Java中常用加减密方式
Posted DREAMINGXIN
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java中常用加减密方式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、加密概述:
加密就是是以某种特殊的算法改变原有的信息数据,使得未授权的用户即使以获得了加密的信息,但因不知解密方式,仍无法了解信息的内容。大体上又分为双向加密和单向加密。
2、单项加密
2.1、概述:
单向加密又称为不可逆加密算法,在加密过程中不使用密钥,明文由系统加密成密文,密文无法破解,一般都是采用验证的方式,具体是:在验证过程中,重新输入明文,并经过同样的加密算法后,得到相同的密文。单向加密广泛用于口令加密。
2.2、特点:
(1)对同一消息反复执行加密得到相同的密文;
(2)加密算法生成密文不可预见;
(3)不可逆,一般不能通过密文获取明文
2.3、类别
2.3.1、MD5加密
2.3.1.1、概述:
MD5的全称是Message-Digest Algorithm 5(信息-摘要算法),在90年代初由MIT Laboratory for Computer Science和RSA Data Security Inc的Ronald L. Rivest开发出来,经MD2、MD3和MD4发展而来。
MD5用于确保信息传输完整一致。是计算机广泛使用的杂凑算法之一(又译摘要算法、哈希算法),主流编程语言普遍已有MD5实现。将数据(如汉字)运算为另一固定长度值,是杂凑算法的基础原理,MD5的前身有MD2、MD3和MD4。
MD5的作用是让大容量信息在用数字签名软件签署私人密钥前被"压缩"成一种保密的格式(就是把一个任意长度的字节串变换成一定长的十六进制数字串)。
2.3.1.2、算法原理:
对MD5算法简要的叙述可以为:MD5以512位分组来处理输入的信息,且每一分组又被划分为16个32位子分组,经过了一系列的处理后,算法的输出由四个32位分组组成,将这四个32位分组级联后将生成一个128位散列值。
在MD5算法中,首先需要对信息进行填充,使其位长对512求余的结果等于448。因此,信息的位长(Bits Length)将被扩展至N*512+448,N为一个非负整数,N可以是零。填充的方法如下,在信息的后面填充一个1和无数个0,直到满足上面的条件时才停止用0对信息的填充。然后,在这个结果后面附加一个以64位二进制表示的填充前信息长度。经过这两步的处理,信息的位长=N*512+448+64=(N+1)*512,即长度恰好是512的整数倍。这样做的原因是为满足后面处理中对信息长度的要求。
2.3.1.3、java代码中使用MD5加密
1 /** 2 * md5计算. 3 * 4 * @param datas 5 * 待计算的数据 6 * @return 计算结果 7 */ 8 public static byte[] md5(byte[] datas) { 9 MessageDigest md = null; 10 try { 11 md = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5"); 12 md.reset(); 13 md.update(datas); 14 return md.digest(); 15 } catch (Exception e) { 16 log.error("MD5计算失败", e); 17 return null; 18 } 19 }
2.3.2、SHA加密
2.3.2.1、概述
其思想是接收一段明文,然后以一种不可逆的方式将它转换成一段(通常更小)的密文。可以简单的理解为取一串输入码(称为预映射或信息),并把他们转化为长度较短、位数固定的输出序列的过程。
安全散列算法SHA(Secure Hash Algorithm,SHA)是美国国家标准技术研究所发布的国家标准FIPS PUB 180,最新的标准已经于2008年更新到FIPS PUB 180-3。其中规定了SHA-1,SHA-224,SHA-256,SHA-384,和SHA-512这几种单向散列算法。SHA-1,SHA-224和SHA-256适用于长度不超过2^64二进制位的消息。SHA-384和SHA-512适用于长度不超过2^128二进制位的消息。
2.3.2.2、原理
SHA-1是一种数据加密算法,该算法的思想是接收一段明文,然后以一种不可逆的方式将它转换成一段(通常更小)密文,也可以简单的理解为取一串输入码(称为预映射或信息),并把它们转化为长度较短、位数固定的输出序列即散列值(也称为信息摘要或信息认证代码)的过程。
单向散列函数的安全性在于其产生散列值的操作过程具有较强的单向性。如果在输入序列中嵌入密码,那么任何人在不知道密码的情况下都不能产生正确的散列值,从而保证了其安全性。SHA将输入流按照每块512位(64个字节)进行分块,并产生20个字节的被称为信息认证代码或信息摘要的输出。
该算法输入报文的长度不限,产生的输出是一个160位的报文摘要。输入是按512 位的分组进行处理的。SHA-1是不可逆的、防冲突,并具有良好的雪崩效应。
通过散列算法可实现数字签名实现,数字签名的原理是将要传送的明文通过一种函数运算(Hash)转换成报文摘要(不同的明文对应不同的报文摘要),报文摘要加密后与明文一起传送给接受方,接受方将接受的明文产生新的报文摘要与发送方的发来报文摘要解密比较,比较结果一致表示明文未被改动,如果不一致表示明文已被篡改。
MAC (信息认证代码)就是一个散列结果,其中部分输入信息是密码,只有知道这个密码的参与者才能再次计算和验证MAC码的合法性。
2.3.2.3、java中的SHA实现
/**
* SHA1签名
* @param paramStr 要加签的字符串
* @return
*/
public static String SHA1(String paramStr) {
MessageDigest alg;
String result = "";
String tmp = "";
try {
alg = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-1");
alg.update(paramStr.getBytes());
byte[] bts = alg.digest();
for (int i = 0; i < bts.length; i++) {
tmp = (Integer.toHexString(bts[i] & 0xFF));
if (tmp.length() == 1)
result += "0";
result += tmp;
}
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
2.4、SHA与MD5的区别:
(1)对强行攻击的安全性:最显著和最重要的区别是:SHA-1的摘要比MD5的摘要长32位。使用强行技术,产生任何一个报文使其摘要等于给定摘要的难度对MD5是是2^128数量级的操作,而对SHA-1则是2^160数量级的操作。这样,SHA-1对强行攻击有更大的强度。
(2)对密码分析的安全性:由于MD5的设计,易受密码分析的攻击,SHA-1不易受这样的攻击。
3、双向加密
3.1概述
大体意思是明文加密后形成密文,可以通过算法还原成明文。
3.2分类
3.2.1对称加密
3.2.1.1概述
对称加密算法是应用较早的加密算法,技术成熟。在对称加密算法中,数据发信方将明文(原始数据)和加密密钥(mi yue)一起经过特殊加密算法处理后,使其变成复杂的加密密文发送出去。收信方收到密文后,若想解读原文,则需要使用加密用过的密钥及相同算法的逆算法对密文进行解密,才能使其恢复成可读明文。在对称加密算法中,使用的密钥只有一个,发收信双方都使用这个密钥对数据进行加密和解密,这就要求解密方事先必须知道加密密钥。
3.2.1.2特点
优点:
(1)算法公开,计算量小、加密速度快、加密效率高
缺点:
(1)交易双方都使用同样的密钥,安全性得不到保证
(2)每对用户每次使用对称加密算法时,都需要使用其他人不知道的唯一密钥,这会使得发收信双方所拥有的钥匙数量呈几何级数增长,密钥管理成为用户的负担。对称加密算法在分布式网络系统上使用较为困难,主要是因为密钥管理困难,使用成本较高。
3.2.1.3常用对称加密算法
基于“对称密钥”的加密算法比较常用的主要有:DES 、 3DES 、AES
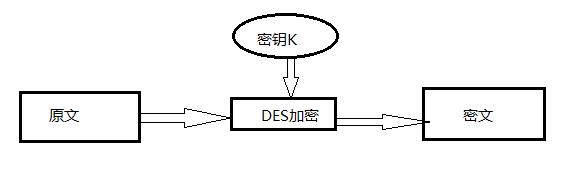
(1)DES
概述:
DES算法全称为Data Encryption Standard,即数据加密算法,它是IBM公司于1975年研究成功并公开发表的。DES算法的入口参数有三个:Key、Data、Mode。其中Key为8个字节共64位,是DES算法的工作密钥;Data也为8个字节64位,是要被加密或被解密的数据;Mode为DES的工作方式,有两种:加密或解密。
算法原理:
DES算法的入口参数有三个:Key、Data、Mode。
(1)Key为8个字节共64位,是DES算法的工作密钥;
(2)Data也为8个字节64位,是要被加密或被解密的数据;
(3)Mode为DES的工作方式,有两种:加密或解密。
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/36767829/answer/68911532
算法应用:
java代码实现:
1 /** 2 * 3DES加密 3 * 4 * @param key 5 * 密钥信息 6 * @param content 7 * 待加密信息 8 * @return 9 * @throws Exception 10 */ 11 public static byte[] encode3DES(byte[] key, byte[] content) throws Exception { 12 Security.addProvider(new org.bouncycastle.jce.provider.BouncyCastleProvider()); 13 // 不是8的倍数的,补足 14 if (key.length % 8 != 0) { 15 int groups = key.length / 8 + (key.length % 8 != 0 ? 1 : 0); 16 byte[] temp = new byte[groups * 8]; 17 Arrays.fill(temp, (byte) 0); 18 System.arraycopy(key, 0, temp, 0, key.length); 19 key = temp; 20 } 21 // 长度为16位,转换成24位的密钥 22 if (key.length == 16) { 23 byte[] temp = new byte[24]; 24 System.arraycopy(key, 0, temp, 0, key.length); 25 System.arraycopy(key, 0, temp, key.length, temp.length - key.length); 26 key = temp; 27 } 28 29 // 不是8的倍数的,补足 30 byte[] srcBytes = content; 31 if (srcBytes.length % 8 != 0) { 32 int groups = content.length / 8 + (content.length % 8 != 0 ? 1 : 0); 33 srcBytes = new byte[groups * 8]; 34 Arrays.fill(srcBytes, (byte) 0); 35 System.arraycopy(content, 0, srcBytes, 0, content.length); 36 } 37 38 SecretKey deskey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "DESede"); 39 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DESede/ECB/NoPadding"); 40 cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, deskey); 41 byte[] temp = cipher.doFinal(srcBytes); 42 byte[] tgtBytes = new byte[content.length]; 43 System.arraycopy(temp, 0, tgtBytes, 0, tgtBytes.length); 44 return tgtBytes; 45 } 46 47 /** 48 * 3DES解密 49 * 50 * @param key 51 * 密钥 52 * @param content 53 * 待解密信息 54 * @return 55 * @throws Exception 56 */ 57 public static byte[] decode3DES(byte[] key, byte[] content) throws Exception { 58 // 不是8的倍数的,补足 59 if (key.length % 8 != 0) { 60 int groups = key.length / 8 + (key.length % 8 != 0 ? 1 : 0); 61 byte[] temp = new byte[groups * 8]; 62 Arrays.fill(temp, (byte) 0); 63 System.arraycopy(key, 0, temp, 0, key.length); 64 key = temp; 65 } 66 // 长度为16位,转换成24位的密钥 67 if (key.length == 16) { 68 byte[] temp = new byte[24]; 69 System.arraycopy(key, 0, temp, 0, key.length); 70 System.arraycopy(key, 0, temp, key.length, temp.length - key.length); 71 key = temp; 72 } 73 74 // 不是8的倍数的,补足 75 byte[] srcBytes = content; 76 if (srcBytes.length % 8 != 0) { 77 int groups = content.length / 8 + (content.length % 8 != 0 ? 1 : 0); 78 srcBytes = new byte[groups * 8]; 79 Arrays.fill(srcBytes, (byte) 0); 80 System.arraycopy(content, 0, srcBytes, 0, content.length); 81 } 82 83 SecretKey deskey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "DESede"); 84 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DESede/ECB/NoPadding"); 85 cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, deskey); 86 byte[] tgtBytes = cipher.doFinal(srcBytes); 87 return tgtBytes; 88 } 89 90 /** 91 * DES加密 92 * 93 * @param key 94 * 密钥信息 95 * @param content 96 * 待加密信息 97 * @return 98 * @throws Exception 99 */ 100 public static byte[] encodeDES(byte[] key, byte[] content) throws Exception { 101 // 不是8的倍数的,补足 102 if (key.length % 8 != 0) { 103 int groups = key.length / 8 + (key.length % 8 != 0 ? 1 : 0); 104 byte[] temp = new byte[groups * 8]; 105 Arrays.fill(temp, (byte) 0); 106 System.arraycopy(key, 0, temp, 0, key.length); 107 key = temp; 108 } 109 110 // 不是8的倍数的,补足 111 byte[] srcBytes = content; 112 if (srcBytes.length % 8 != 0) { 113 int groups = content.length / 8 + (content.length % 8 != 0 ? 1 : 0); 114 srcBytes = new byte[groups * 8]; 115 Arrays.fill(srcBytes, (byte) 0); 116 System.arraycopy(content, 0, srcBytes, 0, content.length); 117 } 118 119 IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(new byte[] { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }); 120 SecureRandom sr = new SecureRandom(); 121 DESKeySpec dks = new DESKeySpec(key); 122 SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES"); 123 SecretKey secretKey = keyFactory.generateSecret(dks); 124 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/CBC/NoPadding"); 125 cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey, iv, sr); 126 byte[] tgtBytes = cipher.doFinal(srcBytes); 127 return tgtBytes; 128 } 129 130 /** 131 * DES解密 132 * 133 * @param key 134 * 密钥信息 135 * @param content 136 * 待加密信息 137 * @return 138 * @throws Exception 139 */ 140 public static byte[] decodeDES(byte[] key, byte[] content) throws Exception { 141 // 不是8的倍数的,补足 142 if (key.length % 8 != 0) { 143 int groups = key.length / 8 + (key.length % 8 != 0 ? 1 : 0); 144 byte[] temp = new byte[groups * 8]; 145 Arrays.fill(temp, (byte) 0); 146 System.arraycopy(key, 0, temp, 0, key.length); 147 key = temp; 148 } 149 // 不是8的倍数的,补足 150 byte[] srcBytes = content; 151 if (srcBytes.length % 8 != 0) { 152 int groups = content.length / 8 + (content.length % 8 != 0 ? 1 : 0); 153 srcBytes = new byte[groups * 8]; 154 Arrays.fill(srcBytes, (byte) 0); 155 System.arraycopy(content, 0, srcBytes, 0, content.length); 156 } 157 158 IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(new byte[] { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }); 159 SecureRandom sr = new SecureRandom(); 160 DESKeySpec dks = new DESKeySpec(key); 161 SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES"); 162 SecretKey secretKey = keyFactory.generateSecret(dks); 163 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/CBC/NoPadding"); 164 cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey, iv, sr); 165 byte[] tgtBytes = cipher.doFinal(content); 166 return tgtBytes; 167 }
(2)3DES
概述:
3DES(或称为Triple DES)是三重数据加密算法(TDEA,Triple Data Encryption Algorithm)块密码的通称。它相当于是对每个数据块应用三次DES加密算法。由于计算机运算能力的增强,原版DES密码的密钥长度变得容易被暴力破解;3DES即是设计用来提供一种相对简单的方法,即通过增加DES的密钥长度来避免类似的攻击,而不是设计一种全新的块密码算法。
算法原理:
1 package cn.mars.app.txn.bjyl; 2 3 import java.security.Key; 4 import java.security.Security; 5 6 import javax.crypto.Cipher; 7 import javax.crypto.SecretKeyFactory; 8 import javax.crypto.spec.DESedeKeySpec; 9 10 /** 11 * 3DES加密 12 * 13 * @version 1.0 14 * @author 15 * 16 */ 17 public class DesUtil { 18 19 /** 20 * 密钥算法 21 */ 22 public static final String KEY_ALGORITHM = "DESede"; 23 public static final String CIPHER_ALGORITHM = "DESede/ECB/PKCS5Padding"; 24 private static String strDefaultKey = "national"; 25 private Cipher encryptCipher = null; 26 private Cipher decryptCipher = null; 27 28 public DesUtil() throws Exception { 29 this(strDefaultKey); 30 } 31 32 public static String byteArr2HexStr(byte[] arrB) throws Exception { 33 int iLen = arrB.length; 34 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(iLen * 2); 35 for (int i = 0; i < iLen; i++) { 36 int intTmp = arrB[i]; 37 while (intTmp < 0) { 38 intTmp = intTmp + 256; 39 } 40 if (intTmp < 16) { 41 sb.append("0"); 42 } 43 sb.append(Integer.toString(intTmp, 16)); 44 } 45 return sb.toString(); 46 } 47 48 public static byte[] hexStr2ByteArr(String strIn) throws Exception { 49 byte[] arrB = strIn.getBytes(); 50 int iLen = arrB.length; 51 byte[] arrOut = new byte[iLen / 2]; 52 for (int i = 0; i < iLen; i = i + 2) { 53 String strTmp = new String(arrB, i, 2); 54 arrOut[i / 2] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(strTmp, 16); 55 } 56 return arrOut; 57 } 58 /** 59 * @param strKey 60 * @throws Exception 61 */ 62 public DesUtil(String strKey) throws Exception { 63 Security.addProvider(new com.sun.crypto.provider.SunJCE()); 64 Key key = getKey(StringUtil.hexStringToByteArray(strKey)); 65 encryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/ECB/NoPadding"); 66 encryptCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key); 67 decryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/ECB/NoPadding"); 68 decryptCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key); 69 } 70 71 public byte[] encrypt(byte[] arrB) throws Exception { 72 return encryptCipher.doFinal(arrB); 73 } 74 75 public String encrypt(String strIn) throws Exception { 76 return byteArr2HexStr(encrypt(strIn.getBytes())); 77 } 78 79 public byte[] decrypt(byte[] arrB) throws Exception { 80 return decryptCipher.doFinal(arrB); 81 } 82 83 public String decrypt(String strIn) throws Exception { 84 return new String(decrypt(hexStr2ByteArr(strIn))); 85 } 86 87 private Key getKey(byte[] arrBTmp) throws Exception { 88 byte[] arrB = new byte[8]; 89 for (int i = 0; i < arrBTmp.length && i < arrB.length; i++) { 90 arrB[i] = arrBTmp[i]; 91 } 92 Key key = new javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec(arrB, "DES"); 93 return key; 94 } 95 96 public static String printbytes(String tip, byte[] b) { 97 String ret = ""; 98 String str; 99 System.out.println(tip); 100 for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) { 101 str = Integer.toHexString((int) (b[i] & 0xff)); 102 if (str.length() == 1) 103 str = "0" + str; 104 System.out.print(str + " "); 105 ret = ret + str + " "; 106 } 107 return ret; 108 } 109 /** 110 * 加密 111 * @param data 112 * @param key 113 * @return 114 * @throws Exception 115 * @author yangxing 116 * 2014-7-22 117 */ 118 public static byte[] encrypt(byte[] data, byte[] key)