《02.Spring Boot连载:Spring Boot实战.Spring Boot核心原理剖析》
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了《02.Spring Boot连载:Spring Boot实战.Spring Boot核心原理剖析》相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在上节中我们通过了一个小的入门案例已经看到了Spring Boot的强大和简单之处。本章将详细介绍Spring Boot的核心注解,基本配置和运行机制。笔者一直认为:精通一个技术一定要深入了解这个技术帮助我们做了哪些动作,深入理解它底层的运行原理,只有达到这个目标才可以熟练使用框架,最终达到融会贯通的目的。
一.启动类与@SpringBootApplication
Spring Boot的项目一般都会有注解*Application标注的入口类,入口类中会有一个main方法,main方法是一个标准的Java应用程序的入口方法,可以直接启动。 @SpringBootApplication注解是Spring Boot的核心注解,用此注解标注的入口类是应用的启动类,通常会在启动类的main方法中通过 SpringApplication.run(App.class, args) 来启动Spring Boot应用项目。 @SpringBootApplication其实是一个组合注解,查看源码如下:
// 程序清单:org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/SpringBootApplication @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) public @interface SpringBootApplication { @AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class, attribute = "exclude") Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; @AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class, attribute = "excludeName") String[] excludeName() default {}; @AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages") String[] scanBasePackages() default {}; @AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses") Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {}; }
(1)@SpringBootConfiguration:这是Spring Boot项目的配置注解,这也是一个组合注解:
//程序清单:org/springframewor/boot/SpringBootConfiguration @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Configuration public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
(2)@EnableAutoConfiguration:启动自动配置,该注解会让Spring Boot根据当前项目所依赖的jar包自动配置项目的相关配置项。 例如,当我们在Spring Boot项目的pom.xml文件中配置了spring-boot-starter-web依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
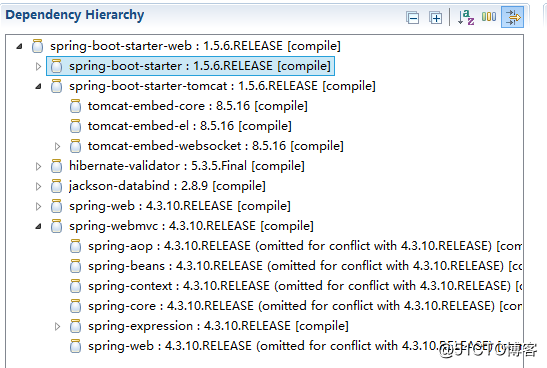
图2.1 spring-boot-starter-web自动配置图
通过上述例子可以看出,如果我们又在项目中添加spring-boot-starter-data-solr依赖,Spring Boot就会自动进行Solr技术的相关配置。 (3) @ComponentScan:扫描配置,Spring Boot默认会扫描@SpringBootApplication所在类的同级包以及它的子包。所以建议将@SpringBootApplication修饰的入口类放置在项目包下(Group Id+Artifact Id),这样做的好处是:可以保证Spring Boot项目自动扫描到项目所有的包。
二.Spring Boot基本配置介绍
1 关闭某个自动配置
通过上节@SpringBootApplication下的@EnableAutoConfiguration得知,Spring Boot会根据项目中的jar包依赖,自动做出配置,Spring Boot支持的自动配置如下(非常多):
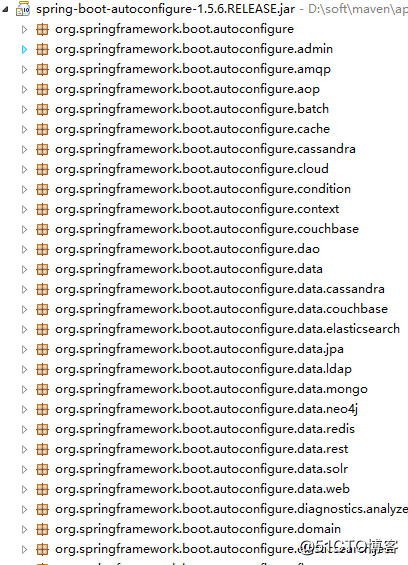
假如我们不需要Spring Boot自动配置,想关闭某一项的自动配置,该如何设置呢? 例如:我们不想自动配置Redis,想自己手动配置呢?通过查看@SpringBootApplication的源码可以看出,关闭特定的自动配置应该使用@SpringBootApplication下的exclude参数,现以关闭Redis自动配置为例: @SpringBootApplication(exclude={RedisAutoConfiguration.class})
2.定制启动Banner
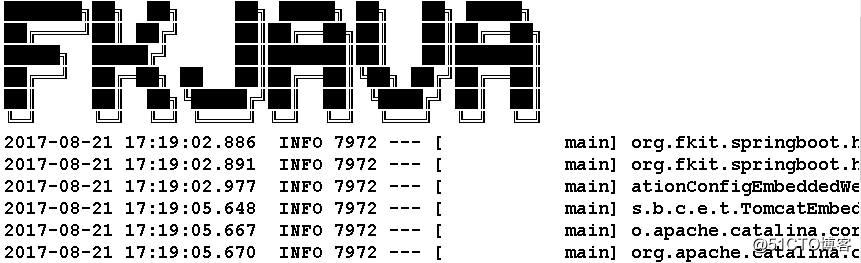
在启动Spring Boot项目的时候我们在控制台下看到了如下默认的启动图案:
如果想自己来指定启动的图案应该如何配置呢?
(1) 在浏览器中打开网站http://patorjk.com/software/taag,如下图:
(2)在第一步所示范的网站上选择左下方的“select & copy”按钮将自定义的banner图案进行复制,然后新建一个banner.txt文件,将复制好的图案写入到banner.txt文件中。
(3)将banner.txt文件放置到项目的src/main/resources目录下。

(4)重新启动程序,查看效果如下:
3. 应用的全局配置文件
可以在Spring Boot项目的src/main/resources目录下或者在类路径下的/config目录下创建一个全局的配置文件application.properties或者是后缀为.yml的application.yml的文件用于修改Spring Boot项目的默认配置值,例如修改项目的默认端口,或者进入DispatcherServlet的请求地址规则等。 通常,在实际开发中我们习惯使用application.properties文件作为应用的全局配置文件,一般我们放到src/main/resources目录下。 例如,在src/main/resources目录下创建一个名称为application.properties的文件,配置内容如下:
server.port=9999 server.servlet-path=*.action
(1)其中, server.port参数用于将Spring Boot项目的默认端口改为9999,启动应用,端口修改后如下图所示:

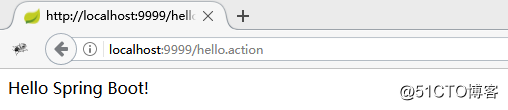
(2) server.servlet-path参数用于将进入DispatcherServlet的规则修改为:*.action,测试如下:
从上面的参数配置可以看出,Spring Boot支持很多参数的配置与参数值的修改,关于其他配置参数的详细说明和描述可以查看官方的文档说明:http://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.6.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#common-application-properties
4 Starters启动器
Spring Boot为我们提供了简化项目开发的Starter启动器,例如我们在项目中使用的pom.xml文件下配置:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
Spring Boot就会自动关联web开发相关的依赖,如Tomcat以及spring-webmvc等,进而对web开发进行支持,同时相关技术的配置也将实现自动配置,程序员即可从繁琐的配置文件中脱身而出了。除此之外,官方还提供了如下Starters:
?spring-boot-starter:这是Spring Boot的核心启动器,包含了自动配置、日志和YAML文件的支持。 ?spring-boot-starter-activemq:为JMS使用Apache ActiveMQ ActiveMQ 是Apache出品,最流行的,能力强劲的开源消息总线 ?spring-boot-starter-amqp:通过spring-rabbit来支持AMQP协议(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol)。 ?spring-boot-starter-aop:支持面向方面的编程即AOP,包括spring-aop和AspectJ。 ?spring-boot-starter-artemis:通过Apache Artemis支持JMS的API(Java Message Service API)。 ?spring-boot-starter-batch:支持Spring Batch,包括HSQLDB数据库。 ?spring-boot-starter-cache:支持Spring的Cache抽象。 ?spring-boot-starter-cloud-connectors:支持Spring Cloud Connectors,简化了在像Cloud Foundry或Heroku这样的云平台上连接服务。 ?spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra:使用Cassandra分布式数据库、Spring Data Cassandra,Apache Cassandra是一套开源分布式NoSQL数据库系统。 ?spring-boot-starter-data-couchbase:使用Couchbase 文件存储数据库、Spring Data Couchbase。Spring Data是一个用于简化数据库访问,并支持云服务的开源框架。 ?spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch:支持ElasticSearch搜索和分析引擎,包括spring-data-elasticsearch。 ?spring-boot-starter-data-gemfire:支持GemFire分布式数据存储,包括spring-data-gemfire。 ?spring-boot-starter-data-jpa:支持JPA(Java Persistence API),包括spring-data-jpa、spring-orm、Hibernate。 ?spring-boot-starter-data-ldap:支持 Spring Data LDAP。 ?spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb:支持MongoDB数据,包括spring-data-mongodb。 ?spring-boot-starter-data-neo4j:使用Neo4j图形数据库、Spring Data Neo4j Neo4j是一个高性能的,NOSQL图形数据库,它将结构化数据存储在网络上而不是表中。 ?spring-boot-starter-redis:支持Redis键值存储数据库,包括spring-redis。 ?spring-boot-starter-data-rest:通过spring-data-rest-webmvc,支持通过REST暴露Spring Data数据仓库。 ?spring-boot-starter-data-solr:支持Apache Solr搜索平台,包括spring-data-solr。 ?spring-boot-starter-freemarker:支持FreeMarker模板引擎。 ?spring-boot-starter-groovy-templates:支持Groovy模板引擎。 ?spring-boot-starter-hateoas:通过spring-hateoas支持基于HATEOAS的RESTful Web服务。 ?spring-boot-starter-integration:支持通用的spring-integration模块。 ?spring-boot-starter-jdbc:支持JDBC数据库。 ?spring-boot-starter-jersey:支持Jersey RESTful Web服务框架。 ?spring-boot-starter-hornetq:通过HornetQ支持JMS。 ?spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos:通过Atomikos支持JTA分布式事务处理。 ?spring-boot-starter-jta-bitronix:通过Bitronix支持JTA分布式事务处理。 ?spring-boot-starter-mail:支持javax.mail模块。 ?spring-boot-starter-mobile:支持spring-mobile。 ?spring-boot-starter-mustache:支持Mustache模板引擎。 ?spring-boot-starter-security:支持spring-security。 ?spring-boot-starter-social-facebook:支持spring-social-facebook ?spring-boot-starter-social-linkedin:支持pring-social-linkedin ?spring-boot-starter-social-twitter:支持pring-social-twitter ?spring-boot-starter-test:支持常规的测试依赖,包括JUnit、Hamcrest、Mockito以及spring-test模块。 ?spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf:支持Thymeleaf模板引擎,包括与Spring的集成。 ?spring-boot-starter-velocity:支持Velocity模板引擎。 ?spring-boot-starter-web:支持全栈式Web开发,包括Tomcat和spring-webmvc。 ?spring-boot-starter-websocket:支持WebSocket开发。 ?spring-boot-starter-ws:支持Spring Web Services。
Spring Boot在进行SpringApplication对象实例化时会加载META-INF/spring.factories文件,将该配置文件中的配置载入到Spring容器,进行自动配置。
1 源码分析
首先进入到启动Spring Boot项目代码SpringApplication.run(App.class, args)的源码下:
程序清单:org/springframework/boot/SpringApplicationpublic static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object[] sources, String[] args) {return new SpringApplication(sources).run(args);}
可以看到run方法实际上在创建SpringApplication对象实例,进入到创建SpringApplication对象实例代码中去:
程序清单:org/springframework/boot/SpringApplicationpublic SpringApplication(Object... sources) {initialize(sources);}
接下来就是调用initialize(sources)方法,进入到该方法源码如下:
程序清单:org/springframework/boot/SpringApplication@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })private void initialize(Object[] sources) {if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) {this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources));}this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment();setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();}
initialize方法中调用了getSpringFactoriesInstances方法,代码如下:
程序清单:org/springframework/boot/SpringApplicationprivate <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicatesSet<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<String>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,classLoader, args, names);AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);return instances;}
在getSpringFactoriesInstances中又调用了loadFactoryNames方法,继续进入到该方法中,查看源码如下:
程序清单:org/springframework/boot.SpringApplicationpublic static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();try {Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {URL url = urls.nextElement();Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));}return result;}catch (IOException ex) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() +"] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);}}
在上述源码中可以查看到加载了一个常量:FACTORIESRESOURCELOCATION,查看该常量的源码如下:
/*** The location to look for factories.* <p>Can be present in multiple JAR files.*/public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
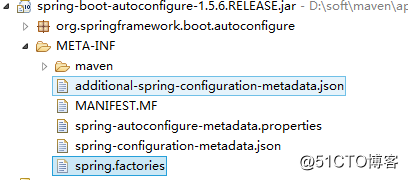
从该源码中可以看出,最终Spring Boot是通过加载META-INF/spring.factories 文件来进行自动配置的。其所在位置如下图所示。
2 spring.factories分析
Spring factories内容如下:
# Initializersorg.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.AutoConfigurationReportLoggingInitializer# Application Listenersorg.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer# Auto Configuration Import Listenersorg.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener# Auto Configuration Import Filtersorg.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition# Auto Configureorg.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapDataAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceResolverAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceDelegatingViewResolverAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.SitePreferenceAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.reactor.ReactorAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.FallbackWebSecurityAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.OAuth2AutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.SocialWebAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.FacebookAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.LinkedInAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.TwitterAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration# Failure analyzersorg.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBeanCreationFailureAnalyzer,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.HikariDriverConfigurationFailureAnalyzer# Template availability providersorg.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.template.TemplateAvailabilityProvider=\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.JspTemplateAvailabilityProvider
在spring.factories中可以看出web开发的自动配置类是:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,在这个类中就自动实现了Sprng MVC的配置。现在以Spring MVC的配置如下:
<bean id="jspViewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"><property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/><property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/></bean>
为例看Spring Boot是如何实现该自动配置的:
(1) 查询WebMvcAutoConfiguration的源码如下:
@[email protected]@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurerAdapter.class })@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
其中@ConditionalOnClass是一个条件注解,意思就是只有当前项目运行环境中有Servlet类,并且有DispatcherServlet类以及WebMvcConfigurerAdapter类时(说明本项目是需要集成Spring MVC的),,Spring Boot才会初始化WebMvcAutoConfiguration进行自动配置。 (2) 自动配置试图解析器ViewResolver。 在WebMvcAutoConfiguration类下找到以下源码:
@[email protected] InternalResourceViewResolver defaultViewResolver() { InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver(); resolver.setPrefix(this.mvcProperties.getView().getPrefix()); resolver.setSuffix(this.mvcProperties.getView().getSuffix()); return resolver;}
@Bean是在这里定义了一个Bean对象InternalResourceViewResolver,以前我们是通过标签来定义的。 @CoditionalOnMissingBean是一个条件注解,是当 前环境下没有这个Bean的时候才会创建该bean。 方法的返回值即是InternalResourceViewResolver,即是我们需要的对象,那么视图解析器中前缀和后缀Spring Boot是如何实现自动配置的呢?
resolver.setPrefix(this.mvcProperties.getView().getPrefix());resolver.setSuffix(this.mvcProperties.getView().getSuffix());该源码会找到一个View对象:public static class View { /** * Spring MVC view prefix. */ private String prefix; /** * Spring MVC view suffix. */ private String suffix; public String getPrefix() { return this.prefix; } public void setPrefix(String prefix) { this.prefix = prefix; } public String getSuffix() { return this.suffix; } public void setSuffix(String suffix) { this.suffix = suffix; }}View对象则会通过获取prefix,suffix加载视图解析器需要的前缀和后缀,该参数的值是可以通过全局配置文件来指定前缀和后缀的,配置如下:
spring.mvc.view.prefix= # Spring MVC view prefix. spring.mvc.view.suffix= # Spring MVC view suffix.

以上是关于《02.Spring Boot连载:Spring Boot实战.Spring Boot核心原理剖析》的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章