Spring源码分析--BeanProcessor
Posted 专注Java后端技术
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring源码分析--BeanProcessor相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、何谓BeanProcessor
BeanPostProcessor是SpringFramework里非常重要的核心接口之一,我先贴出一段源代码:

/* * Copyright 2002-2015 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.beans.factory.config; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; /** * Factory hook that allows for custom modification of new bean instances, * e.g. checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies. * * <p>ApplicationContexts can autodetect BeanPostProcessor beans in their * bean definitions and apply them to any beans subsequently created. * Plain bean factories allow for programmatic registration of post-processors, * applying to all beans created through this factory. * * <p>Typically, post-processors that populate beans via marker interfaces * or the like will implement {@link #postProcessBeforeInitialization}, * while post-processors that wrap beans with proxies will normally * implement {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization}. * * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 10.10.2003 * @see InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor * @see DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor * @see ConfigurableBeanFactory#addBeanPostProcessor * @see BeanFactoryPostProcessor */ public interface BeanPostProcessor { /** * Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean * initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean\'s {@code afterPropertiesSet} * or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values. * The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original. * @param bean the new bean instance * @param beanName the name of the bean * @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one; * if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked * @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet */ Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; /** * Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean * initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean\'s {@code afterPropertiesSet} * or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values. * The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original. * <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean * instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The * post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created * objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks. * <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a * {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method, * in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks. * @param bean the new bean instance * @param beanName the name of the bean * @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one; * if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked * @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean */ Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; }
在这里我先简单解释一下其注释的含义:
这个接口允许我们自定义修改新bean的一个实例,比如说:检查它们的接口或者将他们包装成代理对象等,ApplicationContexts能自动察觉到我们在BeanProcessor里对对象作出的改变,并在后来创建该对象时应用其对应的改变。
这两个方法分别对应IOC容器对对象初始化前的操作和对象初始化后的操作
下面我们来演示一个例子:
StudentEntity:

package org.hzgj.spring.study.entity; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; public class StudentEntity { private Integer id; private String name; private Map<String,String> memerories= new HashMap<>(); public Map<String, String> getMemerories() { return memerories; } public void setMemerories(Map<String, String> memerories) { this.memerories = memerories; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public StudentEntity() { // System.out.println("studentEntity initializer...."); } @Override public String toString() { return "StudentEntity{" + "id=" + id + ", name=\'" + name + \'\\\'\' + \'}\'; } private List<String> hobbies=new ArrayList<>(); public List<String> getHobbies() { return hobbies; } public void setHobbies(List<String> hobbies) { this.hobbies = hobbies; } }
TestBeanPostProcessor:

package org.hzgj.spring.study.context; import org.hzgj.spring.study.entity.StudentEntity; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; public class TestBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean instanceof StudentEntity) { StudentEntity studentEntity = new StudentEntity(); studentEntity.setName(beanName); return studentEntity; } return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean instanceof StudentEntity) System.out.println(bean); return bean; } }
Main方法:

package org.hzgj.spring.study; import org.hzgj.spring.study.entity.StudentEntity; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring-config.xml"); StudentEntity studentEntity = applicationContext.getBean(StudentEntity.class); System.out.println(studentEntity.getName()); } }
spring-config.xml关键代码:

<bean id="studentEntity" class="org.hzgj.spring.study.entity.StudentEntity" depends-on="studentServiceWithFactory"> <property name="hobbies" ref="hobbies"> </property> <property name="memerories"> <map> <entry key="glad" value="play"/> <entry key="cry" value="cry"/> </map> </property> <property name="name" value="admin"/> </bean> <bean id="beanPostProcessor" class="org.hzgj.spring.study.context.TestBeanPostProcessor" />
运行得到如下结果:
![]()
我们可以看到在配置文件里定义的bean属性已经发生改变
二、SpringFramework中BeanPostProcessor经典应用场景
1.初始化BeanPostProcessor的源码
根据 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的构造方法,我们可以看到该类初始化的时候会调用refresh():

/** * Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext with the given parent, * loading the definitions from the given XML files. * @param configLocations array of resource locations * @param refresh whether to automatically refresh the context, * loading all bean definitions and creating all singletons. * Alternatively, call refresh manually after further configuring the context. * @param parent the parent context * @throws BeansException if context creation failed * @see #refresh() */ public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException { super(parent); setConfigLocations(configLocations); if (refresh) { refresh(); } }
那么紧接着在AbstractApplicationContext中找到refresh()方法:

@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset \'active\' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring\'s core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
那么在这里Spring会进行一系列的初始化操作,我们请留意registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);这句代码,追踪一下我们可以看到在该方法里注册Processor:

public static void registerBeanPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when // a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when // a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors. int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); orderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors. List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors. sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); // Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners, // moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc). beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext)); }
2.@Autowired实现的代码跟踪

注意AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor最终也是BeanPostProcessor的实现类,具体类的描述我就不再这里阐述了,大家可自行查看源码
3、SpringBoot中的定制化内嵌web容器
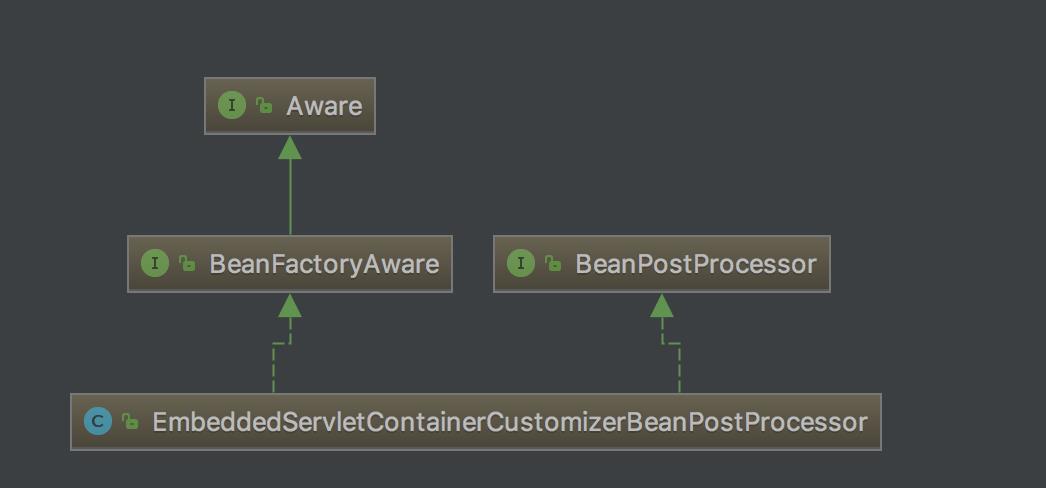
这个EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor直接实现的就是BeanPostProcessor,该类下请关注如下方法:

@Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean instanceof ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer) { postProcessBeforeInitialization((ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer) bean); } return bean; }

private void postProcessBeforeInitialization( ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer bean) { for (EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer customizer : getCustomizers()) { customizer.customize(bean); } }

private Collection<EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer> getCustomizers() { if (this.customizers == null) { // Look up does not include the parent context this.customizers = new ArrayList<EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer>( this.beanFactory .getBeansOfType(EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer.class, false, false) .values()); Collections.sort(this.customizers, AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE); this.customizers = Collections.unmodifiableList(this.customizers); } return this.customizers; }
这里面有一个接口:EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer 该接口有个实现类 ServerProperties 熟悉springboot外部化配置原理的同胞们其实一看便知

/* * Copyright 2012-2018 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web; import java.io.File; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.SessionCookieConfig; import javax.servlet.SessionTrackingMode; import io.undertow.Undertow.Builder; import io.undertow.UndertowOptions; import org.apache.catalina.Context; import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector; import org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve; import org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve; import org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteIpValve; import org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol; import org.apache.coyote.ProtocolHandler; import org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11Protocol; import org.eclipse.jetty.server.AbstractConnector; import org.eclipse.jetty.server.ConnectionFactory; import org.eclipse.jetty.server.Handler; import org.eclipse.jetty.server.HttpConfiguration; import org.eclipse.jetty.server.Server; import org.eclipse.jetty.server.handler.ContextHandler; import org.eclipse.jetty.server.handler.HandlerCollection; import org.eclipse.jetty.server.handler.HandlerWrapper; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerProperties.Session.Cookie; import org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudPlatform; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.Compression; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedServletContainerFactory; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.InitParameterConfiguringServletContextInitializer; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.JspServlet; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.Ssl; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.jetty.JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.jetty.JettyServerCustomizer; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.tomcat.TomcatConnectorCustomizer; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.tomcat.TomcatContextCustomizer; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.tomcat.TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.undertow.UndertowBuilderCustomizer; import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.undertow.UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.DeprecatedConfigurationProperty; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.NestedConfigurationProperty; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletContextInitializer; import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware; import org.springframework.core.Ordered; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /** * {@link ConfigurationProperties} for a web server (e.g. port and path settings). Will be * used to customize an {@link EmbeddedServletContainerFactory} when an * {@link EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor} is active. * * @author Dave Syer * @author Stephane Nicoll * @author Andy Wilkinson * @author Ivan Sopov * @author Marcos Barbero * @author Eddú Meléndez * @author Quinten De Swaef * @author Venil Noronha * @author Aurélien Leboulanger */ @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true) public class ServerProperties implements EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer, EnvironmentAware, Ordered { /** * Server HTTP port. */ private Integer port; /** * Network address to which the server should bind to. */ private InetAddress address; /** * Context path of the application. */ private String contextPath; /** * Display name of the application. */ private String displayName = "application"; @NestedConfigurationProperty private ErrorProperties error = new ErrorProperties(); /** * Path of the main dispatcher servlet. */ private String servletPath = "/"; /** * ServletContext parameters. */ private final Map<String, String> contextParameters = new HashMap<String, String>(); /** * If X-Forwarded-* headers should be applied to the HttpRequest. */ private Boolean useForwardHeaders; /** * Value to use for the Server response header (no header is sent if empty). */ private String serverHeader; /** * Maximum size in bytes of the HTTP message header. */ private int maxHttpHeaderSize = 0; // bytes /** * Maximum size in bytes of the HTTP post content. */ private int maxHttpPostSize = 0; // bytes /** * Time in milliseconds that connectors will wait for another HTTP request before * closing the connection. When not set, the connector\'s container-specific default * will be used. Use a value of -1 to indicate no (i.e. infinite) timeout. */ private Integer connectionTimeout; private Session session = new Session(); @NestedConfigurationProperty private Ssl ssl; @NestedConfigurationProperty private Compression compression = new Compression(); @NestedConfigurationProperty private JspServlet jspServlet; private final Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); private final Jetty jetty = new Jetty(); private final Undertow undertow = new Undertow(); private Environment environment; @Override public int getOrder() { return 0; } @Override public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) { this.environment = environment; } @Override public
