mysql 递归函数with recursive的用法
Posted cyan_orange
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mysql 递归函数with recursive的用法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
AS 用法:
AS在mysql用来给列/表起别名.
有时,列的名称是一些表达式,使查询的输出很难理解。要给列一个描述性名称,可以使用列别名。
要给列添加别名,可以使用AS关键词后跟别名
例子1:
SELECT
[column_1 | expression] AS col_name
FROM table_name;
如果别名包含空格,则必须引用以下内容:
例子2:
SELECT
[column_1 | expression] AS 'col name'
FROM table_name;
with(Common Table Expressions/CTE)用法:
with在mysql中被称为公共表达式,可以作为一个临时表然后在其他结构中调用.如果是自身调用那么就是后面讲的递归.
语法:
with_clause:
WITH [RECURSIVE]
cte_name [(col_name [, col_name] ...)] AS (subquery)
[, cte_name [(col_name [, col_name] ...)] AS (subquery)] ...
cte_name :公共表达式的名称,可以理解为表名,用来表示as后面跟着的子查询
col_name :公共表达式包含的列名,可以写也可以不写
例子1:
WITH
cte1 AS (SELECT a, b FROM table1),
cte2 AS (SELECT c, d FROM table2)
SELECT b, d FROM cte1 JOIN cte2
WHERE cte1.a = cte2.c;
例子2:
WITH cte (col1, col2) AS
(
SELECT 1, 2
UNION ALL
SELECT 3, 4
)
SELECT col1, col2 FROM cte;
例子3:
这里的第一个as后面接的是子查询,第二个as表示列名,而不是子查询.
WITH cte AS
(
SELECT 1 AS col1, 2 AS col2
UNION ALL
SELECT 3, 4
)
SELECT col1, col2 FROM cte;
with的合法用法:
- 在子查询(包括派生的表子查询)的开始处
SELECT ... WHERE id IN (WITH ... SELECT ...) ...
SELECT * FROM (WITH ... SELECT ...) AS dt ...
- 同一级别只允许一个WITH子句。同一级别的WITH后面跟着WITH是不允许的,下面是非法用法:
WITH cte1 AS (...) WITH cte2 AS (...) SELECT ...
改为合法用法:
WITH cte1 AS (SELECT 1)
SELECT * FROM (WITH cte2 AS (SELECT 2) SELECT * FROM cte2 JOIN cte1) AS dt;
在这里面as代表列名,sql不是顺序执行的,这一点了解的话就很好理解这个as了
简单递归用法:
首先我们引出一个问题: 什么叫做递归?
递归:给定函数初始条件,然后反复调用自身直到终止条件.
例子1:递归得到依次递增的序列:
WITH RECURSIVE cte (n) AS
(
SELECT 1
UNION ALL
SELECT n + 1 FROM cte WHERE n < 5
)
SELECT * FROM cte;
运行结果:
+------+
| n |
+------+
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
+------+
官方文档中对于这个写法的解释:
At each iteration, that SELECT produces a row with a new value one greater than the value of n from the previous row set. The first iteration operates on the initial row set (1) and produces 1+1=2; the second iteration operates on the first iteration’s row set (2) and produces 2+1=3; and so forth. This continues until recursion ends, which occurs when n is no longer less than 5.
用python实现就是:
def cte(n):
print(n)
if n<5:
cte(n+1)
也就是说,一个with recursive 由两部分组成.第一部分是非递归部分(union all上方),第二部分是递归部分(union all下方).递归部分第一次进入的时候使用非递归部分传递过来的参数,也就是第一行的数据值,进而得到第二行数据值.然后根据第二行数据值得到第三行数据值.
例子2:递归得到不断复制的字符串
这里的as表示列名,表示说这个CTE有两个列,也可以写为with cte(n,str) as (subquery)
WITH RECURSIVE cte AS
(
SELECT 1 AS n, 'abc' AS str
UNION ALL
SELECT n + 1, CONCAT(str, str) FROM cte WHERE n < 3
)
SELECT * FROM cte;
结果:
+------+------+
| n | str |
+------+------+
| 1 | abc |
| 2 | abc |
| 3 | abc |
+------+------+
这里的话concat是每一次都连接一个str,这个str来自上一行的结果,但是最终输出却是每一行都没有变化的值,这是为什么?
这是因为我们在声明str的时候限制了它的字符长度,使用 类型转换CAST(‘abc’ AS CHAR(30)) 就可以得到复制的字符串了.
**注意:**这里也可能会报错,看mysql模式.在严格模式下这里会显示Error Code: 1406. Data too long for column 'str' at row 1
关于strict SQL mode和nonstrict SQL mode:mysql 严格模式 Strict Mode说明
WITH RECURSIVE cte AS
(
SELECT 1 AS n, CAST('abc' AS CHAR(20)) AS str
UNION ALL
SELECT n + 1, CONCAT(str, str) FROM cte WHERE n < 3
)
SELECT * FROM cte;
+------+--------------+
| n | str |
+------+--------------+
| 1 | abc |
| 2 | abcabc |
| 3 | abcabcabcabc |
+------+--------------+
当然,如果上一行的值有多个,我们还可以对多个值进行重新组合得到我们想要的结果,比如下面这个例子.
例子3:生成斐波那契数列
WITH RECURSIVE fibonacci (n, fib_n, next_fib_n) AS
(
SELECT 1, 0, 1
UNION ALL
SELECT n + 1, next_fib_n, fib_n + next_fib_n
FROM fibonacci WHERE n < 10
)
SELECT * FROM fibonacci;
结果:
+------+-------+------------+
| n | fib_n | next_fib_n |
+------+-------+------------+
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 3 |
| 5 | 3 | 5 |
| 6 | 5 | 8 |
| 7 | 8 | 13 |
| 8 | 13 | 21 |
| 9 | 21 | 34 |
| 10 | 34 | 55 |
+------+-------+------------+
语法说明:
UNION ALL与UNION DISTINCT
- UNION ALL:
非递归部分和递归部分用UNION ALL分隔,那么所有的行都会被加入到最后的表中 - UNION DISTINCT:
非递归部分和递归部分用UNION DISTINCT分隔,重复的行被消除。这对于执行传递闭包的查询非常有用,以避免无限循环。
limit控制递归次数
recursive(第二个select)不能使用的结构:
官网的描述:
-
The recursive SELECT part must not contain these constructs:
Aggregate functions such as SUM() Window functions GROUP BY ORDER BY DISTINCT
限制递归次数/时间:
当出现不符合设置情况的会报错,分为以下几种设置方法:
- cte_max_recursion_depth :default 设置为1000,表达递归的层数.可以使用如下语句修改这个值:
SET SESSION cte_max_recursion_depth = 10; -- permit only shallow recursion
SET SESSION cte_max_recursion_depth = 1000000; -- permit deeper recursion
当然也可以设置为global,也就是set global cte_max_recursion_depth = 1000000;这样子就对全局的递归都有限制
- max_execution_time :设置最近的递归时间
SET max_execution_time = 1000; -- impose one second timeout
- MAX_EXECUTION_TIME:设置全局的递归时间
官网文档说明如下:
-
The cte_max_recursion_depth system variable enforces a limit on the
number of recursion levels for CTEs. The server terminates execution
of any CTE that recurses more levels than the value of this variable. -
The max_execution_time system variable enforces an execution timeout
for SELECT statements executed within the current session. -
The MAX_EXECUTION_TIME optimizer hint enforces a per-query execution
timeout for the SELECT statement in which it appears. -
limit:限之最大行的数量
WITH RECURSIVE cte (n) AS
(
SELECT 1
UNION ALL
SELECT n + 1 FROM cte LIMIT 10000
)
SELECT * FROM cte;
mysql with recursive 递归用法
with recursive 是一个递归的查询子句,他会把查询出来的结果再次代入到查询子句中继续查询。
语法:
WITH RECURSIVE cte_name AS (
初始语句(非递归部分)
UNION ALL
递归部分语句
)
[ SELECT| INSERT | UPDATE | DELETE]
例子1:
WITH RECURSIVE cte (n) AS
(
SELECT 1
UNION ALL
SELECT n + 1 FROM cte WHERE n < 5
)
SELECT * FROM cte;

该语句书写包括如下几步
- 设定递归语法,首先初始执行第一句
SELECT 1,也可以写成select xxx from xxx where xxx - 其结果给到n,当n值发生改变,就会执行:
SELECT n + 1 FROM cte WHERE n < 5 - 最终结果给到n输出
注意:WITH AS () 后面必须跟着 [ SELECT| INSERT | UPDATE | DELETE] 语句,否则报错。
例子2:
有如下行政区划表
create table administrative_division2
(
administrative_division_sn bigint not null comment '行政区划代码'
primary key,
parent_administrative_division_sn bigint null comment '上级行政区划代码',
status tinyint default 1 not null comment '状态',
name varchar(28) not null comment '名称*',
full_name varchar(200) null comment '行政区划全路径名称,省市县全路径名称'
)
comment '行政区划';
INSERT INTO administrative_division2 (administrative_division_sn, parent_administrative_division_sn, status, name, full_name) VALUES (110000, null, 1, '北京市', '');
INSERT INTO administrative_division2 (administrative_division_sn, parent_administrative_division_sn, status, name, full_name) VALUES (110100, 110000, 1, '北京市市辖区', '');
INSERT INTO administrative_division2 (administrative_division_sn, parent_administrative_division_sn, status, name, full_name) VALUES (110101, 110100, 1, '东城区', '');
INSERT INTO administrative_division2 (administrative_division_sn, parent_administrative_division_sn, status, name, full_name) VALUES (110102, 110100, 1, '西城区', '');
INSERT INTO administrative_division2 (administrative_division_sn, parent_administrative_division_sn, status, name, full_name) VALUES (110105, 110100, 1, '朝阳区', '');

我们想补充full_name的值变成如下
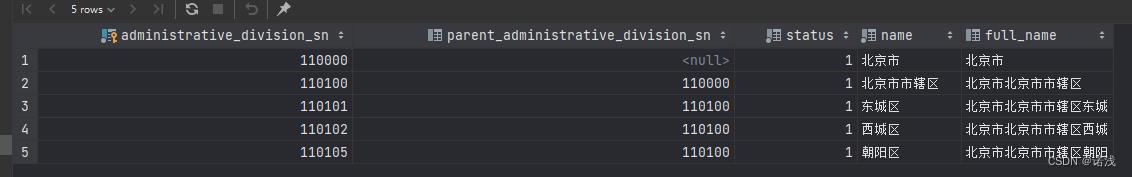
那么可以用如下语句
update administrative_division2 ad,(
with recursive res as (select administrative_division_sn sn, parent_administrative_division_sn pSn, name
from administrative_division2 ad
where parent_administrative_division_sn is null
union
select ad2.administrative_division_sn as sn,
ad2.parent_administrative_division_sn pSn,
concat(res.name, ad2.name) as name
from res
inner join administrative_division2 ad2
on res.sn = ad2.parent_administrative_division_sn)
select * from res
) as t1 set ad.full_name=t1.name where ad.administrative_division_sn=t1.sn;
该语句执行解析如下
- 先设定开始的条件为父ID为空,即所有的父节点
select administrative_division_sn sn, parent_administrative_division_sn pSn, name from administrative_division2 ad where parent_administrative_division_sn is null
- 设置循环的条件为等于这个父节点的子节点
select ad2.administrative_division_sn as sn, ad2.parent_administrative_division_sn pSn, concat(res.name, ad2.name) as name from res inner join administrative_division2 ad2 on res.sn = ad2.parent_administrative_division_sn
- 执行完2此时的res.sn就等于子sn了,然后递归执行2
- 最终执行
set ad.full_name=t1.name where ad.administrative_division_sn=t1.sn把名称赋值为2中的拼接了的名称concat(res.name, ad2.name)
以上是关于mysql 递归函数with recursive的用法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章