Java日志框架:slf4j作用及其实现原理
Posted 五月的仓颉
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java日志框架:slf4j作用及其实现原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
简单回顾门面模式
slf4j是门面模式的典型应用,因此在讲slf4j前,我们先简单回顾一下门面模式,
门面模式,其核心为外部与一个子系统的通信必须通过一个统一的外观对象进行,使得子系统更易于使用。用一张图来表示门面模式的结构为:
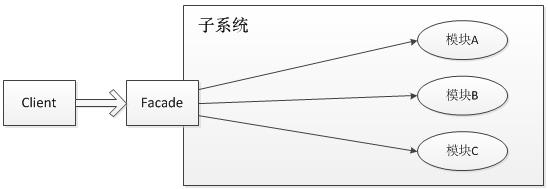
门面模式的核心为Facade即门面对象,门面对象核心为几个点:
- 知道所有子角色的功能和责任
- 将客户端发来的请求委派到子系统中,没有实际业务逻辑
- 不参与子系统内业务逻辑的实现
大致上来看,对门面模式的回顾到这里就可以了,开始接下来对SLF4J的学习。
我们为什么要使用slf4j
我们为什么要使用slf4j,举个例子:
我们自己的系统中使用了logback这个日志系统 我们的系统使用了A.jar,A.jar中使用的日志系统为log4j 我们的系统又使用了B.jar,B.jar中使用的日志系统为slf4j-simple 这样,我们的系统就不得不同时支持并维护logback、log4j、slf4j-simple三种日志框架,非常不便。
解决这个问题的方式就是引入一个适配层,由适配层决定使用哪一种日志系统,而调用端只需要做的事情就是打印日志而不需要关心如何打印日志,slf4j或者commons-logging就是这种适配层,slf4j是本文研究的对象。
从上面的描述,我们必须清楚地知道一点:slf4j只是一个日志标准,并不是日志系统的具体实现。理解这句话非常重要,slf4j只做两件事情:
- 提供日志接口
- 提供获取具体日志对象的方法
slf4j-simple、logback都是slf4j的具体实现,log4j并不直接实现slf4j,但是有专门的一层桥接slf4j-log4j12来实现slf4j。
为了更理解slf4j,我们先看例子,再读源码,相信读者朋友会对slf4j有更深刻的认识。
slf4j应用举例
上面讲了,slf4j的直接/间接实现有slf4j-simple、logback、slf4j-log4j12,我们先定义一个pom.xml,引入相关jar包:
1 <!-- 原文:五月的仓颉http://www.cnblogs.com/xrq730/p/8619156.html --> 2 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 4 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 5 6 <groupId>org.xrq.log</groupId> 7 <artifactId>log-test</artifactId> 8 <version>1.0.0</version> 9 <packaging>jar</packaging> 10 11 <name>log-test</name> 12 <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> 13 14 <properties> 15 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> 16 </properties> 17 18 <dependencies> 19 <dependency> 20 <groupId>junit</groupId> 21 <artifactId>junit</artifactId> 22 <version>4.11</version> 23 <scope>test</scope> 24 </dependency> 25 <dependency> 26 <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> 27 <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> 28 <version>1.7.25</version> 29 </dependency> 30 <dependency> 31 <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> 32 <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> 33 <version>1.2.3</version> 34 </dependency> 35 <dependency> 36 <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> 37 <artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId> 38 <version>1.7.25</version> 39 </dependency> 40 <dependency> 41 <groupId>log4j</groupId> 42 <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> 43 <version>1.2.17</version> 44 </dependency> 45 <dependency> 46 <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> 47 <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> 48 <version>1.7.21</version> 49 </dependency> 50 </dependencies> 51 </project>
写一段简单的Java代码:
1 @Test 2 public void testSlf4j() { 3 Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Object.class); 4 logger.error("123"); 5 }
接着我们首先把上面pom.xml的第30行~第49行注释掉,即不引入任何slf4j的实现类,运行Test方法,我们看一下控制台的输出为:
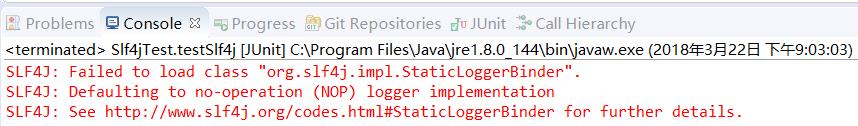
看到没有任何日志的输出,这验证了我们的观点:slf4j不提供日志的具体实现,只有slf4j是无法打印日志的。
接着打开logback-classic的注释,运行Test方法,我们看一下控制台的输出为:
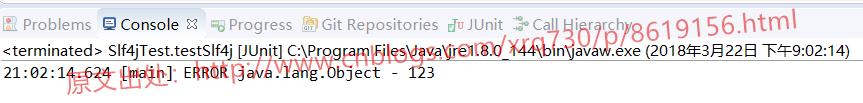
看到我们只要引入了一个slf4j的具体实现类,即可使用该日志框架输出日志。
最后做一个测验,我们把所有日志打开,引入logback-classic、slf4j-simple、log4j,运行Test方法,控制台输出为:
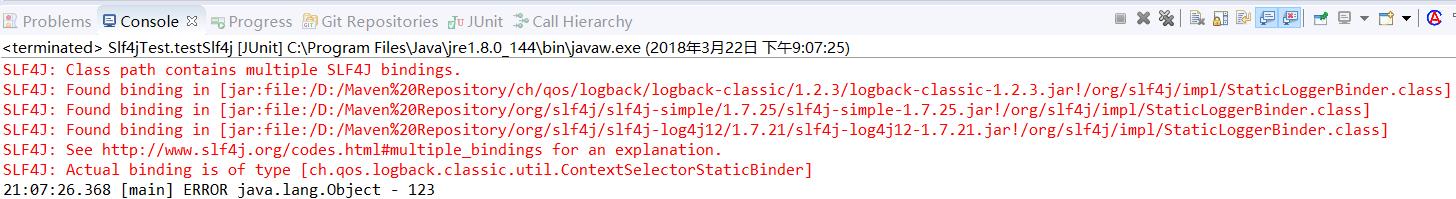
和上面的差别是,可以输出日志,但是会输出一些告警日志,提示我们同时引入了多个slf4j的实现,然后选择其中的一个作为我们使用的日志系统。
从例子我们可以得出一个重要的结论,即slf4j的作用:只要所有代码都使用门面对象slf4j,我们就不需要关心其具体实现,最终所有地方使用一种具体实现即可,更换、维护都非常方便。
slf4j实现原理
上面看了slf4j的示例,下面研究一下slf4j的实现,我们只关注重点代码。
slf4j的用法就是常年不变的一句"Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Object.class);",可见这里就是通过LoggerFactory去拿slf4j提供的一个Logger接口的具体实现而已,LoggerFactory的getLogger的方法实现为:
1 public static Logger getLogger(Class<?> clazz) { 2 Logger logger = getLogger(clazz.getName()); 3 if (DETECT_LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH) { 4 Class<?> autoComputedCallingClass = Util.getCallingClass(); 5 if (autoComputedCallingClass != null && nonMatchingClasses(clazz, autoComputedCallingClass)) { 6 Util.report(String.format("Detected logger name mismatch. Given name: \\"%s\\"; computed name: \\"%s\\".", logger.getName(), 7 autoComputedCallingClass.getName())); 8 Util.report("See " + LOGGER_NAME_MISMATCH_URL + " for an explanation"); 9 } 10 } 11 return logger; 12 }
从第2行开始跟代码,一直跟到LoggerFactory的bind()方法:
1 private final static void bind() { 2 try { 3 Set<URL> staticLoggerBinderPathSet = null; 4 // skip check under android, see also 5 // http://jira.qos.ch/browse/SLF4J-328 6 if (!isAndroid()) { 7 staticLoggerBinderPathSet = findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(); 8 reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(staticLoggerBinderPathSet); 9 } 10 // the next line does the binding 11 StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton(); 12 INITIALIZATION_STATE = SUCCESSFUL_INITIALIZATION; 13 reportActualBinding(staticLoggerBinderPathSet); 14 fixSubstituteLoggers(); 15 replayEvents(); 16 // release all resources in SUBST_FACTORY 17 SUBST_FACTORY.clear(); 18 } catch (NoClassDefFoundError ncde) { 19 String msg = ncde.getMessage(); 20 if (messageContainsOrgSlf4jImplStaticLoggerBinder(msg)) { 21 INITIALIZATION_STATE = NOP_FALLBACK_INITIALIZATION; 22 Util.report("Failed to load class \\"org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder\\"."); 23 Util.report("Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation"); 24 Util.report("See " + NO_STATICLOGGERBINDER_URL + " for further details."); 25 } else { 26 failedBinding(ncde); 27 throw ncde; 28 } 29 } catch (java.lang.NoSuchMethodError nsme) { 30 String msg = nsme.getMessage(); 31 if (msg != null && msg.contains("org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton()")) { 32 INITIALIZATION_STATE = FAILED_INITIALIZATION; 33 Util.report("slf4j-api 1.6.x (or later) is incompatible with this binding."); 34 Util.report("Your binding is version 1.5.5 or earlier."); 35 Util.report("Upgrade your binding to version 1.6.x."); 36 } 37 throw nsme; 38 } catch (Exception e) { 39 failedBinding(e); 40 throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected initialization failure", e); 41 } 42 }
这个地方第7行是一个关键,看一下代码:
1 static Set<URL> findPossibleStaticLoggerBinderPathSet() { 2 // use Set instead of list in order to deal with bug #138 3 // LinkedHashSet appropriate here because it preserves insertion order 4 // during iteration 5 Set<URL> staticLoggerBinderPathSet = new LinkedHashSet<URL>(); 6 try { 7 ClassLoader loggerFactoryClassLoader = LoggerFactory.class.getClassLoader(); 8 Enumeration<URL> paths; 9 if (loggerFactoryClassLoader == null) { 10 paths = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH); 11 } else { 12 paths = loggerFactoryClassLoader.getResources(STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH); 13 } 14 while (paths.hasMoreElements()) { 15 URL path = paths.nextElement(); 16 staticLoggerBinderPathSet.add(path); 17 } 18 } catch (IOException ioe) { 19 Util.report("Error getting resources from path", ioe); 20 } 21 return staticLoggerBinderPathSet; 22 }
这个地方重点其实就是第12行的代码,getLogger的时候会去classpath下找STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH,STATIC_LOGGER_BINDER_PATH值为"org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class",即所有slf4j的实现,在提供的jar包路径下,一定是有"org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class"存在的,我们可以看一下:
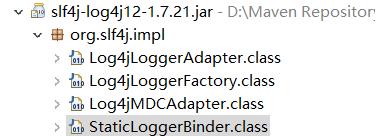
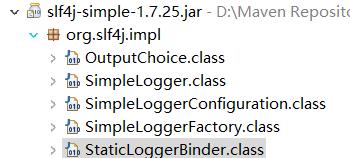
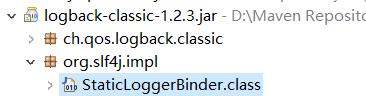
我们不能避免在系统中同时引入多个slf4j的实现,所以接收的地方是一个Set。大家应该注意到,上部分在演示同时引入logback、slf4j-simple、log4j的时候会有警告:
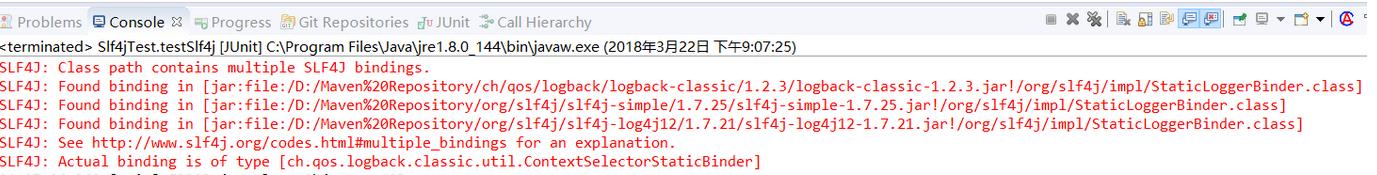
这就是因为有三个"org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class"存在的原因,此时reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity方法控制台输出语句:
1 private static void reportMultipleBindingAmbiguity(Set<URL> binderPathSet) { 2 if (isAmbiguousStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(binderPathSet)) { 3 Util.report("Class path contains multiple SLF4J bindings."); 4 for (URL path : binderPathSet) { 5 Util.report("Found binding in [" + path + "]"); 6 } 7 Util.report("See " + MULTIPLE_BINDINGS_URL + " for an explanation."); 8 } 9 }
那网友朋友可能会问,同时存在三个"org/slf4j/impl/StaticLoggerBinder.class"怎么办?首先确定的是这不会导致启动报错,其次在这种情况下编译期间,编译器会选择其中一个StaticLoggerBinder.class进行绑定,这个地方sfl4j也在reportActualBinding方法中报告了绑定的是哪个日志框架:
1 private static void reportActualBinding(Set<URL> binderPathSet) { 2 // binderPathSet can be null under Android 3 if (binderPathSet != null && isAmbiguousStaticLoggerBinderPathSet(binderPathSet)) { 4 Util.report("Actual binding is of type [" + StaticLoggerBinder.getSingleton().getLoggerFactoryClassStr() + "]"); 5 } 6 }
对照上面的截图,看最后一行,确实是"Actual binding is of type..."这句。
最后StaticLoggerBinder就比较简单了,不同的StaticLoggerBinder其getLoggerFactory实现不同,拿到ILoggerFactory之后调用一下getLogger即拿到了具体的Logger,可以使用Logger进行日志输出。
以上是关于Java日志框架:slf4j作用及其实现原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章