Java方法的应用
Posted xianya
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java方法的应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、方法的定义
方法是类的组成部分,是解决一类问题的步骤的有序组合,包含于类或对象中,在程序中被创建,在其他地方被引用
方法的语法:
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型 参数名.....){ ... 方法体 ... return 返回值; }
根据方法是否带参、是否带返回值,可将方法分为四类:
- 无参无返回值方法
- 无参带返回值方法
- 带参无返回值方法
- 带参带返回值方法
package com.yyx.pratice; public class JavaPratice { public static void main(String[] args) { noParamValue(); String aStr = "有参数", bStr = "无返回值"; noValue(aStr, bStr); System.out.println(noParam()); System.out.println(ParamValue("有参数有返回值")); } public static void noParamValue() { System.out.println("无参数无返回值"); } /** * 有参数无返回值 * * @param aStr * @param bStr */ public static void noValue(String aStr, String bStr) { System.out.println(aStr + bStr); } /** * 无参数有返回值 * * @return */ public static String noParam() { String str = "无参数有返回值"; return str; } /** * 有参数,有返回值 * * @param str * @return */ public static String ParamValue(String str) { return str; } }
二、方法的重载
方法重载的特点:
- 同一个类中
- 方法名必须相同
- 方法的参数列表不同(参数的个数不同或者参数类型不同)
- 方法的重载与方法的返回值类型没有关系
package com.yyx.pratice; public class JavaPratice { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 1, b = 2, c = 3; double m = 2.1, n = 3.2; addNumber(a, b); addNumber(m, n); System.out.println(addNumber(a, b, c)); } public static void addNumber(int a, int b) { System.out.println(a + b); } public static void addNumber(double a, double b) { System.out.println(a + b); } public static int addNumber(int a, int b, int c) { return a + b + c; } }
三、方法的重写
在子类中可以根据需要对从基类继承来的方法进行重写
重写的规则:
- 要求子类方法的“返回值类型 方法名 (参数列表)”与父类的方法一样
- 子类方法的修饰符不能小于父类方法的修饰符
- 若父类方法抛异常,那么子类方法抛的异常类型不能大于父类的。
- 子父类的方法必须同为static或同为非static的
package com.yyx.pratice; public class JavaPratice { public static void main(String[] args) { TestExtend testExtend = new TestExtend(); testExtend.addNumber(5, 6); testExtend.printWord("测试重写方法"); } } class TestInheritance { public void printWord(String str) { System.out.println(str); } } class TestExtend extends TestInheritance implements TestImplements { @Override public void printWord(String str) { System.out.println("子类重新加一句"); } @Override public void addNumber(int m, int n) { System.out.println(m + n); } } interface TestImplements { void addNumber(int m, int n); }
四、方法的参数
1.形参和实参
形参:方法声明时,方法小括号内的参数;实参:调用方法时,实际传入的参数的值
参数传递机制:
- 形参是基本数据类型的:将实参的值传递给形参的基本数据类型的变量,即传递值
- 形参是引用数据类型的:将实参的引用类型变量的值(对应的堆空间的对象实体的首地址值)传递给形参的引用类型变量,即传递地址
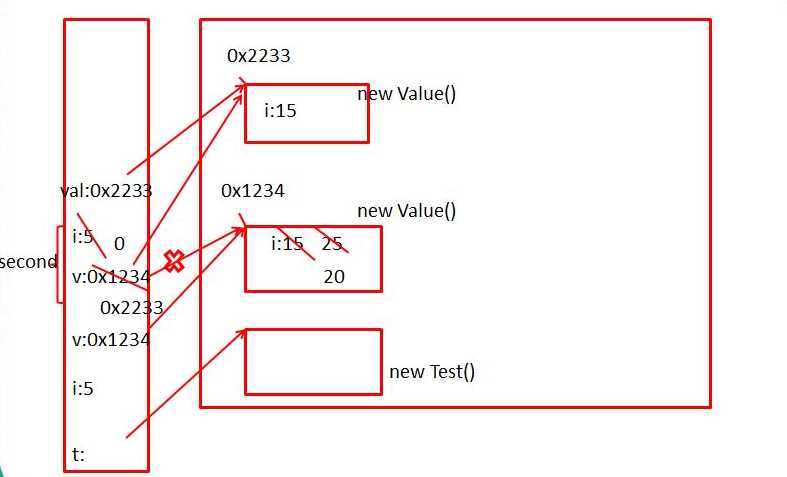
package com.yyx.pratice; public class TestValue { public static void main(String argv[]) { TestValue t = new TestValue(); t.first(); } public void first() { int i = 5; Value v = new Value(); v.i = 25; second(v, i); System.out.println(v.i); } public void second(Value v, int i) { i = 0; v.i = 20; Value val = new Value(); v = val; System.out.println(v.i + " " + i); } } class Value { int i = 15; }
2.可变参数
可变个数的形参的方法:
- 1.格式:对于方法的形参: 数据类型 ... 形参名
- 2.可变个数的形参的方法与同名的方法之间构成重载
- 3.可变个数的形参在调用时,个数从0开始,到无穷多个都可以
- 4.使用可变多个形参的方法与方法的形参使用数组是一致的
- 5.若方法中存在可变个数的形参,那么一定要声明在方法形参的最后
- 6.在一个方法中,最多声明一个可变个数的形参
public class TestArgs { public static void main(String[] args) { TestArgs t = new TestArgs(); // t.sayHello(new String[]{"hello China","hello BeiJing"}); t.sayHello("hello China", "hello BeiJing"); t.sayHello(5, "hello China", "hello BeiJing"); } // 可变个数的形参的方法 public void sayHello(String... args) { for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { System.out.println(args[i] + "$"); } } public void sayHello(int i, String... args) { System.out.println(i); for (int j = 0; j < args.length; j++) { System.out.println(args[j] + "$"); } } /** * 使用可变多个形参的方法与方法的形参使用数组是一致的 */ // public void sayHello(String[] args) { // for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { // System.out.println(args[i]); // } // } }
以上是关于Java方法的应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章