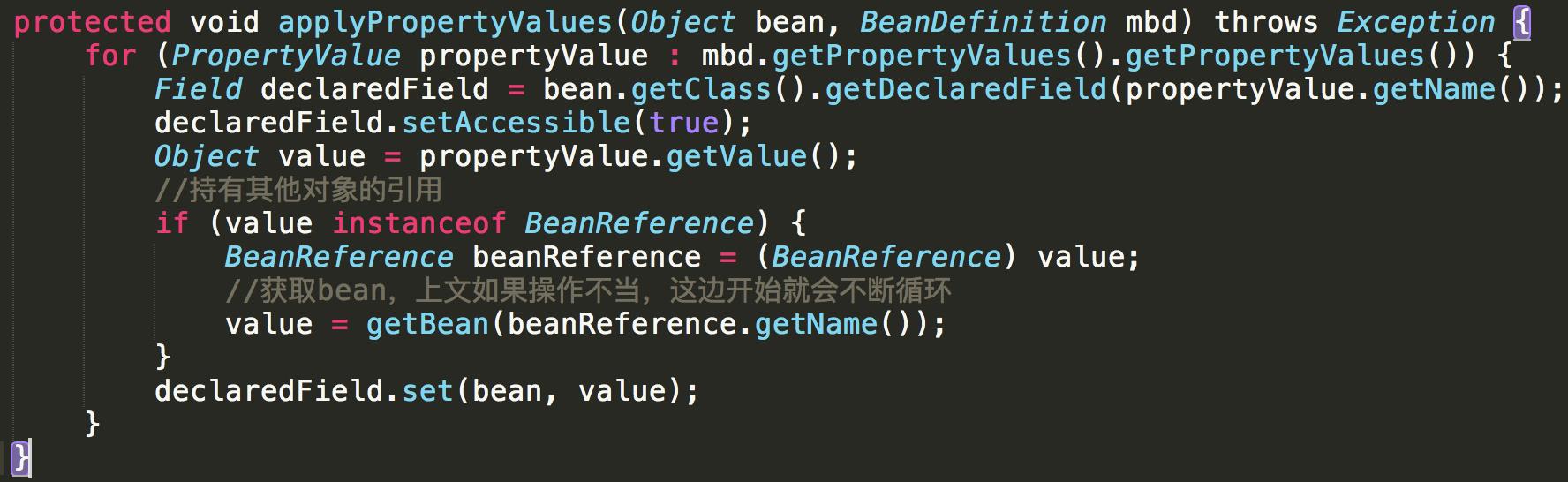
至此![]() 这一行代码已经结束了,容器里面的bean都生成好了。bean也取出来了,下一步执行方法即可。
这一行代码已经结束了,容器里面的bean都生成好了。bean也取出来了,下一步执行方法即可。
总结
本文通过两个问题描述了ioc容器的基本情况,最后又总体介绍了大致的流程。这只是最精简版的ioc容器初始化bean的过程,下一步会把aop也加进来。
以上是关于Spring IOC分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章