个人认为首先要知道两点:
1.异常的父类为 Throwable
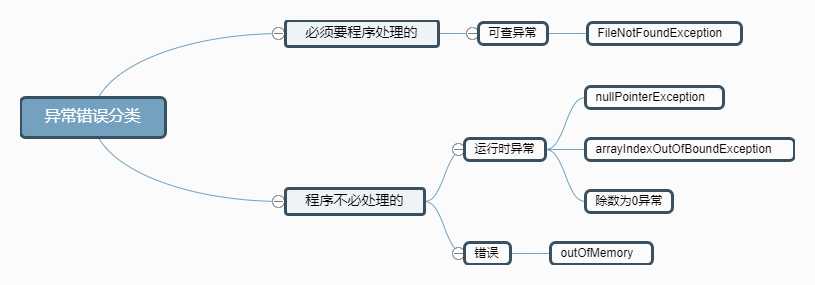
2.错误、异常总共分为三类,但需要程序处理的只有一种
现在写一个小例子:
需求:敌我双方各自英雄进行攻击,如果某方生命值达到0,对方再攻击,则报出英雄已死,无法继续攻击的异常:
1 package javatest; 2 3 class EnemyHeroIsDeadException extends Exception { 4 public EnemyHeroIsDeadException() {} 5 6 public EnemyHeroIsDeadException(String msg) { 7 super(msg); 8 } 9 } 10 11 public class Hero { 12 public String heroName; 13 protected float lifePoint; 14 15 public void attackHero(Hero h) throws EnemyHeroIsDeadException { 16 if (h.lifePoint == 0) { 17 throw new EnemyHeroIsDeadException(h.heroName + " hero has been dead"); 18 } 19 } 20 21 public String toString() { 22 return heroName; 23 } 24 25 public static void main(String[] args) throws EnemyHeroIsDeadException { 26 Hero galan = new Hero(); 27 galan.heroName = "galan"; 28 galan.lifePoint =0; 29 30 Hero mike = new Hero(); 31 mike.heroName = "mike"; 32 mike.lifePoint =10; 33 34 try { 35 mike.attackHero(galan); 36 } catch (EnemyHeroIsDeadException e) { 37 System.out.println("具体原因 " + e.getMessage()); 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 } 41 }
上面这段代码显示了编写自定义异常的一个流程:
1.写一个异常类,继承Exception
2.在调用的地方,用try catch捕捉自定义异常
3.在try中调用可能抛异常的语句