常用类
? 1.1 String和StringBuffer
String类封装了对字符串的常见操作,使用频率非常高,所以应该熟练掌握,
String类的方法比较多,无需死记硬背,而是大概了解,用的时候不清楚再查手册,
有些东西用多了,就熟练了
String类常用方法:
length; indexOf; charAt; equals; replace; split; substring; trim; formate
String类的赋值:
int a = 5;
a = 3;
上面代码含义:在内存里申请一个内存单元,命名为a,赋值为3(将3存储在该内存单元上),再次赋值a为5(再把5存储在该内存单元上),这个内存单元的值在被赋值后修改了
String str1 = "abc";
str1 = "123";
应该这样理解:
String str1 = new String("abc");
str1 = new String("123");
所以对于引用来讲,赋值并非改变原引用对象的值,只是调整了引用关系
那么对于 == 运算符就要特别注意了
String str1 = new String("abc");
String str2 = new String("abc");
System.out.println(str1 == str2); //地址
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); //内容
运行结果
false
true
Str1和str2引用的是不同对象,所以str1 == str2为假
Str1和str2引用的字符串内容相同,所以tr1.equals(str2)为真
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc";
change(str1);
}
/**
* 将字符串中的b替换为B
* @param str1 字符串
*/
private static void change(String str1) {
str1.replace("b","B");
System.out.println(str1);
}
运行结果
abc
字符串并没有被修改,注意String类定义的字符串是不可更改的,此时需要用到StringBuffer类
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "abc";
change1(str1);
System.out.println(str1);
StringBuffer str2 = new StringBuffer("abc");
change2(str2);
System.out.println(str2);
}
/**
* 将字符串中追加一个字符
* @param str1 字符串
*/
private static void change1(String str1) {
str1 += "123";
}
/**
* 将字符串中追加一个字符
* @param str2 字符串
* @return
*/
private static void change2(StringBuffer str2) {
str2.append("123");
}
运行结果
abc
abc123
StringBuffer类常用方法:
append、insert、deleteCharAt、delete、replace、setCharAt、reverse
? 1.2 Array数组类
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] a = {1,7,3,99,16,4};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
int[] array1 = {2, 1, 3};
int[] array2 = {2, 1, 3};
int n1 = array1.length;//数组长度
int n2 = array2.length;
System.out.println(compareArray(n1,n2,array1,array2));
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(array1,array2));//判断数组是否一样
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array1));//打印数组字符串形式
Arrays.sort(array1);//将数组进行升序排序
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array1));
int [] array3 = Arrays.copyOf(array1,array1.length+1);//复制一个数组
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array3));
Arrays.fill(array3,2);//填充
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array3));
Arrays.binarySearch(array3,2);//折半查找,只能用于有序数组
}
/**
*
* @param n1 array1长度
* @param n2 array2长度
* @param array1 数组array1
* @param array2 数组array2
* @return array1array2是否完全相同相等
*/
private static boolean compareArray(int n1, int n2, int[] array1, int[] array2) {
boolean flag =true;
if (n1==n2) {
for (int i = 0;i<n1;i++) {
if(array1[i]!=array2[i]){
flag=false;
break;
}
}
}else {
flag=false;
}
return flag;
}
? 1.3 Math函数
主要提供数学相关的常量和方法,方法都是静态的
常量E,PI(π)
方法:abs;ceil;floor;round;max;min;exp;log;pow;sqrt;random;三角函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 3;
int b = 4;
int c = 7;
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(a*a + b*b)); //开根
System.out.println(Math.random()); //0--1间的随机值
System.out.println(c/b); //向下取整
System.out.println(Math.max(Math.max(a,b),c));//最大值
System.out.println(Math.min(Math.min(a,b),c));//最小值
}
? 1.4 日期类
v Date
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d1 = new Date(); //当前时间(new的那一刻)
System.out.println(d1);
long n = d1.getTime(); //获取自1970-1-1至当前经历的毫秒数(1秒=1000毫秒
System.out.println(n);
n += 1000000;
Date d2 = new Date(n);
System.out.println(d2);
System.out.println(new Date(0));//1970-1-1东8区8时
}
Date d = new Date();
DateFormat df1 = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.LONG);
System.out.println(df1.format(d));
DateFormat df2 = DateFormat.getDateInstance(DateFormat.SHORT);
System.out.println(df2.format(d));
DateFormat df3 = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance();
System.out.println(df3.format(d));
运行结果
LONG2017年12月15日
SHORT2017/12/15
GetDateTime2017年12月15日 下午2:47:11
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
System.out.println(sdf1.format(d));
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yy年MM月");
System.out.println(sdf2.format(d));
SimpleDateFormat sdf3 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm");
System.out.println(sdf3.format(d));
运行结果
"yyyy-MM-dd" 2017-12-15
"yy年MM月" 17年12月
"yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm" 2017-12-15 02:56
v Calendar
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(c); //所有时间及相关信息
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR)); //年
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.MONTH) +1); //月(外国0开始)
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK) - 1); //星期几(外国7开始)
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.DATE)); //日
System.out.println("P.M."+c.get(Calendar.HOUR)); //时AMPM
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY)); //时24
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.MINUTE)); //分
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.SECOND)); //秒
}
c.set(2017,Calendar.NOVEMBER,1); //设置年月日2017-11-1
//c.set(Calendar.YEAR,2017);c.set(Calendar.MONTH,11);c.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,1);
c.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,-1); //日期-1
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)); //得到2017-10月天数
? 1.5 包装类
JAVA中提供的基本类型(int short byte long float double)等,都有对应的包装类
例如:
int →Integer
float →Float
...
为什么需要包装类
基本类型的处理和其它类型的处理是有不同的
例如:
int a = 3;
int b = 5;
a = b;
...
这种修改是直接改变了变量的值,准确的讲是存放的3个内存单元被修改了
案例:之前的泛型的通用数组
此处只能用Integer,不能用int
很多地方为了统一,尤其是用到泛型的地方,系统提供了基本类型对应的封装类
装箱:基本类型→包装类
拆箱:
集合框架
? 2.1 Vector
Vector(向量 )就是动态数组
为什么需要动态数组?很多时候,我们无法事先预定数组元素个数,如果使用静态化数组,小了不够用,大了浪费空间,这时候需要动态数组
v 添加
package 教学.C103_11_Vector;
import java.util.Vector;
public class case1_添加 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector<Integer> x1 = new Vector<>();
System.out.println("Vector默认容量"+x1.capacity());
System.out.println("Vector初始元素个数"+x1.size());
x1.add(1);
x1.add(2);
x1.add(3);
x1.add(4);
x1.add(5);
x1.add(6);
x1.add(7);
x1.add(8);
x1.add(9);
x1.add(10);
x1.add(11);
System.out.println("添加11个元素后,Vector默认容量"+x1.capacity());
System.out.println("添加11个元素后,Vector初始元素个数"+x1.size());
System.out.println(x1);
}
}
Vector默认容量10
Vector初始元素个数0
添加11个元素后,Vector默认容量20
添加11个元素后,Vector初始元素个数11
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]
size:元素个数
capacity:容量
add:在尾部添加元素
v 删除
package 教学.C103_11_Vector;
import java.util.Vector;
public class case2_删除 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a1 = new Integer(11);
Integer a2 = new Integer(22);
Integer a3 = new Integer(33);
Integer a4 = new Integer(44);
Integer a5 = new Integer(55);
Vector<Integer> v1 = new Vector<>(4,2);
v1.add(a1);
v1.add(a2);
v1.add(a3);
v1.add(a4);
v1.add(a5);
System.out.println("容量:"+v1.capacity());
System.out.println("个数:"+v1.size());
System.out.println("(数组)向量:"+v1);
v1.remove(2);//删除下标为2的元素
v1.remove(a1);//删除a1元素
System.out.println("容量:"+v1.capacity());
System.out.println("个数:"+v1.size());
System.out.println("(数组)向量:"+v1);
v1.trimToSize();//修剪;按照现有的元素个数调整容量,元素个数=容量大小
System.out.println("容量:"+v1.capacity());
}
}
方法
remove(int index)删除指定位置的元素
remove(Object obj)删除指定元素
trimToSize()调整容量大小
v 修改
package 教学.C103_11_Vector;
import java.util.Vector;
public class case3_修改 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a1 = new Integer(11);
Integer a2 = new Integer(22);
Integer a3 = new Integer(33);
Integer a4 = new Integer(44);
Integer a5 = new Integer(55);
Vector<Integer> v1 = new Vector<>(4,2);
v1.add(a1);
v1.add(a2);
v1.add(a3);
v1.add(a4);
v1.add(a5);
System.out.println(v1.get(3));//找出下标为3的元素
v1.set(3,99);//把下标为3的元素替换为其它值
System.out.println(v1);
System.out.println(v1.contains(a2));//数组是否包含a2元素,返回boolean
System.out.println(v1.contains(22));//数组是否包含值为22的元素,返回boolean
System.out.println(v1.indexOf(0));//返回数组内值为33的下标,没有的话返回-1
System.out.println(v1.firstElement());//获得数组第一个元素值
}
}
输出结果
44
[11, 22, 33, 99, 55]
true
true
-1
11
方法
contains()
indexOf()
firstElement()
get(int index)
set(int index,Object obj)
? 2.2 Stack堆栈
接口public class Stack<E>
继承自extends Vector<E>
堆栈
在计算机领域,堆栈是一个不容忽视的概念,堆栈是两种数据结构
堆栈都是一种数据项按序排列的数据结构,只能在一端(称为栈顶(top))对数据项进行插入和删除
在单片机应用中,堆栈是个特殊的存储区,主要功能是暂时存放数据和地址,通常用来保护断点和现场
要点:堆,队列优先,先进先出(FIFO—first in first out);栈,先进后出(FILO—First-In/Last-Out)
中文名 堆栈
外文名 stack
领域 计算机
定义 数据结构
功能 对数据项进行插入和删除
package 教学.C103_12_Stack堆栈;
import java.util.Stack;
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(11);
stack.push(22);
stack.push(33);
System.out.println(stack);
System.out.println(stack.peek());//得到栈顶元素
System.out.println(stack);
System.out.println(stack.pop());//移除栈顶元素
System.out.println(stack);
}
}
方法
push() 表示元素压入栈顶
pop() 移除栈顶元素
peek() 读取栈顶元素
? 2.3Interface List
List是一个接口‘public interface List<E>’,继承自Collection ‘extends Collection<E>’
它提供了一个集合数据的增删改查等基本操作,上面讲的Vector和Stack都实现了这个接口,这里再介绍它的一个实现类--ArrayList
ArrayList类的用法与Vector非常相似
package 教学.C103_13_List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(11.1);
list.add(22.1);
list.add(33.1);
list.add(44.1);
System.out.println(list);
list.set(2,99.1);//改变下标为2的元素的值
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(1);//删除下标为1的元素
System.out.println(list);
}
}
输出结果
[11.1, 22.1, 33.1, 44.1]
[11.1, 22.1, 99.1, 44.1]
[11.1, 99.1, 44.1]
方法
list.add
list.set
list.remove
? 2.4 ForEach
package 教学.C103_14_ForEach;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(11.1);
list.add(22.1);
list.add(33.1);
list.add(44.1);
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.printf("%6.2f",list.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
for(Double d:list){
System.out.printf("%6.2f",d);
}
}
}
输出结果
11.10 22.10 33.10 44.10
11.10 22.10 33.10 44.10
从代码中可以看出forEach循环比基本的for循环更简洁,但它只适用于集合相关类
for(Double d:list)的含义:d依次引用到List中每一个元素
? 2.5 Set
Set接口表示无重复元素的集合
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(11);
set.add(12);
set.add(13);
set.add(12);
System.out.println(set);
}
}
输出结果
[11, 12, 13]
从结果可以看出,最后一次添加12没有成功执行,因为12之前已经有了
所谓的重复,指的是e1.equals(e2);true;
先判断HashCode,再判断是否equals
? 2.6 Map映射函数
Map是以键值对(Key,Vaule)的形式存取数据
package 教学.C103_16_Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("num1",11);//存储‘对象’和‘对象关键字’
map.put("num2",22);
map.put("num3",33);
map.put("num4",44);
Integer x = map.get("num3");//通过‘关键字’得到‘对象’
System.out.println(x);
}
}
输出结果
33
方法
map.put()
map.get()
? 2.7 Iterator迭代器
Iterator迭代器:类似于C语言中链表的指针
p = p → next
package 教学.C103_17_Iterator迭代器;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class case2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(11.1);
list.add(22.1);
list.add(33.1);
list.add(44.1);
Iterator<Double> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Double d = iterator.next();
System.out.println(d);
}
}
}
输出结果
11.1
22.1
33.1
44.1
? 2.8 Collections工具类
package 教学.C103_18_Collections工具类;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(22.1);
list.add(11.1);
list.add(44.1);
list.add(33.1);
System.out.println(list);
Collections.reverse(list);//降序;倒序;逆序
System.out.println(list);
Collections.sort(list);//排序
System.out.println(list);
Collections.shuffle(list);//乱序
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(Collections.max(list));//最大值
}
}
输出结果
[22.1, 11.1, 44.1, 33.1]
[33.1, 44.1, 11.1, 22.1]
[11.1, 22.1, 33.1, 44.1]
[11.1, 33.1, 44.1, 22.1]
44.1
IO
? 3.1 流的概念
应用程序和设备(主要是CPU)之间经常需要传输数据,java为了屏蔽硬件细节,简化开发流程,将这种传输封装成流的概念
流有两种:字符流/字节流
字节流 把传输的数据看成是没有特定含义的二进制数据
字符流 把数据看成字符
? 3.2 字节流
InputStream
InputStream提供了字节流的封装,它是一个抽象类
public abstract class InputStream
extends Object
implements Closeable
Direct Known Subclasses: 子类
AudioInputStream, ByteArrayInputStream, FileInputStream, FilterInputStream, InputStream, ObjectInputStream, PipedInputStream, SequenceInputStream, StringBufferInputStream
通过子类的命名前缀可以看出该类是干嘛的
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor and Description
InputStream()
v FileInputStream读取
public class FileInputStream
extends InputStream
package 教学.C103_21_字节流;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
public class Test1_Input {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\\\Users\\\\my\\\\IdeaProjects\\\\C103_JAVA核心编程\\\\src\\\\教学\\\\C103_21_字节流\\\\Student");
int ch;
while (true){
ch = fis.read();
if(-1 == ch){
break;
}
System.out.println((char)ch);
}
fis.close();
}
}
v FileOutputStream输出
数据持久化,把数据存到硬盘/数据库中
FileOutputStream,意为文件输出流,是用于将数据写入File或 FileDescriptor的输出流。
中文名 文件输出流
外文名 FileOutputStream
定义 java.lang.Object
常用方法 返回与此流有关的文件描述符
实现的接口 Closeable, Flushable
package 教学.C103_21_字节流;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class Test2_Output {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileOutputStream fis = new FileOutputStream("C:\\\\Users\\\\my\\\\IdeaProjects\\\\C103_JAVA核心编程\\\\src\\\\教学\\\\C103_21_字节流\\\\Student");
for(int n=1;n<=10;n++){
fis.write(n);
}
fis.close();
}
}
文件路径字符串要特别注意
"E:\\xt.txt"是错误的路径,因为Java会将其中的“\\t”理解成转义字符,所以正确的表示方式是“E:/xt.txt”或“E:\\ \\xt.txt”
此时输出的文件如果用记事本等工具打开,很可能是显示乱七八糟的东西,因为记事本打开文件是要将其中的数据理解成字符,显然有些数据是没有对应的可显示字符
可以借助十六进制编辑器等工具(比如winHex)来打开文件,以十六进制形式来显示文件内容
package 教学.C103_21_字节流;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//调用main函数抛出所有异常
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream ("C:\\\\Users\\\\my\\\\Documents\\\\Music\\\\大谷和夫 - M-23.mp3");//位置读取文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream ("C:\\\\Users\\\\my\\\\Music\\\\大谷和夫 - M-23.mp3");//位置输出文件
int music;
while (true){//边读边写(循环)
music = fis.read();//读取
if(-1 == music){ break; }//读完结束
fos.write(music);//输出
}
fis.close();//关闭读取文件
}
}
? 3.3 字符流
提供了两个顶级父类
Class Reader
java.lang.Object
java.io.Reader
读取字符流的抽象类;这一类必须实现的唯一方法是读(char [],int,int)和();然而,大多数子类将覆盖这里定义的一些方法,以便提供更高的效率、附加功能或两者
子类
BufferedReader, LineNumberReader, CharArrayReader, InputStreamReader, FileReader, FilterReader, PushbackReader, PipedReader, StringReader
Class Writer
java.lang.Object
java.io.Writer
用于字符流写入的抽象类;这一类必须实现的唯一方法是写(char [],int,int),flush(),和();然而,大多数子类将覆盖这里定义的一些方法,以便提供更高的效率、附加功能或两者
子类
Writer, BufferedWriter, CharArrayWriter, FilterWriter, OutputStreamWriter, FileWriter, PipedWriter, PrintWriter, StringWriter
常见IO类继承关系图
箭头表示:子类—-〉父类
字节流:(读取单位为byte)
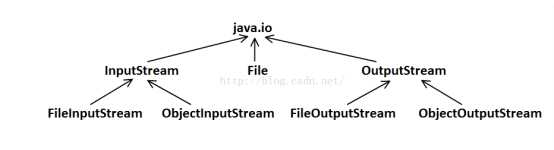
字符流:(读取单位为char)
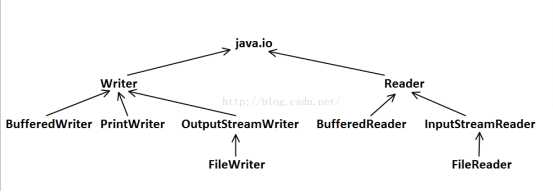
字符流和字节流的区别:
字节流就是按照byte单位来读取,可以用来读取其他格式的文件
字符流是在字节流的基础上实现的,用来读取文本文件,一个字符一个字符的读取
如果字节流是一滴水一滴水的转移,那么字符流是用勺子一勺一勺水的转移,速度明显加快
当然使用缓冲Buffer以后,就是一桶一桶水的转移了
一个字节占8位,java采用unicode编码,占两个字节,即16位,也就是java一个字符是2byte,16位,
那么在文本copy的时候,用字节流就是一byte-byte的copy,字符流就是一个字符一个字符的copy
v FileWriter
package 教学.C103_22_字符流.FileWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("C:\\\\Users\\\\my\\\\IdeaProjects\\\\C103_JAVA核心编程\\\\src\\\\教学\\\\C103_22_字符流\\\\FileWrite\\\\Demo");
fileWriter.write("...");
//fileWriter.flush();//刷新缓冲区
fileWriter.close();//关闭位置文件,执行前会调用flush
}
}
write():往 流 里写内容
flush():刷新缓冲区
close():关闭此流,但要先刷新它(缓冲区),执行前会调用flush
每次往里面写东西时,会覆盖原有的内容
fileWriter.close();//关闭位置文件,执行前会调用flush
fileWriter.write("...");
Exception in thread "main" java.io.IOException: Stream closed
执行close后不能再写入,否则会报错IOException
Windows操作系统下
fileWriter.write("a\\r\\n"+"b\\r\\n"+"c\\r\\n"); //输出文件内换行
fileWriter.write("a\\t"+"b\\t"+"c\\t"); //输出文件内空格
系统通用换行方法
System.getProperty("line.separator");
v FileReader
package 教学.C103_22_字符流.FileReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("C:\\\\Users\\\\my\\\\IdeaProjects\\\\C103_JAVA核心编程\\\\src\\\\教学\\\\C103_22_字符流\\\\FileReader\\\\Demo");
//while (true){
// int num = fileReader.read();
// if (num == -1){break;}
// System.out.println((char)num);
//}
int num;
while ((num = fileReader.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)num);
}
fileReader.close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("C:\\\\Users\\\\my\\\\IdeaProjects\\\\C103_JAVA核心编程\\\\src\\\\教学\\\\C103_22_字符流\\\\FileReader\\\\Demo");
char [] EnglishLetter = new char[26];
fileReader.read(EnglishLetter,0,10);//一次读取26个英文字母前10个
fileReader.close();
System.out.println(EnglishLetter);
}
? 3.4 缓冲区
v BufferedWriter
package 教学.C103_23_缓冲区.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("C:\\\\Users\\\\my\\\\IdeaProjects\\\\C103_JAVA核心编程\\\\src\\\\教学\\\\C103_23_缓冲区\\\\BufferedWriter\\\\Demo");
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
bufferedWriter.write("abc");
bufferedWriter.newLine();//换行
bufferedWriter.write("123");
bufferedWriter.flush();//刷新缓冲区
bufferedWriter.close();
//fileWriter.close();
}
}
? 3.5 File类
字节流和字符流可以实现对文档内容的操作,但是对于文件属性就无能为力。
属性包括:文件名、类型、最后一次修改时间、存储路径、文件大小
- 什么是File对象?
1) 用来将文件或者文件夹封装成对象
2) 方便对文件夹或文件属性信息进行操作
3) File对象作为参数传递给 流 的构造方法(构造方法摘要FileWriter(File file))
- File对象的创建
package 教学.C103_24_File;
import java.io.File;
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
creatFile();
}
private static void creatFile() {
File file1 = new File("C:\\\\a1.txt");
File file2 = new File("C:\\\\","a2.txt");
File file3 = new File("C:\\\\");
File file4 = new File(file3,"a3.txt");
File file5 = new File("C:\\\\"+File.separator+"a4.txt");
System.out.println(file5);
File file6 = new File("C:\\\\Users\\\\my\\\\Documents\\\\Music\\\\大谷和夫 - M-23.mp3");
System.out.println(file6.getName());
}
}
输出结果
C:\\a4.txt
大谷和夫 - M-23.mp3
- File的常用方法
1) 获取相关(名称;路径;大小;最后修改)
2) 创建删除(文件;文件夹;重命名)
3) 判断类(判断是否文件夹;判断是路径还是文件;判断是否存在;判断是否隐藏)
//获取相关 名称;路径;大小;最后修改
public class case1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
getInfo();//演示获取
}
private static void getInfo() {
File file = new File("C:\\\\Users\\\\my\\\\Documents\\\\Music\\\\大谷和夫 - M-5.mp3");
System.out.println(file.getName());//名称
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());//绝对路径
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println(file.length());//文件大小
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println(file.lastModified());//最后修改 时间戳 1970-01-01-00:00至最后修改时间中间的毫秒数
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------------------");
Date date = new Date(file.lastModified());
System.out.println(date);
大谷和夫 - M-5.mp3
-----------------------------------------------------------------
C:\\Users\\my\\Documents\\Music\\大谷和夫 - M-5.mp3
-----------------------------------------------------------------
4898568
-----------------------------------------------------------------
1509526598083
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Wed Nov 01 16:56:38 CST 2017