第十七章 Java的容器
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第十七章 Java的容器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.先来个String的==和equals的区别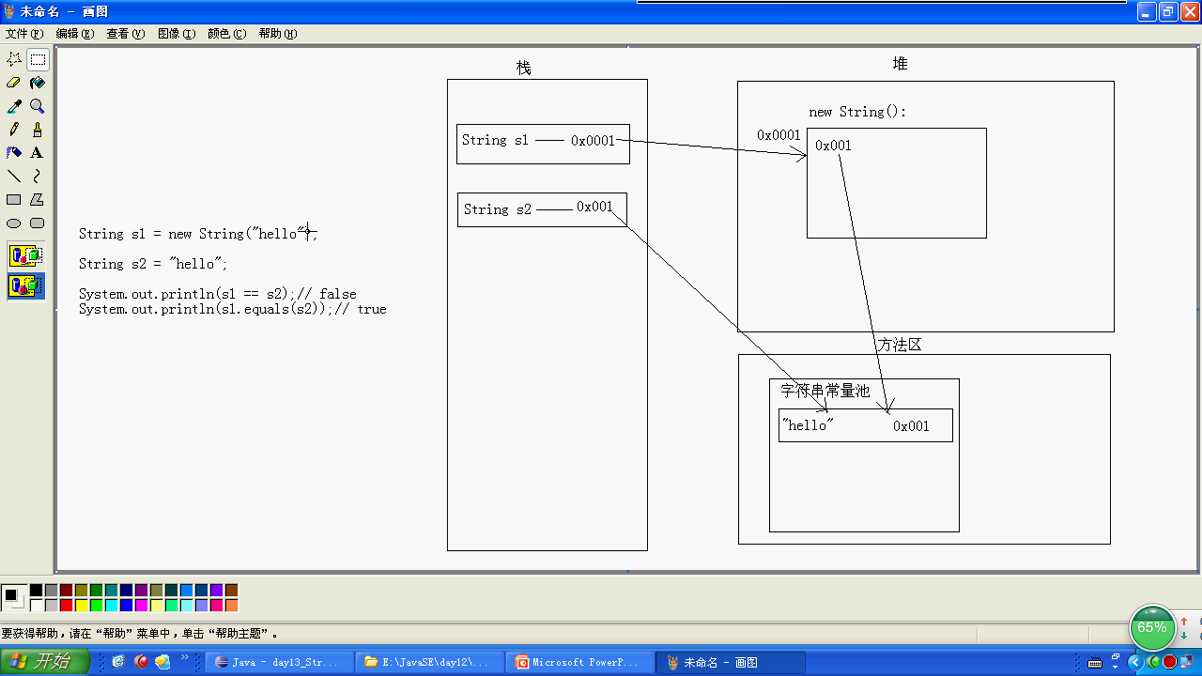
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 /** 3 * ==比较的是地址值是否相同 4 * String类重写了equals方法比较的是内容是否相同 5 */ 6 public class StringDemo { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 //字符串的两种赋值方式 9 String s1 = new String("hello");//创建了两个对象 10 String s2 = new String("hello"); 11 String s3 = "hello";//创建了一个对象 12 String s4 = "hello"; 13 /*System.out.println(s1==s2);//false 14 System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true 15 System.out.println(s2==s3);//false 16 System.out.println(s2.equals(s3));//true 17 System.out.println(s3==s4);//true 18 System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));//true*/ 19 String s = new String("hello"); 20 String s5 = "hello"; 21 //以上两种创建方式的数值都会进入常量池 22 String s6 = "world"; 23 String s7 = "helloworld"; 24 System.out.println((s5+s6)==s7);//false变量相加 25 System.out.println((s5+s6).equals(s7));//true 26 System.out.println((s+s6).equals(s7));//true 27 System.out.println(s7=="hello"+"world");//true常量相加 28 } 29 }
2.collection集合
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 6 /** 7 集合的由来: 8 1.用容器来存储多个对象,数组(长度不可变)和StringBuffer(字符串) 9 2.集合只能存储引用类型 10 */ 11 /** 12 * Collection集合:所有集合的顶层接口并且他继承了Iterable--Interface Iterable<T>{} 13 * 1.添加功能:boolean add(Object obj) 14 * 2.删除功能:void clear() 15 * boolean remove(Object obj) 16 * 3.判断功能:boolean contains(Object obj) 17 * boolean isEmpty() 18 * 4.获取功能:Iterator<T> iterator() 19 返回一个在一组 T 类型的元素上进行迭代的迭代器。 20 5.大小: int size():元素的个数 21 */ 22 23 public class CollectionDemo{ 24 public static void main(String[] args) { 25 //定义一个集合collection 26 Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<String>(); 27 //添加元素 28 c.add("hello"); 29 c.add("world"); 30 c.add("java"); 31 c.add("javase"); 32 //集合的遍历 33 for (String string : c) { 34 System.out.println(string); 35 } 36 System.out.println(c.remove("hello"));//true 37 System.out.println(c.contains("hello"));//false 38 System.out.println(c.contains("world"));//true 39 System.out.println(c.size());//3 40 } 41 }
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 7 public class CollectionDemo2 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // 定义一个集合collection 10 Collection<Student> c = new ArrayList<Student>(); 11 // 添加学生对象元素 12 Student s1 = new Student("张三", 22, "China"); 13 Student s2 = new Student("李四", 33, "China"); 14 Student s3 = new Student("王五", 44, "China"); 15 Student s4 = new Student("马六", 55, "China"); 16 c.add(s1); 17 c.add(s2); 18 c.add(s3); 19 c.add(s4); 20 // 遍历集合元素 21 for (Student s : c) { 22 System.out.println(s.getName() + "--" + s.getAge() + "--" + s.getAddress()); 23 } 24 // 遍历集合 25 Iterator<Student> it = c.iterator(); 26 while (it.hasNext()) { 27 Student s = it.next(); 28 System.out.println(s.getName() + "--" + s.getAge() + "--" + s.getAddress()); 29 } 30 } 31 }
3.list集合
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 import java.util.List; 4 public class ListDemo { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 /**list集合的特点:有序的可重复的 7 * list集合特有的功能: 8 * 1.指定位置添加 void add(int index,Object element) 9 * 2.指定位置删除 Object remove(int index)返回被删的元素 10 * 3.指定位置的获取 Object get(int index)返回指定位置的元素 11 * 4.修改元素 Object set(int index,Object element)返回修改前的元素 12 */ 13 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 14 list.add("hello");//0号元素 15 list.add("world");//1号元素 16 list.add("java");//2号元素 17 list.add("apache");//3号元素 18 //getElement(list);//hello,world,java,apache 19 //在1号位置添加元素 20 //list.add(1, "myWorld"); 21 //list.add(11, "aaa");//不可以在不存在的索引处添加元素 22 //list.add(4, "aaa");//末尾可以添加 23 //getElement(list);//hello,myWorld,world,java,apache 24 //删除指定位置的元素 25 //System.out.println(list.remove(1));//myWorld 26 //修改元素("hello")返回原来的值 27 System.out.println(list.set(0, "bbb")); 28 } 29 //元素的获取1.foreach 2.itrator 3.get()方法 30 public static <E> void getElement(List<E> list){ 31 for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++){ 32 System.out.println(list.get(i)); 33 } 34 } 35 }
package cn.itcast_01; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class ListDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 需求:判断集合是否有java元素,有就在其后添加MyJava 集合迭代器的并发修改异常(Iterator) * list集合特有的迭代器没有这种限制(ListIterator) */ List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("hello"); list.add("world"); list.add("java"); // 遍历集合 for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { if ("java".equals(list.get(i))) { list.add("MyJava"); } System.out.println(list.get(i)); } } }
1 package cn.itcast_01; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Arrays; 5 import java.util.List; 6 import java.util.Scanner; 7 8 //键盘录入多个数据,以0结束,要求在控制台输出这多个数据中的最大值 9 public class ListDemo3 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 // 创建集合存储录入的数据 12 List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 13 // 创建键盘录入对象 14 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); 15 while (true) { 16 System.out.println("请输入一个整数:"); 17 Integer i = scanner.nextInt(); 18 if (i != 0) { 19 list.add(i); 20 } else { 21 break; 22 } 23 } 24 // 将list集合搞成数组 25 Integer[] array = new Integer[list.size()]; 26 array = list.toArray(array); 27 // 数组排序 28 //Arrays.sort(array); 29 sort(array); 30 // 遍历数组循环打印 31 System.out.print("["); 32 for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { 33 if (i == array.length - 1) { 34 System.out.println(array[i] + "]"); 35 } else { 36 System.out.print(array[i] + ","); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 41 // 数组排序的方法 42 public static void sort(Integer[] t) { 43 for (int j = 0; j <t.length-1; j++) { 44 for (int i = j+1; i <t.length; i++) { 45 if (t[i] > t[j]) { 46 int temp = 0; 47 temp = t[i]; 48 t[i] = t[j]; 49 t[j] = temp; 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 }
以上是关于第十七章 Java的容器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章