一、前言
Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。通过这种方式,Spring Boot致力于在蓬勃发展的快速应用开发领域(rapid application development)成为领导者。本文介绍用idea搭建springboot
二、环境搭建
idea搭建springboot步骤如下:
1.打开IDEA,创建新项目,选择Spring Initializr

2.输入Artifact

3.勾选Web

4.点击finish完成
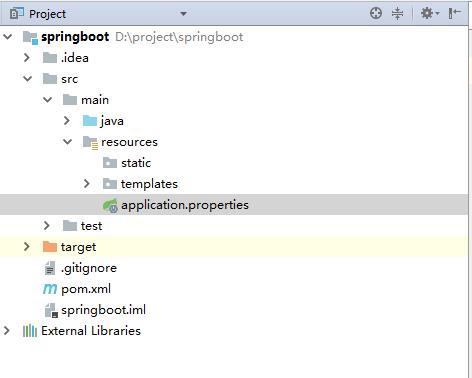
5.进入项目,可以将mvn、mvnw、mvnw.删除得到如下项目目录结构
2.1 添加依赖
在 pom.xml 文件中添加如下依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>springbootdemo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>springbootdemo</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <!--起步依赖--> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.2.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!--开发web项目相关依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!--springboot单元测试--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <!--maven构建--> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
2.2 目录和配置文件含义
application.properties:用于配置项目运行所需的配置数据。
static:用于存放静态资源,如:css、js、图片等。
templates:用于存放模板文件。
目录结构如下:

2.3 启动类
7.程序自动生成的SpringbootdemoApplication,会有一个@SpringBootApplication的注解,这个注解用来标明这个类是程序的入口,如下:
package com.ggband; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; /** 该注解指定项目为springboot,由此类当作程序入口 自动装配 web 依赖的环境 **/ @SpringBootApplication public class SpringbootApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args); } }
@SpringBootApplication开启了Spring的组件扫描和springboot的自动配置功能,相当于将以下三个注解组合在了一起
(1)@Configuration:表名该类使用基于Java的配置,将此类作为配置类
(2)@ComponentScan:启用注解扫描
(3)@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启springboot的自动配置功能
2.4 案例演示
创建 com.ggband.web包,在该包下创建一个 Controller 类,如下:
package com.ggband.web; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class WelcomeController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello() { return "hello,this is a springboot demo"; } }
在 SpringbootApplication 文件中右键 Run as -> Java Application。当看到 “Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http)” 字样说明启动成功。
打开浏览器访问 http://localhost:8080/hello,结果如下:

三、多环境切换
application.properties 是 springboot 在运行中所需要的配置信息。
当我们在开发阶段,使用自己的机器开发,测试的时候需要用的测试服务器测试,上线时使用正式环境的服务器。
这三种环境需要的配置信息都不一样,当我们切换环境运行项目时,需要手动的修改多出配置信息,非常容易出错。
为了解决上述问题,springboot 提供多环境配置的机制,让开发者非常容易的根据需求而切换不同的配置环境。
在 src/main/resources 目录下创建三个配置文件:
application-dev.properties:用于开发环境
application-test.properties:用于测试环境
application-prod.properties:用于生产环境我们可以在这个三个配置文件中设置不同的信息,application.properties 配置公共的信息。
在 application.properties 中配置:
spring.profiles.active=dev表示激活 application-dev.properties 文件配置, springboot 会加载使用 application.properties 和 application-dev.properties 配置文件的信息。
同理,可将 spring.profiles.active 的值修改成 test 或 prod 达到切换环境的目的。
四、配置日志
4.1 配置 logback(官方推荐使用)
4.1.1 配置日志文件
spring boot 默认会加载 classpath:logback-spring.xml 或者 classpath:logback-spring.groovy。
如需要自定义文件名称,在 application.properties 中配置 logging.config 选项即可。
在 src/main/resources 下创建 logback-spring.xml 文件,内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <configuration> <!-- 文件输出格式 --> <property name="PATTERN" value="%-12(%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS}) |-%-5level [%thread] %c [%L] -| %msg%n" /> <!-- test文件路径 --> <property name="TEST_FILE_PATH" value="d:/test.log" /> <!-- pro文件路径 --> <property name="PRO_FILE_PATH" value="/opt/test/log" /> <!-- 开发环境 --> <springProfile name="dev"> <appender name="CONSOLE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"> <encoder> <pattern>${PATTERN}</pattern> </encoder> </appender> <logger name="com.light.springboot" level="debug" /> <root level="info"> <appender-ref ref="CONSOLE" /> </root> </springProfile> <!-- 测试环境 --> <springProfile name="test"> <!-- 每天产生一个文件 --> <appender name="TEST-FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender"> <!-- 文件路径 --> <file>${TEST_FILE_PATH}</file> <rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy"> <!-- 文件名称 --> <fileNamePattern>${TEST_FILE_PATH}/info.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</fileNamePattern> <!-- 文件最大保存历史数量 --> <MaxHistory>100</MaxHistory> </rollingPolicy> <layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout"> <pattern>${PATTERN}</pattern> </layout> </appender> <root level="info"> <appender-ref ref="TEST-FILE" /> </root> </springProfile> <!-- 生产环境 --> <springProfile name="prod"> <appender name="PROD_FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender"> <file>${PRO_FILE_PATH}</file> <rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy"> <fileNamePattern>${PRO_FILE_PATH}/warn.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</fileNamePattern> <MaxHistory>100</MaxHistory> </rollingPolicy> <layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout"> <pattern>${PATTERN}</pattern> </layout> </appender> <root level="warn"> <appender-ref ref="PROD_FILE" /> </root> </springProfile> </configuration>
其中,springProfile 标签的 name 属性对应 application.properties 中的 spring.profiles.active 的配置。
即 spring.profiles.active 的值可以看作是日志配置文件中对应的 springProfile 是否生效的开关。
4.2 配置 log4j2
4.2.1 添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-log4j2</artifactId> </dependency>
4.2.2 配置日志文件
spring boot 默认会加载 classpath:log4j2.xml 或者 classpath:log4j2-spring.xml。
如需要自定义文件名称,在 application.properties 中配置 logging.config 选项即可。
log4j2.xml 文件内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <properties> <!-- 文件输出格式 --> <property name="PATTERN">%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} |-%-5level [%thread] %c [%L] -| %msg%n</property> </properties> <appenders> <Console name="CONSOLE" target="system_out"> <PatternLayout pattern="${PATTERN}" /> </Console> </appenders> <loggers> <logger name="com.light.springboot" level="debug" /> <root level="info"> <appenderref ref="CONSOLE" /> </root> </loggers> </configuration>
log4j2 不能像 logback 那样在一个文件中设置多个环境的配置数据,只能命名 3 个不同名的日志文件,分别在 application-dev,application-test 和 application-prod 中配置 logging.config 选项。
除了在日志配置文件中设置参数之外,还可以在 application-*.properties 中设置,日志相关的配置:
logging.config # 日志配置文件路径,如 classpath:logback-spring.xml
logging.exception-conversion-word # 记录异常时使用的转换词
logging.file # 记录日志的文件名称,如:test.log
logging.level.* # 日志映射,如:logging.level.root=WARN,logging.level.org.springframework.web=DEBUG
logging.path # 记录日志的文件路径,如:d:/
logging.pattern.console # 向控制台输出的日志格式,只支持默认的 logback 设置。
logging.pattern.file # 向记录日志文件输出的日志格式,只支持默认的 logback 设置。
logging.pattern.level # 用于呈现日志级别的格式,只支持默认的 logback 设置。
logging.register-shutdown-hook # 初始化时为日志系统注册一个关闭钩子
五、配置freemarker模板引擎
5.1 添加freemarker依赖
<!-- 添加freemarker资源 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId> </dependency>
5.2 在templates创建index.ftl模板文件

5.2 创建Controller文件
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; @Controller public class WebController { @RequestMapping("/index") public ModelAndView index(ModelAndView modelAndView) { modelAndView.addObject("name","世界"); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; } }
5.3 测试运行http://localhost:8080/index

5.4 spring boot freemarker常用配置
模板文件默认在项目classpath:/templates/下,开发者也可以自己自动定义配置:
在application.properties添加自定义配置:
# freemarker config spring.freemarker.allow-request-override=false spring.freemarker.allow-session-override=false spring.freemarker.cache=false spring.freemarker.charset=UTF-8 spring.freemarker.check-template-location=true spring.freemarker.content-type=text/html spring.freemarker.enabled=true spring.freemarker.expose-request-attributes=false spring.freemarker.expose-session-attributes=false spring.freemarker.expose-spring-macro-helpers=true spring.freemarker.prefer-file-system-access=true spring.freemarker.suffix=.ftl #设定ftl文件路径 spring.freemarker.template-loader-path=classpath:/templates/ spring.freemarker.settings.template_update_delay=0 spring.freemarker.settings.default_encoding=UTF-8 spring.freemarker.settings.classic_compatible=true spring.freemarker.settings.date_format=yyyy-MM-dd spring.freemarker.settings.time_format=HH:mm:ss spring.freemarker.settings.datetime_format=yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss spring.freemarker.order=1
六、打包运行
打包的形式有两种:jar 和 war。
6.1 打包成可执行的 jar 包
默认情况下,通过 maven 执行 package 命令后,会生成 jar 包,且该 jar 包会内置了 tomcat 容器,因此我们可以通过 java -jar 就可以运行项目,如下图:
点击maven projects

执行maven 命令,将在target 目录生成 jar包

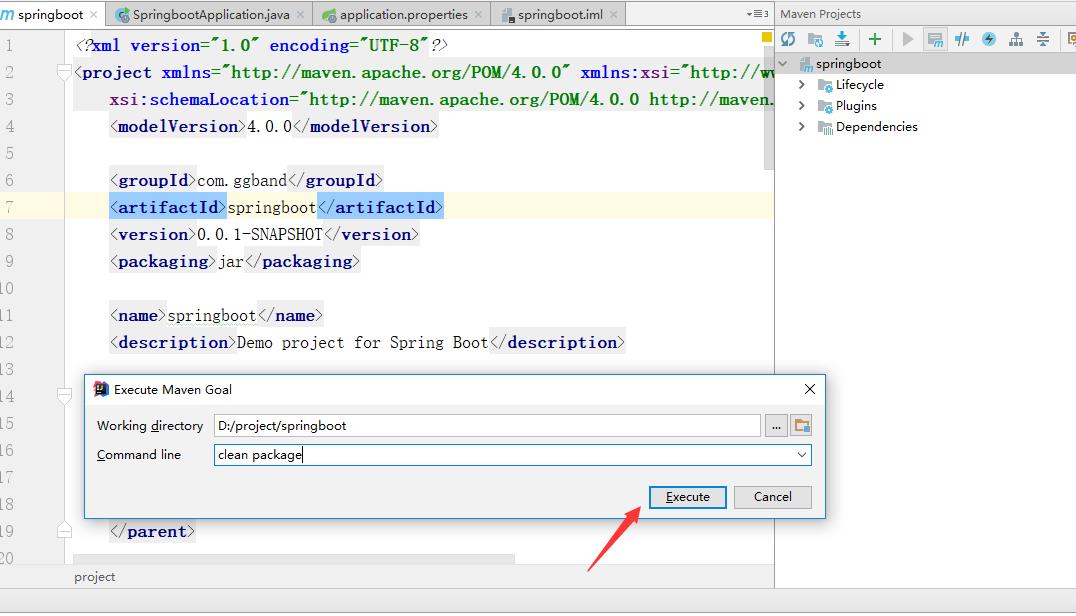

运行jar 文件(这里通过cmd):
java -jar XXX.jar &
关闭控制台让程序挂起:
nohup java -jar **.jar &

部署成功:

6.2 打包成部署的 war 包
让 SpringbootApplication 类继承 SpringBootServletInitializer 并重写 configure 方法,如下:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(SpringbootApplication.class);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
修改 pom.xml 文件,将 jar 改成 war,如下:
<packaging>war</packaging>
打包成功后,将 war 包部署到 tomcat 容器中运行即可。