Struts2
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Struts2 相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1 Struts2的拦截器
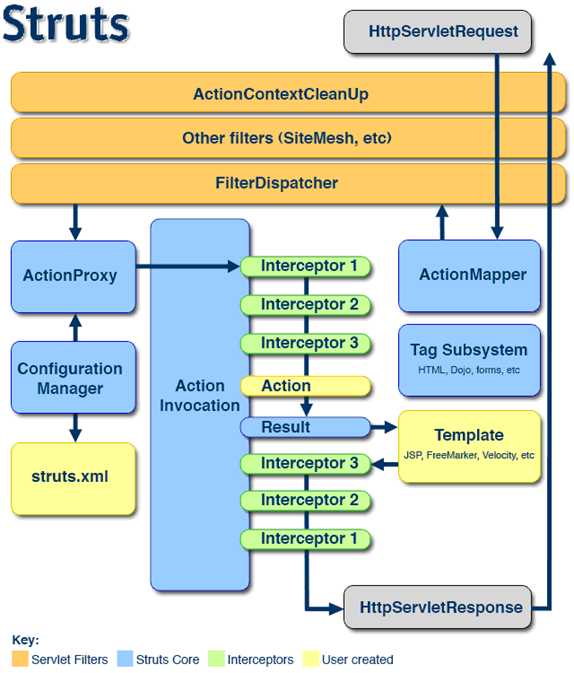
- Struts2拦截器在访问某个Action方法之前或之后实施拦截,拦截器是可插拔的,拦截器是AOP的一种实现。
- Struts2拦截器栈:将拦截器按一定顺序联结成一条链,在访问被拦截的方式的时候,Struts2拦截器链中的拦截器就会按之前定义的顺序被依次调用。。
1.1 Interceptor接口
- 每个拦截器都是实现了com.opensyymphony.xwork2.interceptor接口的java类。
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionInvocation; import java.io.Serializable; public interface Interceptor extends Serializable { void destroy(); void init(); String intercept(ActionInvocation var1) throws Exception; }
- init()方法
- 该方法将在拦截器被创建后立即被调用,它在拦截器的生命周期内只被调用一次,可以在该方法中对相关资源进行必要的初始化。
- intercept()方法
- 每拦截一个动作请求,该方法就会被调用一次。
- destory()方法
- 该方法将在拦截器被销毁之前被带哦用,它在拦截器的生命周期中也只被调用一次。
- Struts2会依次调用程序员为某个Action而注册的每个拦截器的intercept()方法。
- 每次调用intercept()方法的时候,Struts2会传递一个ActionInvocation接口的实例。
- ActionInvocation:代表一个给定动作的执行状态,拦截器可以从该类的对象里获取与该动作相关联的Action对象和Result对象,在完成拦截器自己的任务之后,拦截器将调用ActionInvocation对象的invoke()放阿飞前进到Action处理流程的下一个环节。
- AbstractInterceptor类实现了Interceptor解耦,并未init、destory提供了一个空白的实现。
1.2 自定义拦截器
- ①编写一个实现Interceptor接口,或继承AbstractInterceptor类。
- ②在struts.xml中注册自定义拦截器。
- 示例:
- web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1"> <filter> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> </web-app>
-
- index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>首页</title> </head> <body> <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/update">更新</a> <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/save">保存</a> </body> </html>
-
- User.java
package com.xuweiwei.domain; import java.io.Serializable; public class User implements Serializable { private String username; private String password; public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
-
- CustomerAction.java
package com.xuweiwei.action; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; import com.xuweiwei.domain.User; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; public class CustomerAction extends ActionSupport { //保存方法 public String save(){ System.out.println("保存"); return Action.SUCCESS; } //更新方法 public String update(){ System.out.println("更新"); return Action.SUCCESS; } //登录方法 public String login(){ HttpSession sessoin = ServletActionContext.getRequest().getSession(); sessoin.setAttribute("user",new User()); return Action.SUCCESS; } }
-
- LoginInterceptor.java
package com.xuweiwei.interceptor; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionInvocation; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.interceptor.MethodFilterInterceptor; import com.xuweiwei.domain.User; import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; public class LoginInterceptor extends MethodFilterInterceptor { @Override protected String doIntercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { HttpSession session = ServletActionContext.getRequest().getSession(); User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user"); if(user != null){ return invocation.invoke(); }else{ return Action.LOGIN; } } }
-
- struts.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"> <struts> <package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <interceptors> <interceptor name="LoginInterceptor" class="com.xuweiwei.interceptor.LoginInterceptor"> <param name="excludeMethods">login</param> </interceptor> <interceptor-stack name="myDefaultStack"> <interceptor-ref name="LoginInterceptor"/> <interceptor-ref name="defaultStack"/> </interceptor-stack> </interceptors> <default-interceptor-ref name="myDefaultStack"/> <global-results> <result name="login" type="redirect">/login.jsp</result> </global-results> <action name="save" class="com.xuweiwei.action.CustomerAction" method="save"> <result name="success">/success.jsp</result> </action> <action name="update" class="com.xuweiwei.action.CustomerAction" method="update"> <result name="success">/success.jsp</result> </action> <action name="login" class="com.xuweiwei.action.CustomerAction" method="login"> <result name="success">/index.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
-
- success.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>成功</title> </head> <body> 成功 </body> </html>
-
- login.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>登录</title> </head> <body> <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login">登录</a> </body> </html>
- 执行过程:
- ①当用户访问index.jsp中的超链接,不管是保存还是更新,都需要经过LoginInterceptor拦截器。
- ②LoginInterceptor拦截器会从session中访问是否有登录的标记,如果没有,那么就跳转到login视图。
- ③我们查看struts.xml文件可以知道login视图是一个全局视图,然后重定向或转发到login,jsp(我这里使用的是重定向)。
- ④当用户点击登录按钮的时候,这次我们查看struts.xml可以LoginInterceptor拦截器将login方法放行了,这个时候,执行login()方法,一旦login()方法执行了,就向session中放入登录的标记,然后转到index.jsp。
- ⑤当用户再次点击保存或更新的时候,会再次经过LoginInterceptor,这个时候,LoginInterceptor会判断session中有登录标记,那么就放行,然后去执行save或update方法,执行完毕之后,跳转到success.jsp。
2 表单重复提交
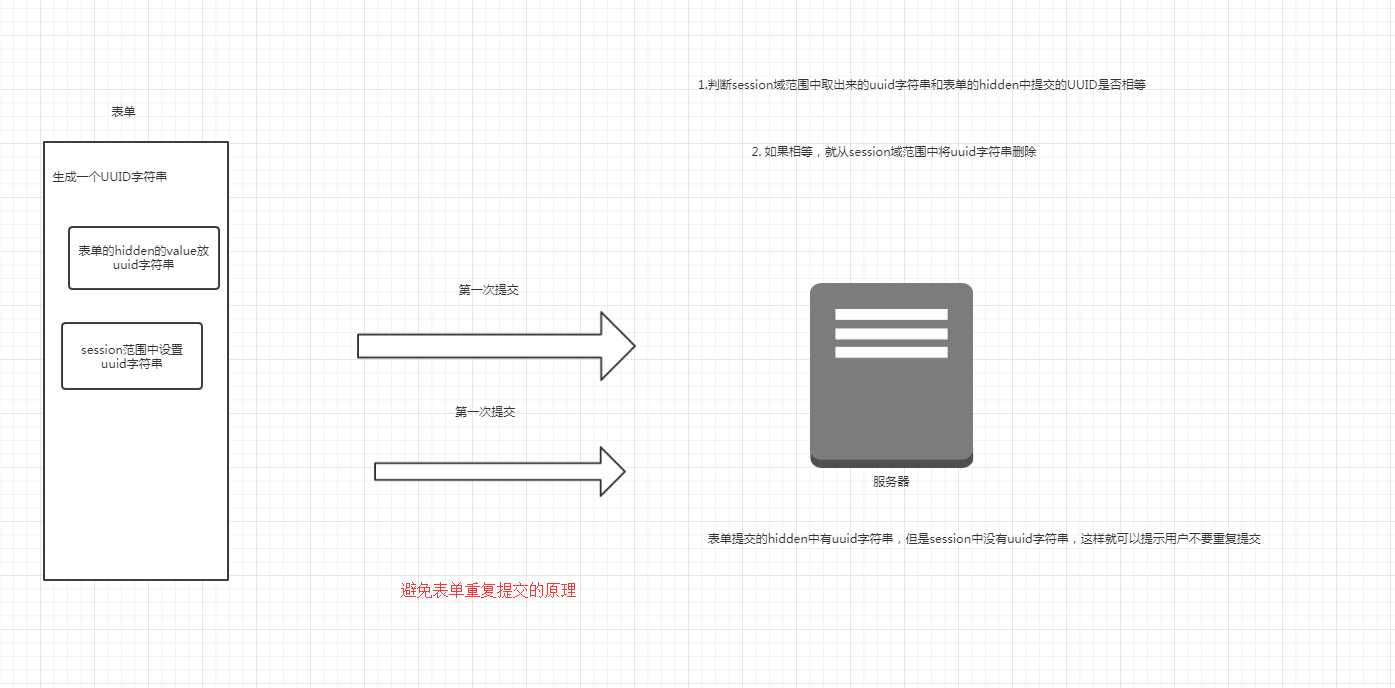
- 还有一种解决方案就是:当用户提交成功之后,就进行页面的重定向,这样路径就不一样了,即使用户不停的刷新f5,也是不一样的。
3 OGNL
3.1 OGNL的概述
- OGNL:对象图导航语言的缩写,是一个开源项目。
3.2 OGNL相对其它表达式语言具有下面的优势
- 前提:在Struts2中用OGNL,需要用到标签。
- 支持对象方法的调用。
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %> <html> <head> <title>首页</title> </head> <body> <s:property value="‘abcdefg‘.endsWith(‘a‘)"></s:property> </body> </html>
- 支持类的静态属性的调用
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %> <html> <head> <title>首页</title> </head> <body> <s:property value="@[email protected]_VALUE"></s:property> </body> </html>
- 支持类的静态方法的调用(在Struts2中默认是关闭的,所以需要开启)
- Struts.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"> <struts> <constant name="struts.ognl.allowStaticMethodAccess" value="true"></constant> </struts>
-
- index.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %> <html> <head> <title>首页</title> </head> <body> <s:property value="@[email protected]()"></s:property> </body> </html>
- 支持赋值操作和表达式的串联
- 访问OGNL上下文和ActionContext
- 操作集合对象
4 ValueStack
4.1 ValueStack的生命周期
- 每次Action的访问都会创建一个ValueStack,动作类的实例生命周期也是每次访问的时候创建的。
4.2 ValueStack和ActionContext的关系(源码解析)
- ActionContext.java
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package com.opensymphony.xwork2; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.inject.Container; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.Map; public class ActionContext implements Serializable { static ThreadLocal<ActionContext> actionContext = new ThreadLocal(); public static final String ACTION_NAME = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name"; public static final String VALUE_STACK = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"; public static final String SESSION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session"; public static final String APPLICATION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application"; public static final String PARAMETERS = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters"; public static final String LOCALE = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale"; public static final String TYPE_CONVERTER = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.typeConverter"; public static final String ACTION_INVOCATION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation"; public static final String CONVERSION_ERRORS = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors"; public static final String CONTAINER = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container"; private Map<String, Object> context; public ActionContext(Map<String, Object> context) { this.context = context; } public void setActionInvocation(ActionInvocation actionInvocation) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation", actionInvocation); } public ActionInvocation getActionInvocation() { return (ActionInvocation)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation"); } public void setApplication(Map<String, Object> application) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application", application); } public Map<String, Object> getApplication() { return (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application"); } public static void setContext(ActionContext context) { actionContext.set(context); } public static ActionContext getContext() { return (ActionContext)actionContext.get(); } public void setContextMap(Map<String, Object> contextMap) { getContext().context = contextMap; } public Map<String, Object> getContextMap() { return this.context; } public void setConversionErrors(Map<String, Object> conversionErrors) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors", conversionErrors); } public Map<String, Object> getConversionErrors() { Map<String, Object> errors = (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors"); if (errors == null) { errors = new HashMap(); this.setConversionErrors((Map)errors); } return (Map)errors; } public void setLocale(Locale locale) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale", locale); } public Locale getLocale() { Locale locale = (Locale)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale"); if (locale == null) { locale = Locale.getDefault(); this.setLocale(locale); } return locale; } public void setName(String name) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name", name); } public String getName() { return (String)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name"); } public void setParameters(Map<String, Object> parameters) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters", parameters); } public Map<String, Object> getParameters() { return (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters"); } public void setSession(Map<String, Object> session) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session", session); } public Map<String, Object> getSession() { return (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session"); } public void setValueStack(ValueStack stack) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack", stack); } public ValueStack getValueStack() { return (ValueStack)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"); } public void setContainer(Container cont) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container", cont); } public Container getContainer() { return (Container)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container"); } public <T> T getInstance(Class<T> type) { Container cont = this.getContainer(); if (cont != null) { return cont.getInstance(type); } else { throw new XWorkException("Cannot find an initialized container for this request."); } } public Object get(String key) { return this.context.get(key); } public void put(String key, Object value) { this.context.put(key, value); } }
- ValueStack.java
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package com.opensymphony.xwork2.util; import java.util.Map; public interface ValueStack { String VALUE_STACK = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"; String REPORT_ERRORS_ON_NO_PROP = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ReportErrorsOnNoProp"; Map<String, Object> getContext(); void setDefaultType(Class var1); void setExprOverrides(Map<Object, Object> var1); Map<Object, Object> getExprOverrides(); CompoundRoot getRoot(); void setValue(String var1, Object var2); void setParameter(String var1, Object var2); void setValue(String var1, Object var2, boolean var3); String findString(String var1); String findString(String var1, boolean var2); Object findValue(String var1); Object findValue(String var1, boolean var2); Object findValue(String var1, Class var2); Object findValue(String var1, Class var2, boolean var3); Object peek(); Object pop(); void push(Object var1); void set(String var1, Object var2); int size(); }
- CompoundRoot.java
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package com.opensymphony.xwork2.util; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class CompoundRoot extends ArrayList { public CompoundRoot() { } public CompoundRoot(List list) { super(list); } public CompoundRoot cutStack(int index) { return new CompoundRoot(this.subList(index, this.size())); } public Object peek() { return this.get(0); } public Object pop() { return this.remove(0); } public void push(Object o) { this.add(0, o); } }
- ①我们查看CompoundRoo可以看出这个类继承了ArrayList,但是它同时也是一个栈结构。
- ②解析ActionContext
static ThreadLocal<ActionContext> actionContext = new ThreadLocal();
- 从上面的代码中,我们可以看出ActionContext是和线程绑定在一起的,也就是说,同一个线程,是可以共享ActionContext的。
public static final String ACTION_NAME = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name"; public static final String VALUE_STACK = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"; public static final String SESSION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session"; public static final String APPLICATION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application"; public static final String PARAMETERS = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters"; public static final String LOCALE = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale"; public static final String TYPE_CONVERTER = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.typeConverter"; public static final String ACTION_INVOCATION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation"; public static final String CONVERSION_ERRORS = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors"; public static final String CONTAINER = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container";
- 从上面的代码中,我们可以看出这里的ActionContext中的常量,其中需要注意的VALUE_STACK这个常量。因为ValueStack接口的全类名就是这个常量的值。
private Map<String, Object> context;
- 从上面的代码中,我们可以看出ActionContext中维护了一个名为context的Map接口。
public ActionContext(Map<String, Object> context) { this.context = context; }
- 从上面的代码中,我们可以看出通过构造方法来给context这个属性赋值。
public void put(String key, Object value) { this.context.put(key, value); }
- 从上面的代码中,我们可以看出这个方法就是向名为context的Map中添加值。
public void setActionInvocation(ActionInvocation actionInvocation) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation", actionInvocation); }
- 从上面的代码中,我们可以看出这个方法就是向名为context的Map设置key为com.opensymphony.xworks.ActionContext.actionInvocation,value为ActionInvocation的实例对象。
public ActionInvocation getActionInvocation() { return (ActionInvocation)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation"); }
- 从上面的代码中,我们可以看出这个方法就是从context的Map中获取key为com.opensymphony.xworks.ActionContext.actionInvocation的value,即ActionContext的实例对象。
this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application", application); } public Map<String, Object> getApplication() { return (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application"); }
public void setConversionErrors(Map<String, Object> conversionErrors) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors", conversionErrors); } public Map<String, Object> getConversionErrors() { Map<String, Object> errors = (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors"); if (errors == null) { errors = new HashMap(); this.setConversionErrors((Map)errors); } return (Map)errors; }
public void setLocale(Locale locale) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale", locale); } public Locale getLocale() { Locale locale = (Locale)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale"); if (locale == null) { locale = Locale.getDefault(); this.setLocale(locale); } return locale; }
public void setName(String name) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name", name); } public String getName() { return (String)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name"); }
public void setParameters(Map<String, Object> parameters) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters", parameters); } public Map<String, Object> getParameters() { return (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters"); }
public void setSession(Map<String, Object> session) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session", session); } public Map<String, Object> getSession() { return (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session"); }
public void setValueStack(ValueStack stack) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack", stack); } public ValueStack getValueStack() { return (ValueStack)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"); }
public void setContainer(Container cont) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container", cont); } public Container getContainer() { return (Container)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container"); } public <T> T getInstance(Class<T> type) { Container cont = this.getContainer(); if (cont != null) { return cont.getInstance(type); } else { throw new XWorkException("Cannot find an initialized container for this request."); } }
- 这些代码的功能,和上述的相同,就是向名为context的Map中存值和取值。
public Object get(String key) { return this.context.get(key); }
- 从上面的代码中,我们可以看出这个方法,是可以从Map中获取指定的key的value。
public static void setContext(ActionContext context) { actionContext.set(context); } public static ActionContext getContext() { return (ActionContext)actionContext.get(); }
- 从上面的代码中,我们可以看出就是将context这个属性对象设置到ThreadLocal中。
public void setContextMap(Map<String, Object> contextMap) { getContext().context = contextMap; } public Map<String, Object> getContextMap() { return this.context; }
- 从上面的代码中,我们可以看出其就是将传递过来的Map对象,直接设置到ThreadLocal中。
- ③解析ValueStack接口
Map<String, Object> getContext();
- 从上面的代码中,我们可以看出这个方法的功能就是获取ActionContext对象内部的那个名为context的Map集合。
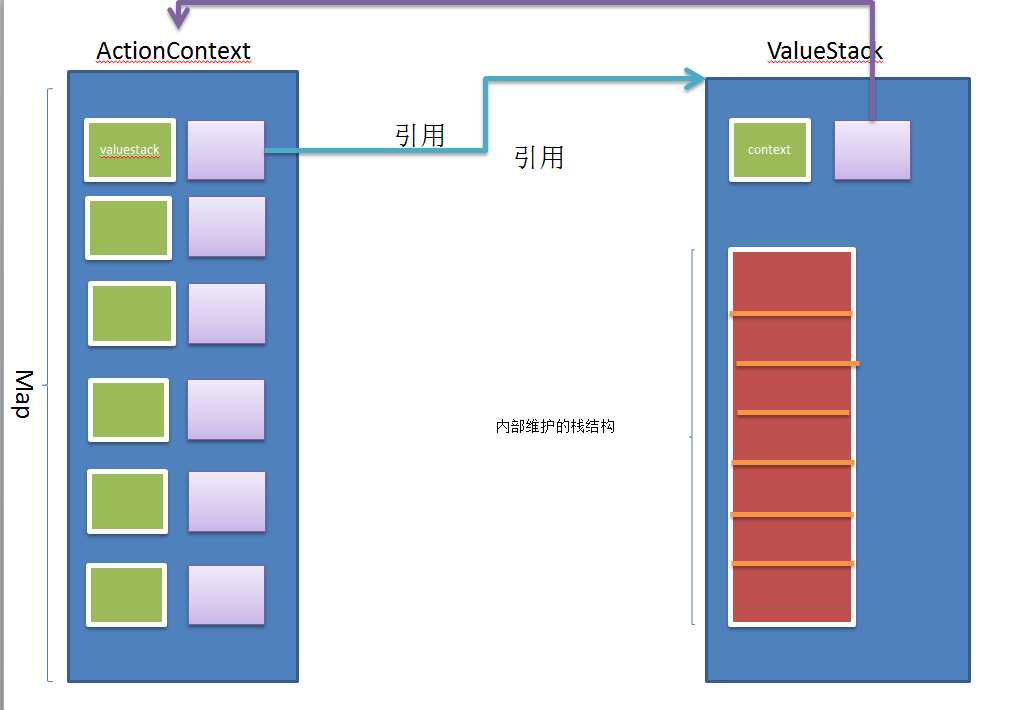
- 图解:ActionContext和ValueStack的关系
4.3 获取ValueStack的三种方式
- 方式一:
ValueStack valueStack = ActionContext.getContext().getValueStack();
- 方式二:
ValueStack valueStack = (ValueStack) ActionContext.getContext().get(ValueStack.VALUE_STACK);
- 方式三:
ValueStack valueStack = (ValueStack) ServletActionContext.getRequest().getAttribute("struts.valueStack");
4.4 ValueStack常用的方法
- 先获取根栈栈顶的Map,如果不存在,压入一个新的Map,把key和value方法这个新创建的Map中,如果Map已经存在,那么就是存放key和value。
void set(String var1, Object var2);
- String是一个OGNL表达式,如果表达式是以#开头,操作的是contextMap,如果不是,设置根栈中对象的某个属性,从栈顶依次查找
void setValue(String ognlExp, Object var2);
- String是一个OGNL表达式,如果以#开头,从contextMap中找key值对应的对象,如果不是,搜索根栈中对象的属性。【注意】如果编写的表达式不是以#开头,先搜索根栈对象的所有属性,如果没有找到,会把它当做key设置到contextMap中。
Object findValue(String var1);
- 和findValue的功能一样,但是把OGNL表达式虎丘的对象转换为String。
String findString(String var1);
以上是关于Struts2 的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章