Java集合框架
Posted Code_exploration
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java集合框架相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、集合与数组的对比
使用array存储对象时具有一些弊端,而java集合就像一种容器,可以动态的把多个对象的引用放入容器中。
数组的弊端:长度一旦设定,就不可改变;数组里的元素的个数不可知。
二、集合概况
|---Collection集合
|---List接口:有序,可重复序列。
|---ArrayList集合(List的主要表现形式)
|---LinkedList
|---Vector
|---Set接口:无序,不可重复。
|---TreeSet
|---HashSet
|---Map集合:key-->value 键值对
三、Collection常用方法

1.size():返回集合元素的个数 2.add():向集合中添加新元素 3.addAll():将形参collection中的元素复制到当前集合中 4、isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空 5、clear():清空当前集合 6、contains(Object obj):判断集合中是否包含obj元素 7、containsAll(Collection col):判断当前集合中是否包含col集合中的所有元素。 8、retainAll():取当前集合和参数集合的交集,并保留给当前集合 9、remove(Object obj):删除当前集合中的第一次出现的obj, 10、removeAll(Collection coll):删除当前集合中在参数集合中也包含的元素。 11、equals():比较此 collection 与指定对象是否相等 12、toArray():将当前结合转化成数组 13、hashCode(): 14、iterator():返回一个Iterator接口实现类的对象。
注意:如果像集合中添加自定义类型时,比较对象是否相等,必须重写equals()方法。
四、集合的遍历
(1)for(int)
(2)增强for()
(3)迭代器Iterator,hasNext(),next()。
五、List
特点:有序可重复的代码。
常用方法:
(1)void add(int index,Object obj);
(2)boolean addAll(int index,Collection coll);
(3)Object get(int index);
(4)int indexOf(Object obj);
(5)int lastOf(Object obj);
(6)Object remove(int index);
(7)Object set(int index,Object obj);
(8)List subList(int fromIndex,int toIndex);
六、集合框架结构
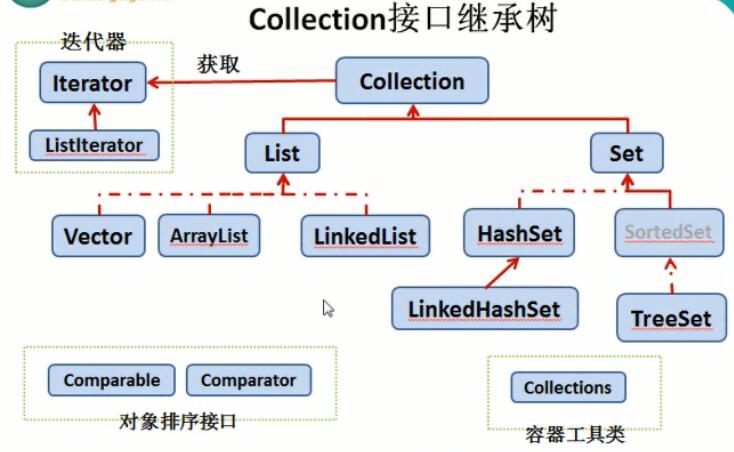
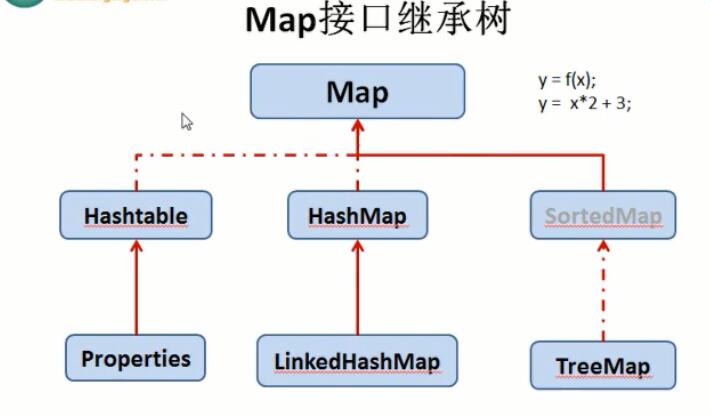
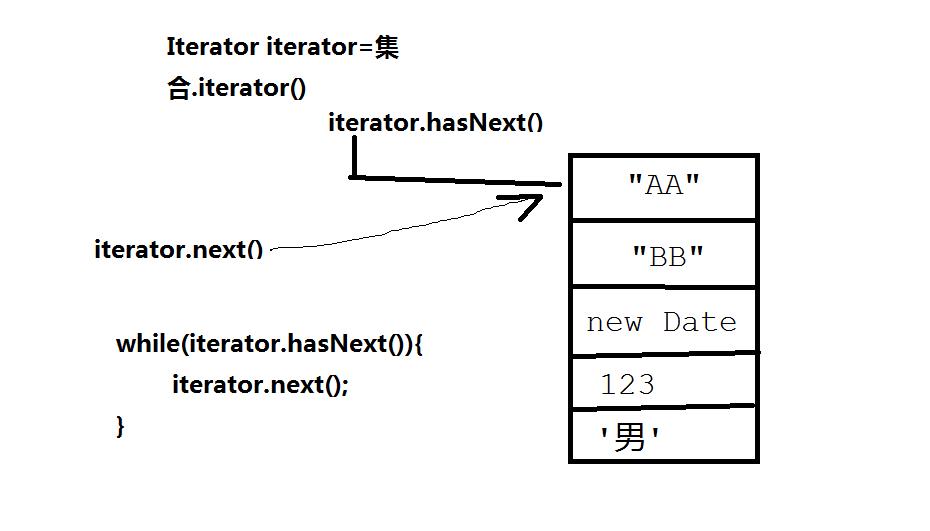
七、集合工具类(Collections)
里面提供了常用的方法,其中就有sort(),用来给集合排序,既然能使用sort对集合进行排序,说明元素是之间是可以比较大小的,必须重写接口里的CompareTo(Object obj)方法,这个方法是用来进行元素之间的比较的。
this>obj 返回>0的数
this<obj 返回<0的数
this=obj 返回0
Comparable-----compareTo(Object a)
Comparator-----compare(Object a,Object b)

1 import org.junit.Test; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 import java.util.Collections; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 7 public class Te { 8 @Test 9 public void test() throws Exception{ 10 List<Cell> list = new ArrayList<>(); 11 Cell cell1 = new Cell("1das",11); 12 Cell cell2 = new Cell("1das",13); 13 Cell cell3 = new Cell("1das",9); 14 list.add(cell1); 15 list.add(cell2); 16 list.add(cell3); 17 System.out.println(list); 18 Collections.sort(list); 19 System.out.println(list); 20 } 21 } 22 class Cell implements Comparable{ 23 String name; 24 int age; 25 public Cell(){} 26 public Cell(String name,int age){ 27 this.name = name; 28 this.age = age; 29 } 30 public int compareTo(Object a){ 31 Cell c = new Cell(); 32 if(a instanceof Cell){ 33 c = (Cell) a; 34 } 35 return this.age-c.age; 36 } 37 38 @Override 39 public String toString() { 40 return "Cell{" + 41 "name=\'" + name + \'\\\'\' + 42 ", age=" + age + 43 \'}\'; 44 } 45 }

1 import org.junit.Test; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 public class Te { 6 @Test 7 public void test() throws Exception{ 8 List<Cell> list = new ArrayList<>(); 9 Cell cell1 = new Cell("2das",11); 10 Cell cell2 = new Cell("1das",11); 11 Cell cell3 = new Cell("1das",9); 12 list.add(cell1); 13 list.add(cell2); 14 list.add(cell3); 15 Cell cell = new Cell(); 16 System.out.println(list); 17 Collections.sort(list,cell); 18 System.out.println(list); 19 } 20 } 21 class Cell implements Comparator { 22 String name; 23 int age; 24 public Cell(){} 25 public Cell(String name,int age){ 26 this.name = name; 27 this.age = age; 28 } 29 public int compare(Object a,Object b){ 30 Cell c = new Cell(); 31 Cell c1 = new Cell(); 32 if(a instanceof Cell){ 33 c = (Cell) a; 34 } 35 if(b instanceof Cell){ 36 c1 = (Cell) b; 37 } 38 if(c1.age!=c.age) 39 return c.age-c1.age; 40 else 41 return c.name.compareTo(c1.name); 42 } 43 44 @Override 45 public String toString() { 46 return "Cell{" + 47 "name=\'" + name + \'\\\'\' + 48 ", age=" + age + 49 \'}\'; 50 } 51 }

1 import org.junit.Test; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 public class Te { 6 @Test 7 public void test() throws Exception{ 8 Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); 9 map.put("aa",11); 10 map.put("ab",31); 11 map.put("ad",38); 12 map.put("ac",7); 13 for(Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Integer> > i = map.entrySet().iterator();i.hasNext(); ){ 14 Map.Entry<String,Integer> c = i.next(); 15 System.out.println(c.getKey()+" "+c.getValue()); 16 } 17 List<Map.Entry<String,Integer> >list = new ArrayList<>(map.entrySet()); 18 19 Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() { 20 @Override 21 public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o1, Map.Entry<String, Integer> o2) { 22 return o2.getValue()-o1.getValue();//按value值从大到小排序 23 } 24 }); 25 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); 26 for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> i:list){ 27 System.out.println(i.getKey()+" "+i.getValue()); 28 } 29 } 30 }
总结:HashMap是无序的,TreeMap默认是升序的,是对Key进行升序排序,当我们有对Value进行排序的需求时可以看上述代码。
图片略丑啊,哈哈哈,今天为大家更新了集合的内容,如果觉得对你有帮助的话,就请点点赞吧!!!
以上是关于Java集合框架的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
