理论知识:
什么是事务?
指作为单个逻辑工作单位执行的一系列操作,要么完全的执行,要么完全不执行。事务处理可以确保非事务性单元内的所有操作都完全完成,否则永久不会更新面向数据的资源。通过将一组操作组合为一个要么成功要么失败的单元,可以简化错误恢复并使应用程序更加可靠。
事务并发的问题:
(1)脏读:读到另一个事务未提交前的数据。
(2)不可重复读:同一条记录2次读取到的数据不一样。
(3)幻读(虚读):同一个表,2次查询到的数据不一样。
事务的隔离级别:
(1)读,未提交(read uncommited):什么都没解决,性能最好,一般不用。
(2)读已提交数据(read commited):Oracle默认,解决了脏读。
(3)可重复读(repeatable read):mysql默认,解决了脏读,不可重复读。
(4)串行化(serializable序列化),容易产生死锁。解决所有上述并发问题。
#查询事务隔离级别 SELECT @@tx_isolation; #修改隔离级别 SET SESSION TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL read UNCOMMITTED ;
案例演示:
A向B转账,A金额减少,B金额增加。 若转账中出现问题,则A和B的金额都不变。

public class User { private Integer uid; // private String uid; private String name; private String password; private Double balance; //金额 public Integer getUid() { return uid; } public void setUid(Integer uid) { this.uid = uid; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public Double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(Double balance) { this.balance = balance; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "uid=" + uid + ", name=‘" + name + ‘\\‘‘ + ", password=‘" + password + ‘\\‘‘ + ", balance=" + balance + ‘}‘; } }

1 <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC 2 "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" 3 "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> 4 <hibernate-mapping> 5 <!-- 6 name:User的相对路径 7 table:数据库表的名称 8 --> 9 <class name="a_helloworld.entity.User" table="t_user"> 10 <!-- 11 一个类标签里面必须有一个id. 12 hibernate要求实体类有一个属性是唯一值。 13 column:数据库列名 可以省略,省略的话默认和name的值一样 14 --> 15 <id name="uid" column="uid"> 16 <!-- 17 主键的生成策略 18 native:主键自动增长 19 uuid:自动生成一个长度为32的字符串 20 --> 21 <generator class="native"></generator> 22 </id> 23 <!-- 24 其他普通属性 25 type:一般不去设置 框架会自动对应 26 not-null:非空 27 --> 28 <property name="name"></property> 29 <property name="password"></property> 30 <property name="balance"></property> 31 </class> 32 </hibernate-mapping>

1 <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC 2 "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" 3 "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> 4 <hibernate-configuration> 5 <session-factory> 6 <!--1 数据库信息--> 7 <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> 8 <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate001?characterEncording=UTF-8</property> 9 <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> 10 <property name="hibernate.connection.password">123456</property> 11 12 <!--2 配置hibernate信息 可选部分--> 13 <!--在控制台输出底层sql语句 14 项目在开发阶段设置为true 项目发布的时候改成false 15 因为日志信息会写在文件中(io操作),浪费额外的资源 16 --> 17 <property name="show_sql">true</property> 18 <!--对输出的sql语句进行格式化--> 19 <property name="format_sql">true</property> 20 21 <!--hibernate帮助我们创建表的策略需要配置 22 create:每次执行都重新创建表,数据会丢失 23 update:如果已经有表,更新。如果没有就创建(一般使用) 24 create-drop:每次执行都重新创建,数据丢失(开发的时候使用) 25 validate:校验。每次运行校验数据库表是否正确(不会更新或创建表) 26 --> 27 <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> 28 29 <!--配置数据库方言 30 告诉hibernate你用的是什么方言 31 Mysql:limit 32 oracle:rownum 33 让hibernate识别不同数据库的自己特有的语句 34 --> 35 <property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect</property> 36 37 <!--设置事务隔离级别--> 38 <property name="hibernate.connection.isolation">4</property> 39 40 <!--当前session绑定本地线程--> 41 <property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property> 42 43 <!--3 把映射文件加载--> 44 <mapping resource="b_Query/entity/User.hbm.xml"></mapping> 45 </session-factory> 46 </hibernate-configuration>

public interface UserService { public void transfer(Integer from,Integer to,Double money); }

1 public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { 2 private UserDAO userDAO = new UserDAOImpl(); 3 @Override 4 public void transfer(Integer from, Integer to, Double money) { 5 6 Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); 7 8 /* //验证 session是否相同 9 Session session1 = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); 10 System.out.println(session == session1);*/ 11 12 Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction(); 13 14 try { 15 //from 减少金额 16 userDAO.reduce(from,money); 17 18 int i =5/0; 19 //to 增加金额 20 userDAO.increase(to,money); 21 transaction.commit(); 22 }catch (Exception e){ 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 transaction.rollback(); 25 } 26 27 } 28 }

public interface UserDAO { public void increase(Integer id,Double money); public void reduce(Integer id,Double money); }

public class UserDAOImpl implements UserDAO { @Override public void increase(Integer id, Double money) { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); User user = session.get(User.class, id); user.setBalance(user.getBalance()+money); session.update(user); } @Override public void reduce(Integer id, Double money) { Session session = HibernateUtils.getCurrentSession(); User user = session.get(User.class, id); user.setBalance(user.getBalance()-money); session.update(user); } }

public class HibernateUtils { private static Configuration configure; private static SessionFactory sessionFactory; static { configure = new Configuration().configure(); sessionFactory = configure.buildSessionFactory(); } public static SessionFactory getsessionFactory(){ return sessionFactory; } //获取session public static Session getSession(){ return sessionFactory.openSession(); } //拿到和当前线程绑定的session public static Session getCurrentSession(){ Session currentSession = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession(); return currentSession; } }

public class BalanceDemo { @Test public void transfer(){ UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl(); userService.transfer(2,1,5.0); } }
在业务层如果转账过程中出现了问题,事务回滚,可以保证数据库的一致性。
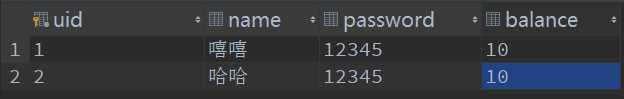
转账前的记录:
处理业务时产生异常:
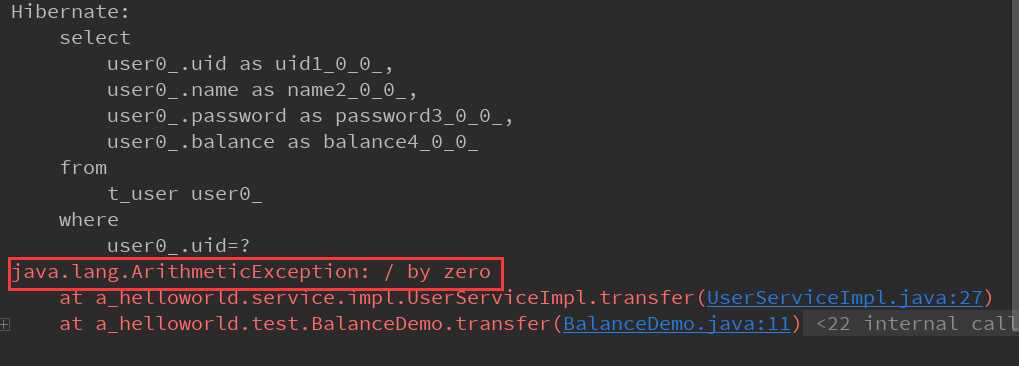
这时后刷新记录发现记录中的balance字段(表示金额)数值不变。业务逻辑实现类中,转账后捕获到了异常事务进行了回滚。
若没有产生异常,则两条记录的金额都发生变化。
注意:
1.在hibernate.cfg.xml核心配置文件中可以配置事务隔离级别 4表示repeatable read
<property name="hibernate.connection.isolation">4</property>
2.在DAO层操作数据库需要用到session,在service层获取事务也需要session,我们要确保2个session为同一个对象
解决:将session与本地线程绑定。
需要在hibernate.cfg.xml核心配置文件中配置
<!--当前session绑定本地线程-->
<property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property>
