Java——IO流
Posted CoDeiSlifE
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java——IO流相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、io简介
字节:byte,计算机中存储数据的单元,一个字节有8位,是一个很具体的存储空间
字符:人们使用的记号,抽象意义上的符号,如 ‘1’ ‘中’ ‘a\' \'$\'
字符集和编码:
- 有哪些字符
- 规定每个字符分别用一个还是多个字节存储、用哪些字节存储
io就是输入与输出,即“读”和“写”
根据数据走向:输入流、输出流;根据处理的数据类型:字节流、字符流

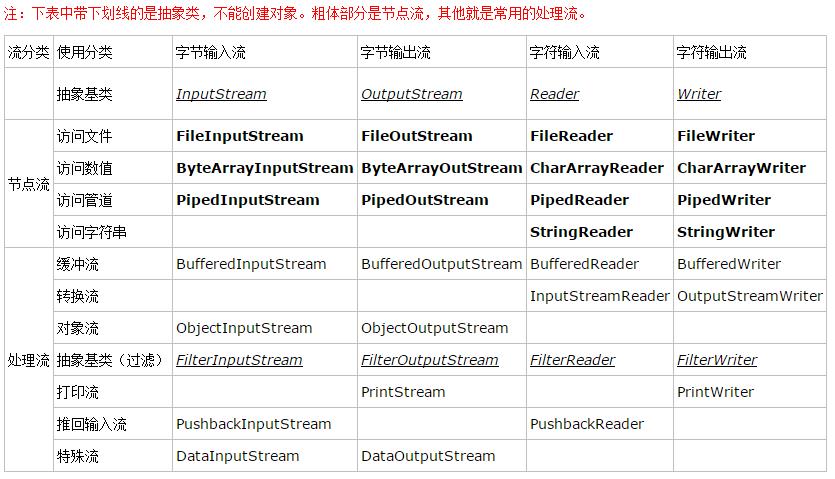
二、字节流
1、字节输入流
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class InputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("text.txt");
try {
// 1、创建一个名为text的文件
file.createNewFile();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("text.txt");
//从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节,返回0-255间的int值,读到末尾返回-1
// fis.read();
// 将输入流中的数据读取到字节数组中
byte[] input = new byte[1];
fis.read(input);
String str = new String(input);
System.out.println(str);
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
String 和 byte []间的转换
- byte [] strbyte = str.getBytes();
- String st = new String(byte);
2、字节输出流

1 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 4 public class OutputStreamTest { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 try { 8 // 打开输入流 9 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("textw.txt"); 10 11 // 要写入的数据 12 String str = "写入数据:1234"; 13 byte[] out = str.getBytes(); 14 15 // 把数据写入到指定文件中 16 fos.write(out); 17 18 // 关闭流 19 fos.close(); 20 21 } catch (IOException e) { 22 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } 25 } 26 27 }
3、通过字节流实现文件拷贝

1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 6 public class CopyStream { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 try { 10 // 创建输入输出流,从text.txt文件中读取数据,把读取到的数据存到textnew.txt中 11 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("text.txt"); 12 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("textnew.txt"); 13 14 // 存储数据的数组 15 byte[] shuju = new byte[50]; 16 17 while (fis.read(shuju) != -1) { 18 fis.read(shuju); 19 } 20 21 // 将字节数组中的数据写入到textnew.txt 22 fos.write(shuju); 23 24 fis.close(); 25 fos.close(); 26 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 27 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } catch (IOException e) { 30 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } 33 34 } 35 36 }
4、带缓冲的字节流实现拷贝

1 import java.io.BufferedInputStream; 2 import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 8 public class BufferdeCopyStream { 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 try { 12 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("text.txt"); 13 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("textnew2.txt"); 14 15 // 不指定缓冲区大小 16 // BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); 17 // BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); 18 // 带缓冲区大小 19 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis, 10000); 20 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos, 10000); 21 22 byte[] input = new byte[30]; 23 long before = System.currentTimeMillis(); 24 int count = 0; 25 26 while (bis.read(input) != -1) { 27 bos.write(input); 28 count++; 29 } 30 bis.close(); 31 fis.close(); 32 bos.close(); 33 bos.close(); 34 System.out.println("读取了" + count + "次"); 35 System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - before + "ms"); 36 37 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } catch (IOException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 } 43 44 }
增加读写速度的方法为 :适当增加字节数组的大小 或者增加缓冲区大小
三、字符流
1.字符流实现文件拷贝

1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 6 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 7 import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; 8 9 public class ReadAndWrite { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 try { 13 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("text.txt"); 14 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("text3.txt"); 15 16 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis); 17 OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos); 18 19 char[] input = new char[40]; 20 int len = 0; 21 while ((len = isr.read(input)) != -1) { 22 osw.write(input, 0, len); 23 } 24 25 isr.close(); 26 fis.close(); 27 osw.close(); 28 fos.close(); 29 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } catch (IOException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 37 } 38 39 }
2.带缓冲的字符流实现文件拷贝

1 import java.io.BufferedReader; 2 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 8 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 9 import java.io.PrintWriter; 10 11 public class BufferedReadAndWrite { 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 try { 15 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("text.txt"); 16 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("text4.txt"); 17 18 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis); 19 OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos); 20 21 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); 22 // BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);//没换行、必须显示指定bw.flush(); 23 PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(osw, true);// 有换行、设置true就不需要pw.flush() 24 25 String str; 26 27 while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) { 28 // bw.write(str); 29 pw.println(str); 30 } 31 32 // bw.flush(); 33 br.close(); 34 // bw.close(); 35 pw.close(); 36 isr.close(); 37 fis.close(); 38 osw.close(); 39 fos.close(); 40 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 } catch (IOException e) { 43 e.printStackTrace(); 44 } 45 46 } 47 48 }
四、RandomAccessFile随机文件读写
http://blog.csdn.net/akon_vm/article/details/7429245
以上是关于Java——IO流的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
