SpringBoot系列十二:SpringBoot整合 Shiro
Posted 小不点啊
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SpringBoot系列十二:SpringBoot整合 Shiro相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
声明:本文来源于MLDN培训视频的课堂笔记,写在这里只是为了方便查阅。
1、概念:SpringBoot 整合 Shiro
2、具体内容
Shiro 是现在最为流行的权限认证开发框架,与它起名的只有最初的 SpringSecurity(这个开发框架非常不好用,但是千万不要 以为 SpringSecurity 没有用处,它在 SpringCloud 阶段将发挥重大的作用)。但是现在如果要想整合 Shiro 开发框架有一点很遗憾, SpringBoot 没有直接的配置支持,它不像整合所谓的 Kafka、Redis、DataSource,也就是说如果要想整合 Shiro 开发框架那么就必须 自己来进行配置。
2.1、项目开发准备
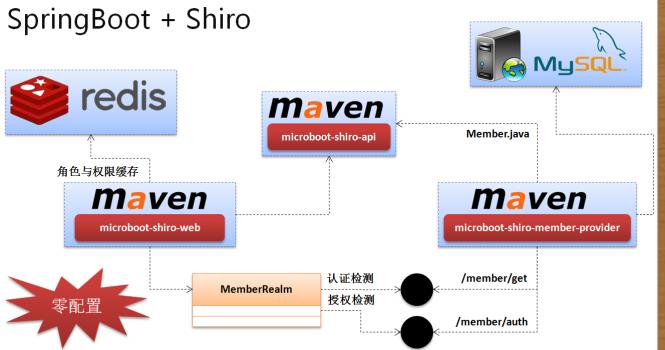
在整个的 Shiro 之中最为重要的部分:认证以及授权处理(Realm),在 Realm 里面实际上在开发之中所需要调用的业务方法 只有两类:根据用户编号取得用户的完整信息,在认证通过之后根据用户编号获得用户对应的所有的角色以及权限信息,而且既然已经到了微架构的阶段,那么不得不去面对一个问题,对于这种用户的业务操作是放在 WEB 端还是单独提出来做成一个 Rest 服务? 很明显,应该作为一个服务进行抽象出来,也就是说在整体的调用处理之中,Realm 需要进行 Rest 服务调用(RestTemplate 存在可 以让整个的调用更加容易)。
那么按照如上的设计方案,现在的整体的项目里面认为应该包含有如下的几个开发模块:
· microboot-shiro-api:应该提供有服务的 VO 类、各种加密处理的工具类;
· microboot-shiro-member-provider:进行用户认证与授权 REST 服务的提供,要暴露两个接口:用户信息获得、角色与权限信息获得;
· microboot-shiro-web:主要进行 Shiro 的认证与授权检测处理。
1、 【microboot-shiro-member-provider】保存本次的数据库脚本
-- 删除数据库 DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS study ; -- 创建数据库 CREATE DATABASE study CHARACTER SET UTF8 ; -- 使用数据库 USE study ; CREATE TABLE member( mid VARCHAR(50) , name VARCHAR(50) , password VARCHAR(32) , locked INT , CONSTRAINT pk_mid PRIMARY KEY(mid) ) ; CREATE TABLE role ( rid VARCHAR(50) , title VARCHAR(50) , CONSTRAINT pk_rid PRIMARY KEY(rid) ) ; CREATE TABLE action ( actid VARCHAR(50) , title VARCHAR(50) , rid VARCHAR(50) , CONSTRAINT pk_actid PRIMARY KEY(actid) ) ; CREATE TABLE member_role ( mid VARCHAR(50) , rid VARCHAR(50) ) ; INSERT INTO member(mid,name,password,locked) VALUES (\'studyjava\',\'study\',\'2E866BF58289E01583AD418F486A69DF\',0) ; INSERT INTO member(mid,name,password,locked) VALUES (\'admin\',\'admin\',\'2E866BF58289E01583AD418F486A69DF\',0) ; INSERT INTO role(rid,title) VALUES (\'emp\',\'雇员管理\') ; INSERT INTO role(rid,title) VALUES (\'dept\',\'部门管理\') ; INSERT INTO action(actid,title,rid) VALUES (\'emp:add\',\'雇员入职\',\'emp\') ; INSERT INTO action(actid,title,rid) VALUES (\'emp:remove\',\'雇员离职\',\'emp\') ; INSERT INTO action(actid,title,rid) VALUES (\'emp:list\',\'雇员列表\',\'emp\') ; INSERT INTO action(actid,title,rid) VALUES (\'emp:edit\',\'雇员编辑\',\'emp\') ; INSERT INTO action(actid,title,rid) VALUES (\'dept:list\',\'部门列表\',\'dept\') ; INSERT INTO action(actid,title,rid) VALUES (\'dept:edit\',\'部门编辑\',\'dept\') ; INSERT INTO member_role(mid,rid) VALUES (\'studyjava\',\'emp\') ; INSERT INTO member_role(mid,rid) VALUES (\'admin\',\'emp\') ; INSERT INTO member_role(mid,rid) VALUES (\'admin\',\'dept\') ;
2、 【microboot-shiro-api】建立一个 Member 程序类,保存认证返回的信息;
· Shiro 进行认证处理的时候是要求根据一个用户的编号获得用户对应的完整信息,而后再进行用户是否存在的判断、密码 是否正确的判断、是否被锁定的判断。
package cn.study.vo; import java.io.Serializable; @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class Member implements Serializable { private String mid ; private String name ; private String password ; private Integer locked ; public String getMid() { return mid; } public void setMid(String mid) { this.mid = mid; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public Integer getLocked() { return locked; } public void setLocked(Integer locked) { this.locked = locked; } @Override public String toString() { return "Member [mid=" + mid + ", name=" + name + ", password=" + password + ", locked=" + locked + "]"; } }
3、 【microboot-shiro-api】密码的加密处理;
package cn.study.util.enctype; public class MD5Code { /* * 下面这些S11-S44实际上是一个4*4的矩阵,在原始的C实现中是用#define 实现的, 这里把它们实现成为static * final是表示了只读,且能在同一个进程空间内的多个 Instance间共享 */ static final int S11 = 7; static final int S12 = 12; static final int S13 = 17; static final int S14 = 22; static final int S21 = 5; static final int S22 = 9; static final int S23 = 14; static final int S24 = 20; static final int S31 = 4; static final int S32 = 11; static final int S33 = 16; static final int S34 = 23; static final int S41 = 6; static final int S42 = 10; static final int S43 = 15; static final int S44 = 21; static final byte[] PADDING = { -128, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; /* * 下面的三个成员是MD5计算过程中用到的3个核心数据,在原始的C实现中 被定义到MD5_CTX结构中 */ private long[] state = new long[4];// state (ABCD) private long[] count = new long[2];// number of bits, modulo 2^64 (lsb // first) private byte[] buffer = new byte[64]; // input buffer /* * digestHexStr是MD5的唯一一个公共成员,是最新一次计算结果的 16进制ASCII表示. */ public String digestHexStr; /* * digest,是最新一次计算结果的2进制内部表示,表示128bit的MD5值. */ private byte[] digest = new byte[16]; /* * getMD5ofStr是类MD5最主要的公共方法,入口参数是你想要进行MD5变换的字符串 * 返回的是变换完的结果,这个结果是从公共成员digestHexStr取得的. */ public String getMD5ofStr(String inbuf) { md5Init(); md5Update(inbuf.getBytes(), inbuf.length()); md5Final(); digestHexStr = ""; for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) { digestHexStr += byteHEX(digest[i]); } return digestHexStr; } // 这是MD5这个类的标准构造函数,JavaBean要求有一个public的并且没有参数的构造函数 public MD5Code() { md5Init(); return; } /* md5Init是一个初始化函数,初始化核心变量,装入标准的幻数 */ private void md5Init() { count[0] = 0L; count[1] = 0L; // /* Load magic initialization constants. state[0] = 0x67452301L; state[1] = 0xefcdab89L; state[2] = 0x98badcfeL; state[3] = 0x10325476L; return; } /* * F, G, H ,I 是4个基本的MD5函数,在原始的MD5的C实现中,由于它们是 * 简单的位运算,可能出于效率的考虑把它们实现成了宏,在java中,我们把它们 实现成了private方法,名字保持了原来C中的。 */ private long F(long x, long y, long z) { return (x & y) | ((~x) & z); } private long G(long x, long y, long z) { return (x & z) | (y & (~z)); } private long H(long x, long y, long z) { return x ^ y ^ z; } private long I(long x, long y, long z) { return y ^ (x | (~z)); } /* * FF,GG,HH和II将调用F,G,H,I进行近一步变换 FF, GG, HH, and II transformations for * rounds 1, 2, 3, and 4. Rotation is separate from addition to prevent * recomputation. */ private long FF(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) { a += F(b, c, d) + x + ac; a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s)); a += b; return a; } private long GG(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) { a += G(b, c, d) + x + ac; a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s)); a += b; return a; } private long HH(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) { a += H(b, c, d) + x + ac; a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s)); a += b; return a; } private long II(long a, long b, long c, long d, long x, long s, long ac) { a += I(b, c, d) + x + ac; a = ((int) a << s) | ((int) a >>> (32 - s)); a += b; return a; } /* * md5Update是MD5的主计算过程,inbuf是要变换的字节串,inputlen是长度,这个 * 函数由getMD5ofStr调用,调用之前需要调用md5init,因此把它设计成private的 */ private void md5Update(byte[] inbuf, int inputLen) { int i, index, partLen; byte[] block = new byte[64]; index = (int) (count[0] >>> 3) & 0x3F; // /* Update number of bits */ if ((count[0] += (inputLen << 3)) < (inputLen << 3)) count[1]++; count[1] += (inputLen >>> 29); partLen = 64 - index; // Transform as many times as possible. if (inputLen >= partLen) { md5Memcpy(buffer, inbuf, index, 0, partLen); md5Transform(buffer); for (i = partLen; i + 63 < inputLen; i += 64) { md5Memcpy(block, inbuf, 0, i, 64); md5Transform(block); } index = 0; } else i = 0; // /* Buffer remaining input */ md5Memcpy(buffer, inbuf, index, i, inputLen - i); } /* * md5Final整理和填写输出结果 */ private void md5Final() { byte[] bits = new byte[8]; int index, padLen; // /* Save number of bits */ Encode(bits, count, 8); // /* Pad out to 56 mod 64. index = (int) (count[0] >>> 3) & 0x3f; padLen = (index < 56) ? (56 - index) : (120 - index); md5Update(PADDING, padLen); // /* Append length (before padding) */ md5Update(bits, 8); // /* Store state in digest */ Encode(digest, state, 16); } /* * md5Memcpy是一个内部使用的byte数组的块拷贝函数,从input的inpos开始把len长度的 * 字节拷贝到output的outpos位置开始 */ private void md5Memcpy(byte[] output, byte[] input, int outpos, int inpos, int len) { int i; for (i = 0; i < len; i++) output[outpos + i] = input[inpos + i]; } /* * md5Transform是MD5核心变换程序,有md5Update调用,block是分块的原始字节 */ private void md5Transform(byte block[]) { long a = state[0], b = state[1], c = state[2], d = state[3]; long[] x = new long[16]; Decode(x, block, 64); /* Round 1 */ a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[0], S11, 0xd76aa478L); /* 1 */ d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[1], S12, 0xe8c7b756L); /* 2 */ c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[2], S13, 0x242070dbL); /* 3 */ b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[3], S14, 0xc1bdceeeL); /* 4 */ a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[4], S11, 0xf57c0fafL); /* 5 */ d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[5], S12, 0x4787c62aL); /* 6 */ c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[6], S13, 0xa8304613L); /* 7 */ b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[7], S14, 0xfd469501L); /* 8 */ a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[8], S11, 0x698098d8L); /* 9 */ d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[9], S12, 0x8b44f7afL); /* 10 */ c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[10], S13, 0xffff5bb1L); /* 11 */ b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[11], S14, 0x895cd7beL); /* 12 */ a = FF(a, b, c, d, x[12], S11, 0x6b901122L); /* 13 */ d = FF(d, a, b, c, x[13], S12, 0xfd987193L); /* 14 */ c = FF(c, d, a, b, x[14], S13, 0xa679438eL); /* 15 */ b = FF(b, c, d, a, x[15], S14, 0x49b40821L); /* 16 */ /* Round 2 */ a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[1], S21, 0xf61e2562L); /* 17 */ d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[6], S22, 0xc040b340L); /* 18 */ c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[11], S23, 0x265e5a51L); /* 19 */ b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[0], S24, 0xe9b6c7aaL); /* 20 */ a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[5], S21, 0xd62f105dL); /* 21 */ d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[10], S22, 0x2441453L); /* 22 */ c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[15], S23, 0xd8a1e681L); /* 23 */ b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[4], S24, 0xe7d3fbc8L); /* 24 */ a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[9], S21, 0x21e1cde6L); /* 25 */ d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[14], S22, 0xc33707d6L); /* 26 */ c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[3], S23, 0xf4d50d87L); /* 27 */ b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[8], S24, 0x455a14edL); /* 28 */ a = GG(a, b, c, d, x[13], S21, 0xa9e3e905L); /* 29 */ d = GG(d, a, b, c, x[2], S22, 0xfcefa3f8L); /* 30 */ c = GG(c, d, a, b, x[7], S23, 0x676f02d9L); /* 31 */ b = GG(b, c, d, a, x[12], S24, 0x8d2a4c8aL); /* 32 */ /* Round 3 */ a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[5], S31, 0xfffa3942L); /* 33 */ d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[8], S32, 0x8771f681L); /* 34 */ c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[11], S33, 0x6d9d6122L); /* 35 */ b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[14], S34, 0xfde5380cL); /* 36 */ a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[1], S31, 0xa4beea44L); /* 37 */ d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[4], S32, 0x4bdecfa9L); /* 38 */ c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[7], S33, 0xf6bb4b60L); /* 39 */ b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[10], S34, 0xbebfbc70L); /* 40 */ a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[13], S31, 0x289b7ec6L); /* 41 */ d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[0], S32, 0xeaa127faL); /* 42 */ c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[3], S33, 0xd4ef3085L); /* 43 */ b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[6], S34, 0x4881d05L); /* 44 */ a = HH(a, b, c, d, x[9], S31, 0xd9d4d039L); /* 45 */ d = HH(d, a, b, c, x[12], S32, 0xe6db99e5L); /* 46 */ c = HH(c, d, a, b, x[15], S33, 0x1fa27cf8L); /* 47 */ b = HH(b, c, d, a, x[2], S34, 0xc4ac5665L); /* 48 */ /* Round 4 */ a = II(a, b, c, d, x[0], S41, 0xf4292244L); /* 49 */ d = II(d, a, b, c, x[7], S42, 0x432aff97L); /* 50 */ c = II(c, d, a, b, x[14], S43, 0xab9423a7L); /* 51 */ b = II(b, c, d, a, x[5], S44, 0xfc93a039L); /* 52 */ a = II(a, b, c, d, x[12], S41, 0x655b59c3L); /* 53 */ d = II(d, a, b, c, x[3], S42, 0x8f0ccc92L); /* 54 */ c = II(c, d, a, b, x[10], S43, 0xffeff47dL); /* 55 */ b = II(b, c, d, a, x[1], S44, 0x85845dd1L); /* 56 */ a = II(a, b, c, d, x[8], S41, 0x6fa87e4fL); /* 57 */ d = II(d, a, b, c, x[15], S42, 0xfe2ce6e0L); /* 58 */ c = II(c, d, a, b, x[6], S43, 0xa3014314L); /* 59 */ b = II(b, c, d, a, x[13], S44, 0x4e0811a1L); /* 60 */ a = II(a, b, c, d, x[4], S41, 0xf7537e82L); /* 61 */ d = II(d, a, b, c, x[11], S42, 0xbd3af235L); /* 62 */ c = II(c, d, a, b, x[2], S43, 0x2ad7d2bbL); /* 63 */ b = II(b, c, d, a, x[9], S44, 0xeb86d391L); /* 64 */ state[0] += a; state[1] += b; state[2] += c; state[3] += d; } /* * Encode把long数组按顺序拆成byte数组,因为java的long类型是64bit的, 只拆低32bit,以适应原始C实现的用途 */ private void Encode(byte[] output, long[] input, int len) { int i, j; for (i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i++, j += 4) { output[j] = (byte) (input[i] & 0xffL); output[j + 1] = (byte) ((input[i] >>> 8) & 0xffL); output[j + 2] = (byte) ((input[i] >>> 16) & 0xffL); output[j + 3] = (byte) ((input[i] >>> 24) & 0xffL); } } /* * Decode把byte数组按顺序合成成long数组,因为java的long类型是64bit的, * 只合成低32bit,高32bit清零,以适应原始C实现的用途 */ private void Decode(long[] output, byte[] input, int len) { int i, j; for (i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i++, j += 4) output[i] = b2iu(input[j]) | (b2iu(input[j + 1]) << 8) | (b2iu(input[j + 2]) << 16) | (b2iu(input[j + 3]) << 24); return; } /* * b2iu是我写的一个把byte按照不考虑正负号的原则的"升位"程序,因为java没有unsigned运算 */ public static long b2iu(byte b) { return b < 0 ? b & 0x7F + 128 : b; } /* * byteHEX(),用来把一个byte类型的数转换成十六进制的ASCII表示, * 因为java中的byte的toString无法实现这一点,我们又没有C语言中的 sprintf(outbuf,"%02X",ib) */ public static String byteHEX(byte ib) { char[] Digit = { \'0\', \'1\', \'2\', \'3\', \'4\', \'5\', \'6\', \'7\', \'8\', \'9\', \'A\', \'B\', \'C\', \'D\', \'E\', \'F\' }; char[] ob = new char[2]; ob[0] = Digit[(ib >>> 4) & 0X0F]; ob[1] = Digit[ib & 0X0F]; String s = new String(ob); return s; } }
package cn.study.util.enctype; import java.util.Base64; public class PasswordUtil { private static final String SEED = "studyjava" ; // 该数据为种子数,如果要加密则需要使用Base64做多次迭代 private static final int NE_NUM = 3 ; // 密码迭代处理3次 private PasswordUtil() {} private static String createSeed() { //以上是关于SpringBoot系列十二:SpringBoot整合 Shiro的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章Springboot系列(三十二):Springboot集成 kafka(环境搭建+演示)|超级详细,建议收藏
Springboot系列(三十二):Springboot集成 kafka(环境搭建+演示)|超级详细,建议收藏
Springboot系列(三十二):Springboot集成 kafka(环境搭建+演示)|超级详细,建议收藏
springboot系列(二十二):集成easypoi实现Excel文件的导入导出(准备篇)