C#学习笔记--泛型函数的==和Equals(看完你一定能学到!)
Posted 就一枚小白
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C#学习笔记--泛型函数的==和Equals(看完你一定能学到!)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
工作的同事发现了这个问题,觉得实际游戏开发中会有这样的问题,所以在此记录
准备
- 开一个Unity项目,新建一个Test.cs脚本,并且生成一个Cube,直接把Test.cs挂在Cube上
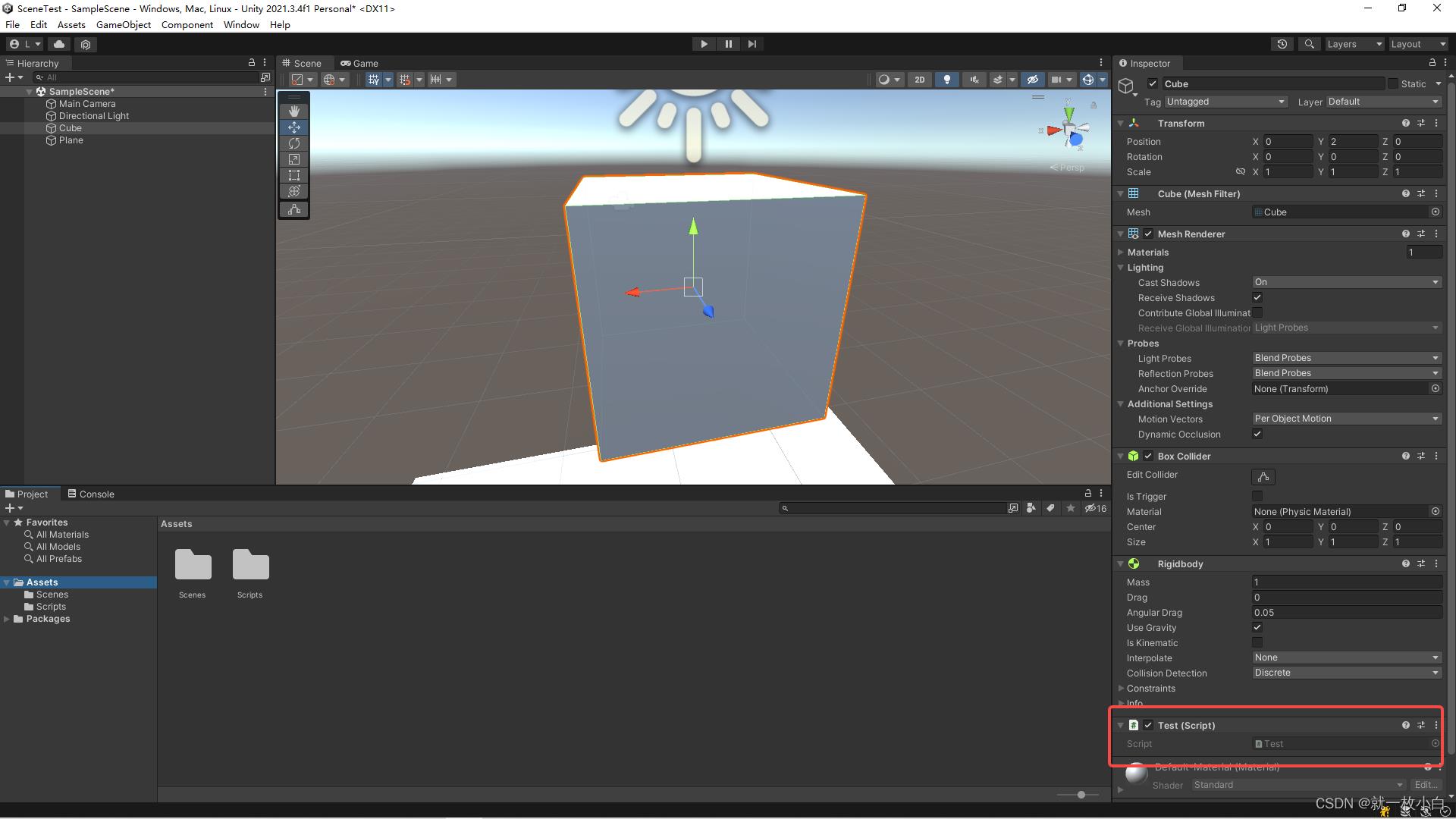
- 写一个Nulltest.cs脚本
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Nulltest : MonoBehaviour
public Test test;
private void Awake()
Destroy(test);
private void Update()
Check(test);
private void Check<T>(T test)
if (test == null)
print($"test == null : test == null");
return;
if (test.Equals(null))
print($"test.Equals(null) : test.Equals(null)");
return;
if (ReferenceEquals(test, null))
print($"ReferenceEquals(test, null) : ReferenceEquals(test, null)");
return;
- 把Nulltest挂在MainCamera上,并且把Cube拖拽给test属性
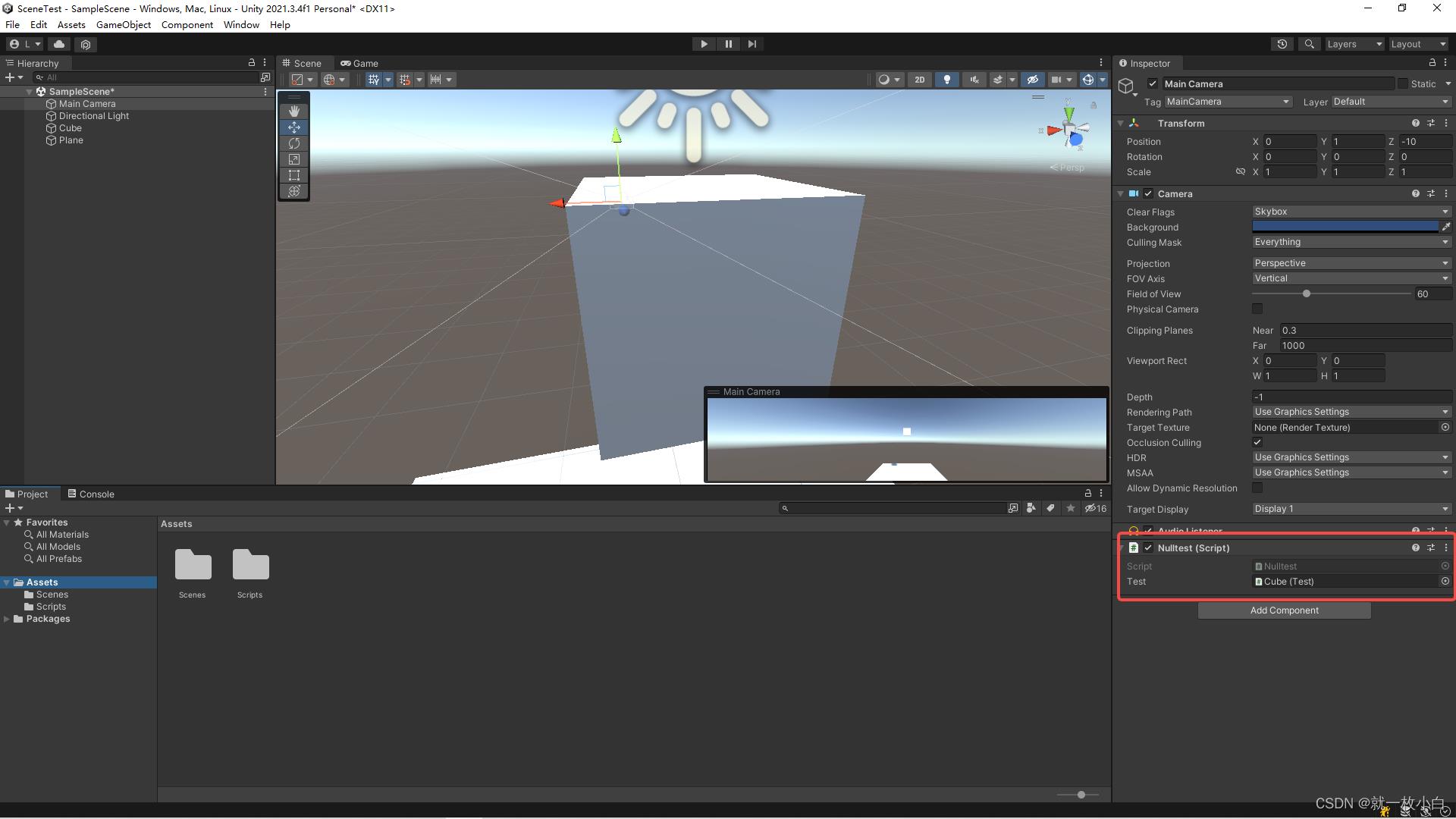
验证
现在打断点验证,会发现一个很神奇的结果
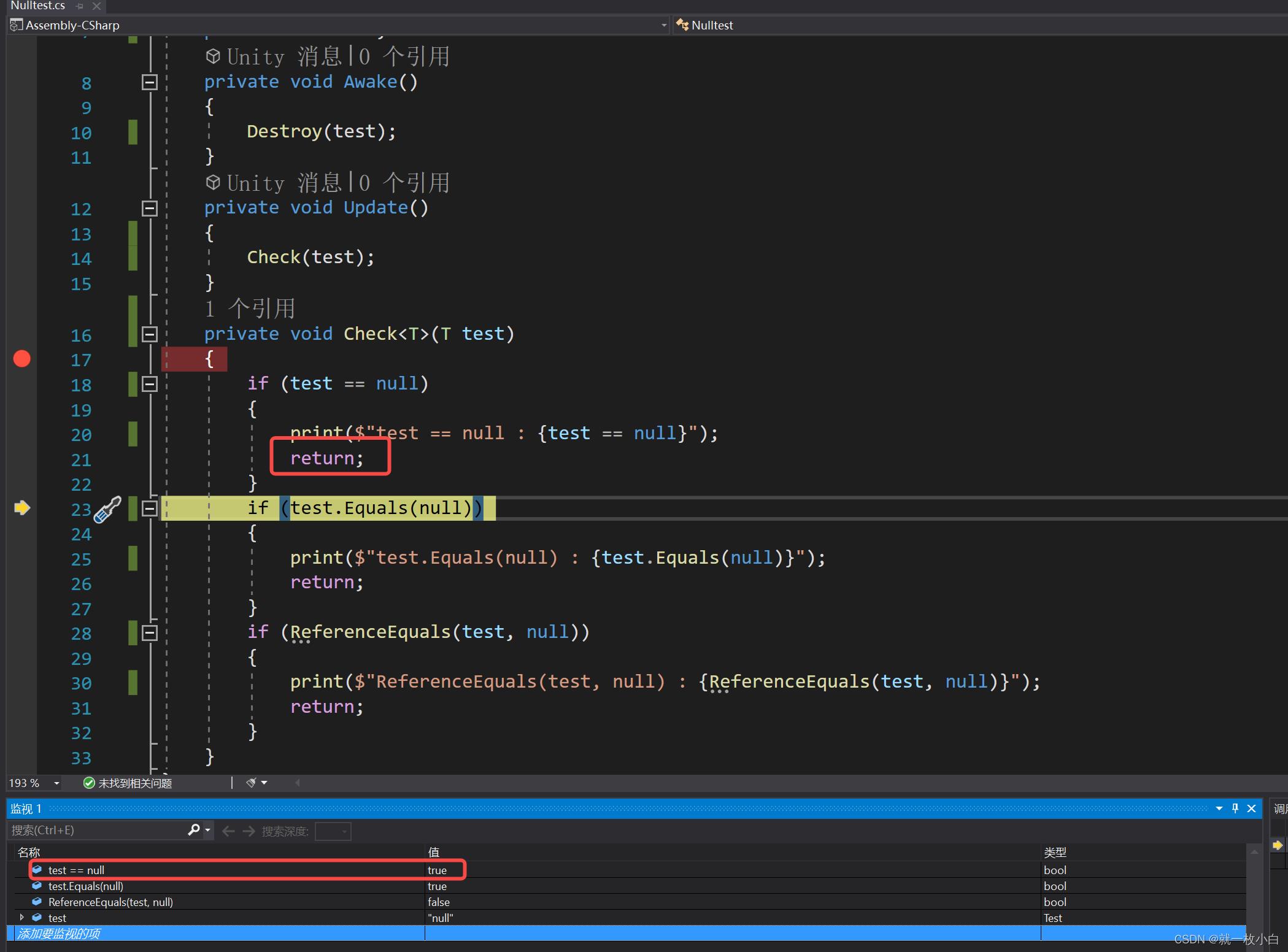
我们看到vs下面的监视窗口,发现 test == null 是true,按道理应该直接return掉了,为什么还能执行到下面的语句???
查找问题
在上图中,我们看到obj是能展开的(而且值里有双引号),所以肯定是一个对象,不是null,这样应该是Component里做了或Equals的重载,于是查了一下源码,果不其然,Component继承UnityEngine.Object,而UnityEngine.Object对和Equal都进行了重载:
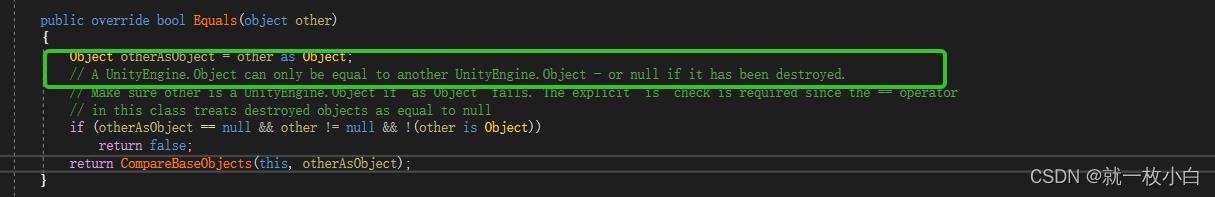
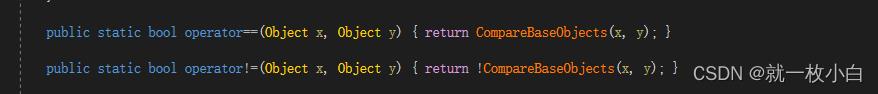
注意绿框里的注释,如果一个Object被Destroy了,那么它与null是相等的,这个规则适用于==和Equals,具体的逻辑在CompareBaseObjcets里
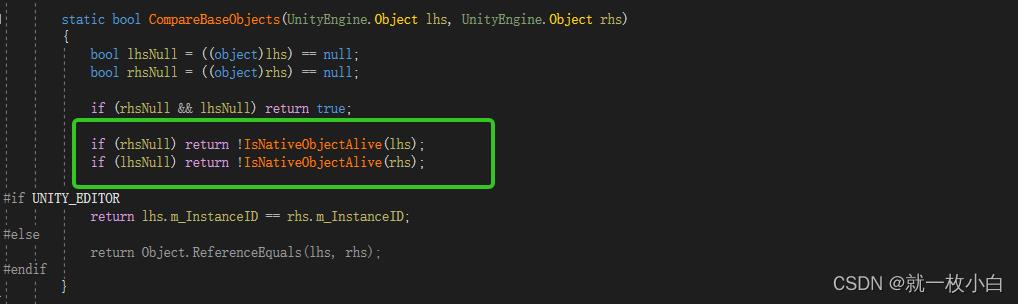
那么问题来了:为什么在上面的逻辑能走到obj.Equals(null)分支里而没有进入obj == null的分支呢,这是因为上面的函数是一个泛型函数:c#的泛型实现与C++的模板不一样,它不会在编译器根据你泛型的类型去生成代码,而是把T作为一个占位符生成一份模板代码,然后再在运行时去做JIT,所以在生成模板代码的时候,编译器并不知道你的T是啥,保险起见,它会使用System.Object的去判定,所以在运行时执行 obj == null判定为false(obj和null不是同一个对象),但vs知道obj时Component,调用的是UnityEngine.Object的,所以是true。但Equals不一样,它走的是虚函数的逻辑,所以在运行时可以找到UnityEngine.Objec.Equals,所以返回true。
解决
知道问题是泛型引起的,解决方案就好办了,只要加一个UnityEngine.Object的特例化函数就好了。
但同时又引出了另一个问题,PyObjectFrom里的类型有可能是数值类型,而编译器为了保险起见,同样会把obj当作对象处理,这样就会造成了一个装箱的行为,为了避免这个装箱,需要加一个where T : Struct的版本。
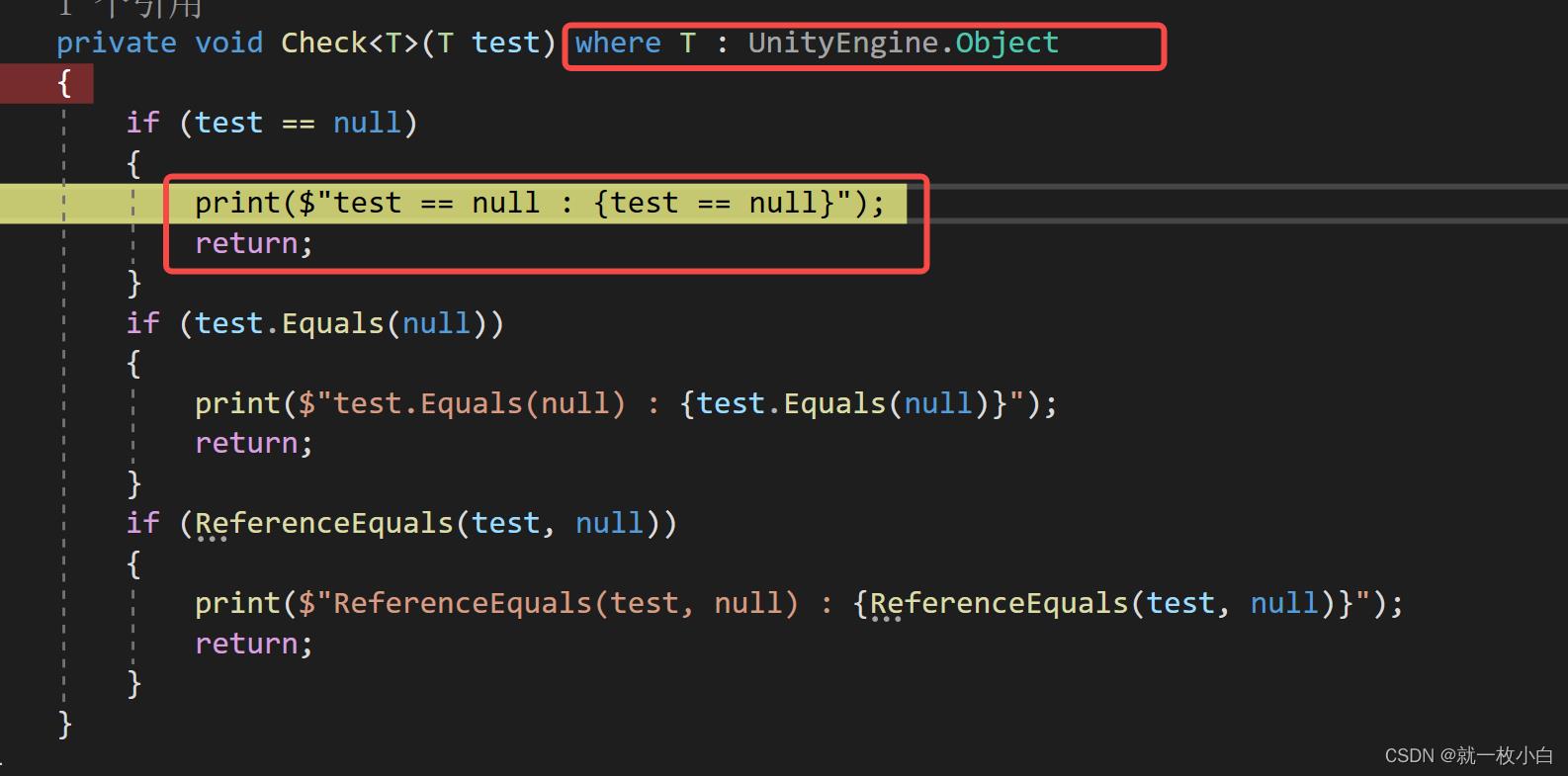
可以看到我们加了一个泛型约束就可以进来了
最后感谢同事的发现,大家以后可以在代码里多注意下
C#学习笔记---基础入门
泛型<T>
使用泛型能够最大限度的重用代码/保护类型安全,提高性能
泛型成员因为类型的不确定性,不能使用算术运算符/比较运算符
类型参数可以有多个,可以是编译器能够识别的任何类型
类型参数的名字不能随便起,不能重名

//使用泛型 //数组类Array //泛型类-需要在类名前加上泛型类型 //定义的时候需要用T泛型类型表示任意一种数据类型 //T-Type,S/U/V 表示其他类型 //K/V-key/value public class Array<T,S,U,V> { //索引器 public T this[int index] { set { _arr[index] = value; } get { return _arr[index]; } } public int Count { get { return _count; } } public void Log() { string str = "当前数组中包含" + Count + "个元素 ("; for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++) { str += _arr[i]; if (i < Count - 1) { str += ", "; } } str += ")"; Console.WriteLine(str); Console.ReadLine(); } public void Add(T value) { _arr[_count] = value; _count++; } public Array() { _arr = new T[100]; } private T[] _arr; private int _count = 0; } static void Main(string[] args) { //当具体需要使用的时候才需要确定实际的类型,可以将int改为其他类型 Array<int> arr = new Array<int>(); arr.Log(); arr.Add(2); arr.Log(); arr.Add(34); arr.Log(); }
ArrayList
arraylist 属于一种集合
集合是种容器,在程序中,使用集合管理相关对象组,集合分为非泛型集合和泛型集合

ArrayList是一个特殊的数组,通过添加或者删除元素就可以动态改变数组长度
可以灵活地插入/删除,访问元素,不是强类型,速度跟普通的数组比要慢。ArrayList存入的数据类型系统会默认为Object类型,因此接收元素需要强制转换。

public static void Log(ArrayList arr) { string str = "当前数组中包含" + arr.Count + "个元素 ("; for (int i = 0; i < arr.Count; i++) { str += arr[i]; if (i < arr.Count - 1) { str += ", "; } } str += ")"; Console.WriteLine(str); Console.ReadLine(); } public static void Main(string[] args) { //首先创建对象 ArrayList arr = new ArrayList(); Log(arr); //使用Add()方法添加元素,对元素类型没有限制 arr.Add(17); arr.Add(4.5f); arr.Add("xiaoli"); Log(arr); //使用下标获取指定位置的元素 //获取当前数组中元素的数量 int count = arr.Count; //使用insert方法向指定下标位置插入元素 arr.Insert(1, "hello"); Log(arr); //使用Remove方法从数组中删除指定元素 arr.Remove(4.5f); Log(arr); //RemoveAt方法将指定下标位置删除 arr.RemoveAt(0); Log(arr); //是否存在指定元素 Console.WriteLine(arr.Contains("hello")); //清空整个数组 arr.Clear(); Log(arr); }
List
List属于泛型集合,是一种强类型列表,其方法的使用与ArrayList相似。更推荐使用List类型,因为更安全。
声明一个List对象:List<string> arr=new List<string>();//List 对元素类型有限制,一旦确定为某类型,就必须是某类型
字典
Dictionary是存储键和值的集合,属于泛型集合,使用时需引入泛型集合命名空间
Dictionary是无序的,键Key是唯一的

public static void Main(string[] args) { //创建一个字典对象,key的类型是string,value的类型是int Dictionary<string, int> dic = new Dictionary<string, int>(); //Add方法用来添加键值对 dic.Add("laowang", 13); dic.Add("hello", 15); //删除键值对 dic.Remove("hello"); //清空 dic.Clear(); //获取当前字典中Key,value的个数 int count = dic.Count; Console.WriteLine(count); //检查字典中是否包含指定的key bool b = dic.ContainsKey("xiaoming"); //检查字典中是否包含指定的value bool c = dic.ContainsValue(13); //尝试获取指定的key所对应的value int s; bool bb = dic.TryGetValue("xiaoming", out s); //如果当前包含“xiaoming”这个key,则获取对应的value并保存在s中,bb=true //如果当前不包含“xiaomign”这个key,则s=null,bb=false //通过Key获取value int age = dic["laowang"]; Console.WriteLine(age); Console.ReadLine(); }
栈<stack>与队列<Queue>
属于泛型集合。栈遵循后进先出原则
队列遵循先进先出原则栈与队列根据需要容量自动添加
栈与队列都允许重复元素

public static void Main(string[] args) { //栈 Stack<string> s = new Stack<string>(); int count = s.Count; s.Clear(); bool a = s.Contains("xiao"); //将元素放入栈,使用Push方法 s.Push("xiaomign"); s.Push("helllo"); s.Push("tian"); //使用Pop方法把元素出栈,后进先出 //队列 先进先出 Queue<string> q = new Queue<string>(); q.Clear(); int cou = q.Count; bool d = q.Contains("xiaomign"); //添加元素 q.Enqueue("xiaomign"); q.Enqueue("haha"); q.Enqueue("lala"); //取出元素 string s1 = q.Dequeue(); Console.WriteLine(s1);//输出xiaoming Console.ReadLine(); }
委托
委托是一种特殊的类型,用于引用方法
定义委托需要用delegate关键字
委托可以把方法当作参数来传递
委托可以使用+-运算符合并/解绑委托

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Collections; namespace test2 { class Program { //定义委托-访问修饰符 delegate 返回值类型 委托名(参数列表); public delegate void Something(string name); public class Student { //可以像普通类型一样当作方法参数传递 public void Do(Something something) { //可以像普通方法一样调用 //真正调用了方法A--方法回掉 something(name); } public Student(string name) { this.name = name; } private string name; } public class Teacher { public void Hungry() { Student s = new Student("laowang"); //创建委托变量 Something a = new Something(A); Something b= new Something(B); s.Do(a+b);//委托对象可以使用+,-来绑定解除委托 } public void A(string name) { Console.WriteLine("hello"+name); Console.ReadLine(); } public void B(string name) { Console.WriteLine("你好" + name); Console.ReadLine(); } } public static void Main(string[] args) { Teacher t = new Teacher(); t.Hungry(); } } }
事件
event和delegate的关系就好像是字段和属性的关系
event会限制delegate不能够直接赋值操作,防止将委托替换掉,只能使用+=和-=来绑定或解除委托
event还限定了delegate只能在定义的类中被调用

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Collections; namespace test2 { class Program { public delegate void Something(string name); public class Student { //event就是delegate的“属性” public event Something something; public void Do() { something(name); } public Student(string name) { this.name = name; } private string name; } public class Teacher { public void Hungry() { Student s = new Student("laowang"); //使用事件后不能够直接赋值操作,防止将委托替换掉,只能使用+=和-=来绑定或解除委托 s.something += new Something(A); //使用事件后不能在Student外界调用委托-s.something("hello"); s.Do(); } public void A(string name) { Console.WriteLine("hello"+name); Console.ReadLine(); } } public static void Main(string[] args) { Teacher t = new Teacher(); t.Hungry(); } } }
以上是关于C#学习笔记--泛型函数的==和Equals(看完你一定能学到!)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
