OpenSourceC#Unity框架-QFramework
Posted PartnerLv
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了OpenSourceC#Unity框架-QFramework相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
我在纠结这个放到哪个栏目,放到【UnityGamePlay】的话,这是个框架代码,放到
【开源代码解读】的话,我估计后面会看一些代码例子来讲解这个框架的使用。
纠结完还是决定放这里吧,如果后面写具体的例子了再放到【UnityGamePlay】里。
老规矩先放源码链接:QFramework
这个框架里还有许多其他工具,比如UIKit,这里先不管这些Kit,只看QFramework.cs 这一个文件,这一个就是框架的所有代码。
这是一个Unity前端的MVC框架,MVC就不用说了,感觉是最好理解的框架了。
游戏开发实践
首先以游戏开发角度理解一下QFramework里的几个概念:
Control 对UI和游戏进度的控制。
System 是游戏具有哪些功能模块,对这些模块的功能支持。
Model 是用到了哪些数据,对数据的封装。
Utility 实现一些与逻辑无关的工具类
Commond 是对要去做某件事的封装。
Event 是达成了某个条件,让所有注册此事件的回调执行。
-------2022.11.21 update start-------
时隔几个月,对框架和游戏开发更熟悉了,再看这个框架,又有了不同的理解,来补充一下。
MVC主要是在ui管理中使用,具体的游戏逻辑比较复杂,根据情况而定。
Controller 主要是界面控制,ViewController,当做View层使用,监听一些需要改变数据的事件。
Model 层是数据层,可以发送事件,可以利用BindableProperty 在数据变化时发送ViewController监听的事件,更改UI。
System,可以当做MVC中的Controll层来用,也可以实现独立的游戏系统,当成Controller用的话,就是修改Model,发送View监听的事件,修改界面
最近看的xlua-framework中的ui框架也是mvc模式,主要是层级间的调用关系略有不同。
这个框架里,view可以读model,可以调用ctrl,ctrl可以读写model,model不能操作vc,view在Update()中每帧去读model更新UI。
对应到QF里,就是ViewController可以读写Model,可以调用System,System可以读写Model,Model层只可以发送事件。
-------2022.11.21 update end-------
Architecture
这个可以理解成整个框架的Main。
从这个接口定义就能看出这个框架的所有功能,如下。
public interface IArchitecture
void RegisterSystem<T>(T system) where T : ISystem;
void RegisterModel<T>(T model) where T : IModel;
void RegisterUtility<T>(T utility) where T : IUtility;
T GetSystem<T>() where T : class, ISystem;
T GetModel<T>() where T : class, IModel;
T GetUtility<T>() where T : class, IUtility;
void SendCommand<T>() where T : ICommand, new();
void SendCommand<T>(T command) where T : ICommand;
TResult SendQuery<TResult>(IQuery<TResult> query);
void SendEvent<T>() where T : new();
void SendEvent<T>(T e);
IUnRegister RegisterEvent<T>(Action<T> onEvent);
void UnRegisterEvent<T>(Action<T> onEvent);
Architecture 管理所有的System、Model、Utility,提供注册和获取接口。除此之外,有发送Command 、 注册发送Event 和查询功能。
具体实现可以看接下来的抽象类 public abstract class Architecture<T> : IArchitecture where T : Architecture<T>, new(),这个代码过长就不贴了。
其中mContainer 存储所有注册的对象,所有对象都有Init() 接口,在初始化时会依次调用。
发送Commond 时实际就是调用它的Execute() 方法。
事件的注册与发送依赖TypeEventSystem 类型。注意事件注册返回的是IUnRegister 接口,后面再说这个的作用。
Architecture<T> 里面要注意的就这么多吧,代码不难,但是要理解为什么这样写,就要明白这些类和接口的作用。
后面的OnGlobalEventExtension ,它的作用是扩展TypeEventSystem.Global 的事件注册功能。这种写法就是为了给原始类型扩展方法,特点:1、静态类 2、静态方法 3、第一个参数前加this。理解这个很重要,因为这个框架几乎所有接口都用这种写法扩展方法。不得不说这个写法实在是巧妙。
Controller
框架中只定义了一个接口,但这个接口提供了Controller 所具有的的功能
#region Controller
public interface IController : IBelongToArchitecture, ICanSendCommand, ICanGetSystem, ICanGetModel,
ICanRegisterEvent, ICanSendQuery
#endregion
这作者名字起的挺通俗易懂的,直接看这接口名就知道这个IController 有什么功能了,一次是:属于这个框架,可以发送Command,可以取到Ststem和Model,可以注册事件,可以查询。
注意理解上面说过的“扩展方法”的用法,然后来看为什么继承这几个接口就实现了这几个功能。
Rule
这个规则就是使用扩展方法定义了几种接口,使用哪种接口就是使用这个接口的扩展方法,一共有好几种接口,不过都是下面这三个结构的格式。
public interface IBelongToArchitecture
IArchitecture GetArchitecture();
public interface ICanGetModel : IBelongToArchitecture
public static class CanGetModelExtension
public static T GetModel<T>(this ICanGetModel self) where T : class, IModel
return self.GetArchitecture().GetModel<T>();
IBelongToArchitecture 提供了获得本架构的接口,之后定义的规则都要继承这个接口,如这个ICanGetModel ,这个接口就提供了获得Model的功能,通过下面的扩展CanGetModelExtension 实现的。
也就是说,继承了ICanGetModel 接口,就能调用GetModel<T>() 这个方法来获得Model。
理解了后再看上面的IController,也就是说Controller 能调用GetModel 获得Model,之后看具体例子的时候会理解更深。
剩下还有几个规则接口,就不全部说了,理解了上面这个就都懂了。
System 与 Model
这两个代码类似,主要是继承的接口不同,Model除了和架构相关的接口,只能获得Utility工具和发送事件。System能做的事情更多。
SetArchitecture 是设置架构,在Architecture 的注册代码中先调用这个方法。为了让Model持有架构的引用,这样才能像self.GetArchitecture().GetModel<T>();这样调用。
自定义的System和Model需要重载OnInit() 方法。
Utility
工具类,不能只用其他功能,只能是通用的工具。
Command
这个可以理解成要做什么,在发送Command的时候会调用它的Execute方法,也就是说在实现Command的时候重载它的OnExecute() 方法。
代码没什么说的,就不贴了,看看示例怎么用的就懂了。
Query
和Command类似
IOC
见:IOC
BindableProperty
这个主要实现的类似MVVM 中的ViewModel、Binder 的作用,定义这个类的变量,在修改时会执行回调函数mOnValueChanged,当然回调函数要自己实现。
应用场景,比如血量这个属性,当血量变化时要修改UI显示信息,就可以把血量定义成这个类,然后在回调函数中处理UI变化信息。
注意 Register 返回的是BindablePropertyUnRegister ,这是一个继承IUnRegister 接口的类,这个接口有一个扩展方法UnRegisterExtension,它实现的是把gameObject添加一个UnRegisterOnDestroyTrigger 组件。
看这个组件的实现,它是一个Mono 类,在OnDestroy,会调用unRegister.UnRegister(); 解除事件注册,这里调用的实际是下面这个UnRegister。
public class BindablePropertyUnRegister<T> : IUnRegister
public BindableProperty<T> BindableProperty get; set;
public Action<T> OnValueChanged get; set;
public void UnRegister()
BindableProperty.UnRegister(OnValueChanged);
BindableProperty = null;
OnValueChanged = null;
而这个又调用的BindableProperty.UnRegister(OnValueChanged);,就是把BindableProperty的值变化回调给删除了。
public void UnRegister(Action<T> onValueChanged)
mOnValueChanged -= onValueChanged;
理解了这个调用链,那这个有什么用呢?看下面这个例子,这没有用BindableProperty,用的是接下来要说的Event,不过用法是一样的注册了一个事件后,又调用了.UnRegisterWhenGameObjectDestroyed(gameObject),看名字就知道,在销毁的时候把注册的事件清除。
this.RegisterEvent<GamePassEvent>(e => transform.Find("Enemies").gameObject.SetActive(false); )
.UnRegisterWhenGameObjectDestroyed(gameObject);
不过这里也有个疑惑,Event用这个机制没问题,因为它的事件是全局的,不取消注册就会越来越多,但BindableProperty 不是一个单独的变量吗,如果对象都销毁了,就算不取消注册也应该没事吧。不懂,疑惑先保留,如果以后解决了再来补充。
Event
最后一个模块了。看到这里会发现好像每个模块都能看懂,但又都不知道这有什么用,不用担心,先看完,然后看个例子,再来看框架就懂了。
前面都是和UnRegister 相关的代码,上节说的那个调用流程已经值得这是怎么用的了,其他看看就懂了。
主要是看TypeEventSystem 和EasyEvent。
Event只提供了3个用法吧,一是Global全局事件注册,二是发送事件,三是注册与取消事件。TypeEventSystem 是对这三种用法的包装,实际是靠EasyEvent实现的。(ps:不知道从哪个版本开始改成这样的,之前只有TypeEventSystem)
但上述只提供了Action<T> 一种写法,TypeEventSystem 意思就是类型事件系统,T就是这个事件的类型。
EasyEvent 还重载了多参数的Action,和一个不依赖任何接口的EasyEvents,自己看吧,没什么说的。
Over,框架就这么多了,之后看情况找个使用这个框架的项目讲讲吧。
Unity 框架QFramework v1.0 使用指南 架构篇:05. 引入 Utility | Unity 游戏框架 | Unity 游戏开发 | Unity 独立游戏
05. 引入 Utility
在这一篇,我们来支持 CounterApp 的存储功能。
其代码也非常简单,只需要修改一部分 Model 的代码即可,如下:
// 定义一个 Model 对象
public class CounterAppModel : AbstractModel
private int mCount;
public int Count
get => mCount;
set
if (mCount != value)
mCount = value;
PlayerPrefs.SetInt(nameof(Count),mCount);
protected override void OnInit()
Count = PlayerPrefs.GetInt(nameof(Count), mCount);
这样就支持了非常基本的数据存储功能。
当然还是有一些问题,如果时候未来我们需要存储的数据非常多的时候,Model 层就会充斥大量存储、加载相关的代码。
还有就是,我们以后如果不想使用 PlayperPrefs 了,想使用 EasySave 或者 SQLite 的时候,就会造成大量的修改工作量。
于是 QFramework 提供了一个 Utility 层,专门用来解决上述两个问题的,使用方法非常简单,如下:
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;
namespace QFramework.Example
// 1. 定义一个 Model 对象
public class CounterAppModel : AbstractModel
private int mCount;
public int Count
get => mCount;
set
if (mCount != value)
mCount = value;
PlayerPrefs.SetInt(nameof(Count),mCount);
protected override void OnInit()
var storage = this.GetUtility<Storage>();
Count = storage.LoadInt(nameof(Count));
// 可以通过 CounterApp.Interface 监听数据变更事件
CounterApp.Interface.RegisterEvent<CountChangeEvent>(e =>
this.GetUtility<Storage>().SaveInt(nameof(Count), Count);
);
// 定义 utility 层
public class Storage : IUtility
public void SaveInt(string key, int value)
PlayerPrefs.SetInt(key,value);
public int LoadInt(string key, int defaultValue = 0)
return PlayerPrefs.GetInt(key, defaultValue);
// 2.定义一个架构(提供 MVC、分层、模块管理等)
public class CounterApp : Architecture<CounterApp>
protected override void Init()
// 注册 Model
this.RegisterModel(new CounterAppModel());
// 注册存储工具的对象
this.RegisterUtility(new Storage());
// 定义数据变更事件
public struct CountChangeEvent // ++
// 引入 Command
public class IncreaseCountCommand : AbstractCommand
protected override void OnExecute()
this.GetModel<CounterAppModel>().Count++;
this.SendEvent<CountChangeEvent>(); // ++
public class DecreaseCountCommand : AbstractCommand
protected override void OnExecute()
this.GetModel<CounterAppModel>().Count--;
this.SendEvent<CountChangeEvent>(); // ++
// Controller
public class CounterAppController : MonoBehaviour , IController /* 3.实现 IController 接口 */
// View
private Button mBtnAdd;
private Button mBtnSub;
private Text mCountText;
// 4. Model
private CounterAppModel mModel;
void Start()
// 5. 获取模型
mModel = this.GetModel<CounterAppModel>();
// View 组件获取
mBtnAdd = transform.Find("BtnAdd").GetComponent<Button>();
mBtnSub = transform.Find("BtnSub").GetComponent<Button>();
mCountText = transform.Find("CountText").GetComponent<Text>();
// 监听输入
mBtnAdd.onClick.AddListener(() =>
// 交互逻辑
this.SendCommand<IncreaseCountCommand>();
);
mBtnSub.onClick.AddListener(() =>
// 交互逻辑
this.SendCommand(new DecreaseCountCommand(/* 这里可以传参(如果有) */));
);
UpdateView();
// 表现逻辑
this.RegisterEvent<CountChangeEvent>(e =>
UpdateView();
).UnRegisterWhenGameObjectDestroyed(gameObject);
void UpdateView()
mCountText.text = mModel.Count.ToString();
// 3.
public IArchitecture GetArchitecture()
return CounterApp.Interface;
private void OnDestroy()
// 8. 将 Model 设置为空
mModel = null;
代码非常简单,我们运行下 Unity 看下结果:
运行正确。
这样当我们,想要将 PlayerPrefs 方案替换成 EasySave 的时候,只需要对 Storage 里的代码进行修改即可。
最后给出流程图,如下:
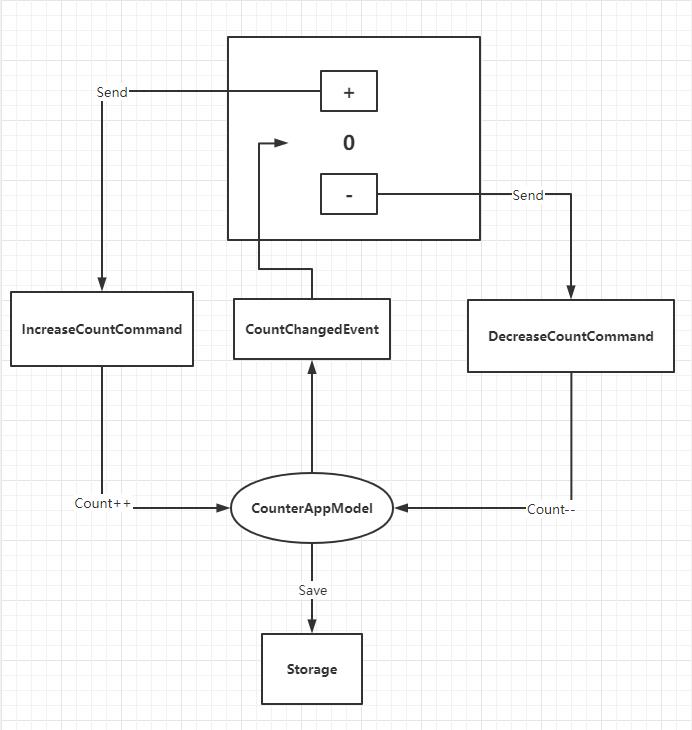
好了,这篇就介绍到这里。
更多内容
- 转载请注明地址:liangxiegame.com
- QFramework 主页:qframework.cn
- QFramework Github 地址: https://github.com/liangxiegame/qframework
- QFramework Gitee 地址:https://gitee.com/liangxiegame/QFramework
以上是关于OpenSourceC#Unity框架-QFramework的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章