牛客刷题--SQL篇SQL9查找除复旦大学的用户信息&&SQL10用where过滤空值练习
Posted 与自己作战
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了牛客刷题--SQL篇SQL9查找除复旦大学的用户信息&&SQL10用where过滤空值练习相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
💖个人主页:@与自己作战
💯作者简介:大数据领域优质创作者、CSDN@内容合伙人、阿里云专家博主
💞牛客刷题系列篇:【SQL篇】】【Python篇】【Java篇】
📌推荐刷题网站注册地址:【牛客网–SQL篇】
💘推荐理由:从0-1起步,循序渐进
🆘希望大佬们多多支持,携手共进
📝 如果文章对你有帮助的话,欢迎评论💬点赞👍收藏📂加关注
⛔如需要支持请私信我,💯必支持
👩👩👦👦网址注册地址:【牛客网–注册地址】👩👩👦👦
文章目录
一、条件查询
1、基础操作符
1.1 SQL9 查找除复旦大学的用户信息
- 描述
题目:现在运营想要查看除复旦大学以外的所有用户明细,请你取出相应数据
- 示例1
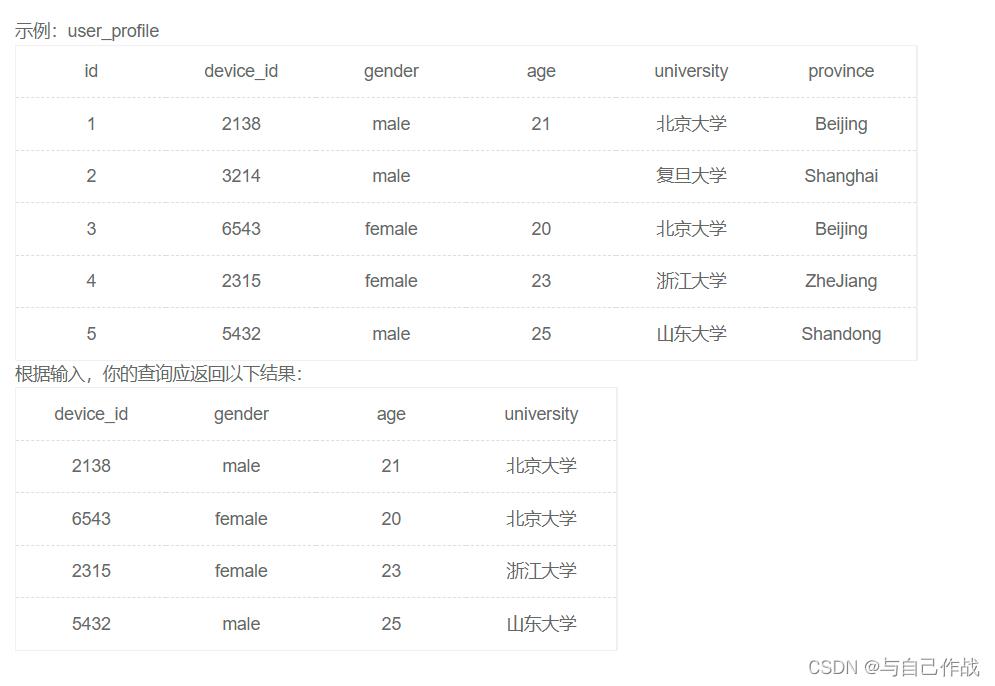
输入:
drop table if exists user_profile;
CREATE TABLEuser_profile(
idint NOT NULL,
device_idint NOT NULL,
gendervarchar(14) NOT NULL,
ageint ,
universityvarchar(32) NOT NULL,
provincevarchar(32) NOT NULL);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(1,2138,‘male’,21,‘北京大学’,‘BeiJing’);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(2,3214,‘male’,null,‘复旦大学’,‘Shanghai’);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(3,6543,‘female’,20,‘北京大学’,‘BeiJing’);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(4,2315,‘female’,23,‘浙江大学’,‘ZheJiang’);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(5,5432,‘male’,25,‘山东大学’,‘Shandong’);
输出:
2138|male|21|北京大学
6543|female|20|北京大学
2315|female|23|浙江大学
5432|male|25|山东大学
输入:
drop table if exists user_profile;
CREATE TABLE `user_profile` (
`id` int NOT NULL,
`device_id` int NOT NULL,
`gender` varchar(14) NOT NULL,
`age` int ,
`university` varchar(32) NOT NULL,
`province` varchar(32) NOT NULL);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(1,2138,'male',21,'北京大学','BeiJing');
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(2,3214,'male',null,'复旦大学','Shanghai');
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(3,6543,'female',20,'北京大学','BeiJing');
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(4,2315,'female',23,'浙江大学','ZheJiang');
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(5,5432,'male',25,'山东大学','Shandong');
输出:
2138|male|21|北京大学
6543|female|20|北京大学
2315|female|23|浙江大学
5432|male|25|山东大学
1.1.1 SQL语句 第一种方法(执行效率略高)
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
university
from
user_profile
where
university != ‘复旦大学’
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
university
from
user_profile
where
university != '复旦大学'
1.1.2 SQL语句 第二种方法(执行效率略低)
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
university
from
user_profile
where
university <> ‘复旦大学’
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
university
from
user_profile
where
university <> '复旦大学'
1.2 SQL10 用where过滤空值练习
- 描述
题目:现在运营想要对用户的年龄分布开展分析,在分析时想要剔除没有获取到年龄的用户,请你取出所有年龄值不为空的用户的设备ID,性别,年龄,学校的信息。
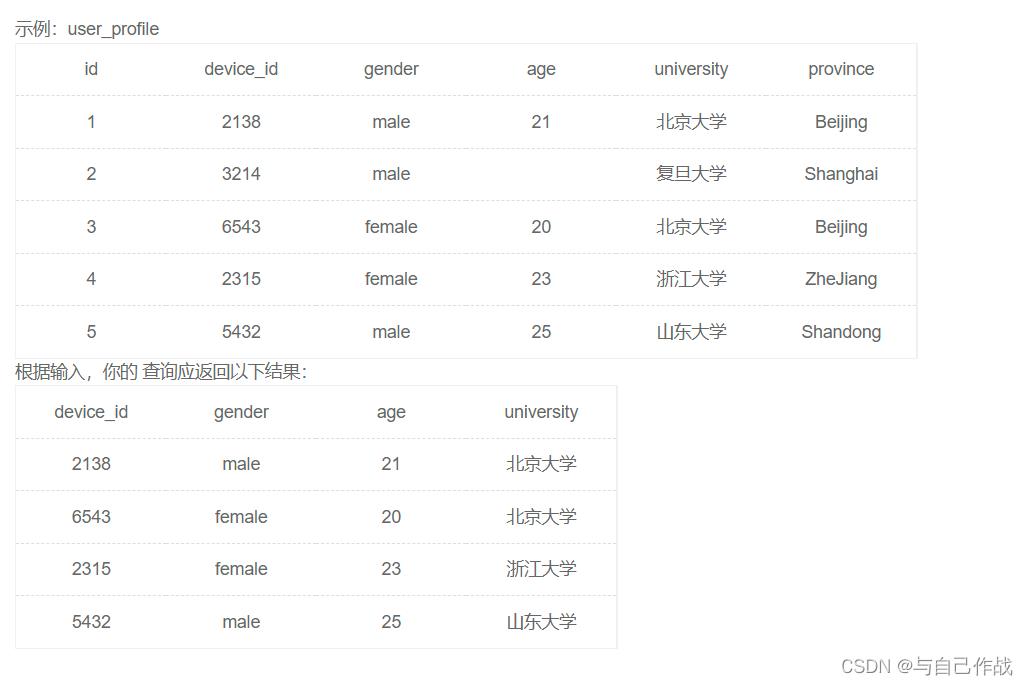
- 示例1
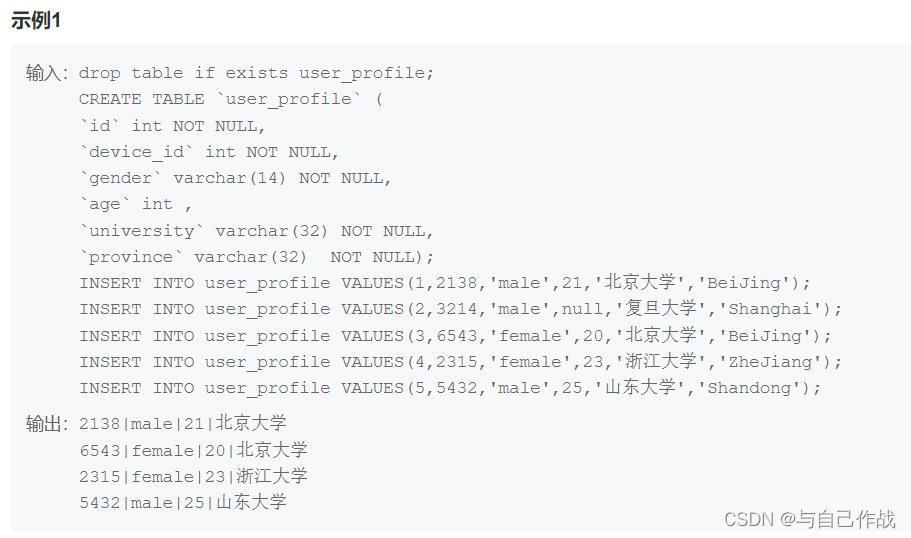
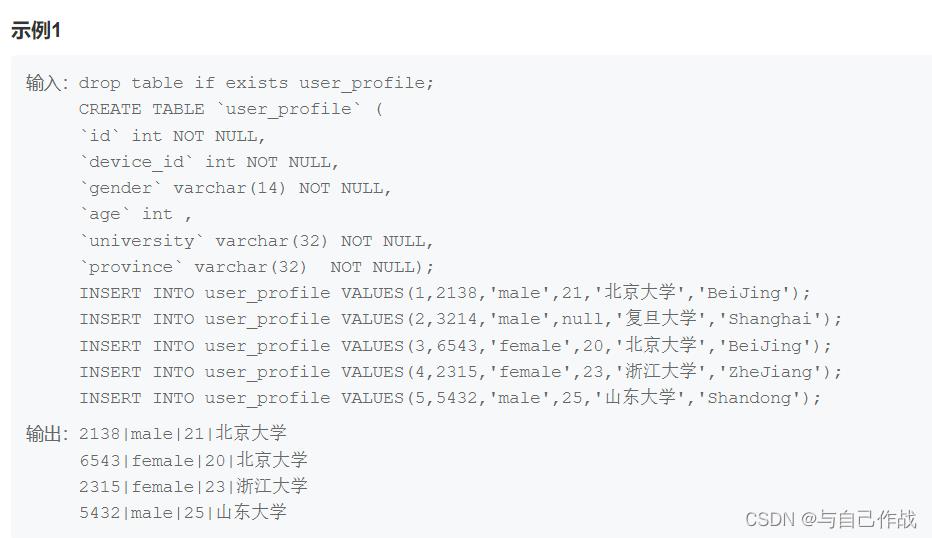
输入:
drop table if exists user_profile;
CREATE TABLEuser_profile(
idint NOT NULL,
device_idint NOT NULL,
gendervarchar(14) NOT NULL,
ageint ,
universityvarchar(32) NOT NULL,
provincevarchar(32) NOT NULL);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(1,2138,‘male’,21,‘北京大学’,‘BeiJing’);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(2,3214,‘male’,null,‘复旦大学’,‘Shanghai’);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(3,6543,‘female’,20,‘北京大学’,‘BeiJing’);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(4,2315,‘female’,23,‘浙江大学’,‘ZheJiang’);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(5,5432,‘male’,25,‘山东大学’,‘Shandong’);
输出:
2138|male|21|北京大学
6543|female|20|北京大学
2315|female|23|浙江大学
5432|male|25|山东大学
输入:
drop table if exists user_profile;
CREATE TABLE `user_profile` (
`id` int NOT NULL,
`device_id` int NOT NULL,
`gender` varchar(14) NOT NULL,
`age` int ,
`university` varchar(32) NOT NULL,
`province` varchar(32) NOT NULL);
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(1,2138,'male',21,'北京大学','BeiJing');
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(2,3214,'male',null,'复旦大学','Shanghai');
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(3,6543,'female',20,'北京大学','BeiJing');
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(4,2315,'female',23,'浙江大学','ZheJiang');
INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(5,5432,'male',25,'山东大学','Shandong');
输出:
2138|male|21|北京大学
6543|female|20|北京大学
2315|female|23|浙江大学
5432|male|25|山东大学
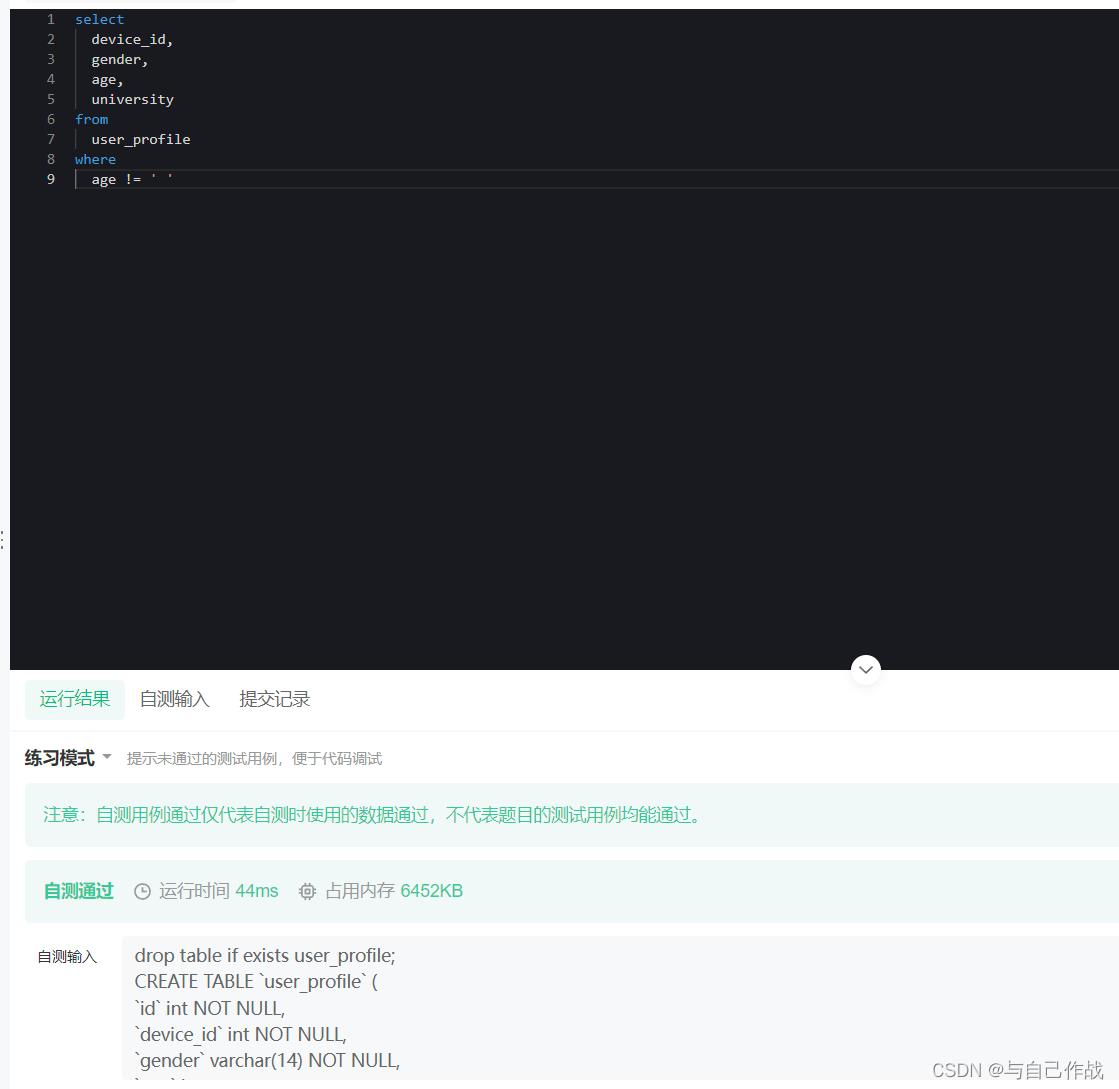
1.2.1 SQL语句 第一种方法(执行效率略低)
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
university
from
user_profile
where
age != ’ ’
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
university
from
user_profile
where
age != ' '
1.2.2 SQL语句 第二种方法(执行效率略高)
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
university
from
user_profile
where
age <> ’ ’
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
university
from
user_profile
where
age <> ' '
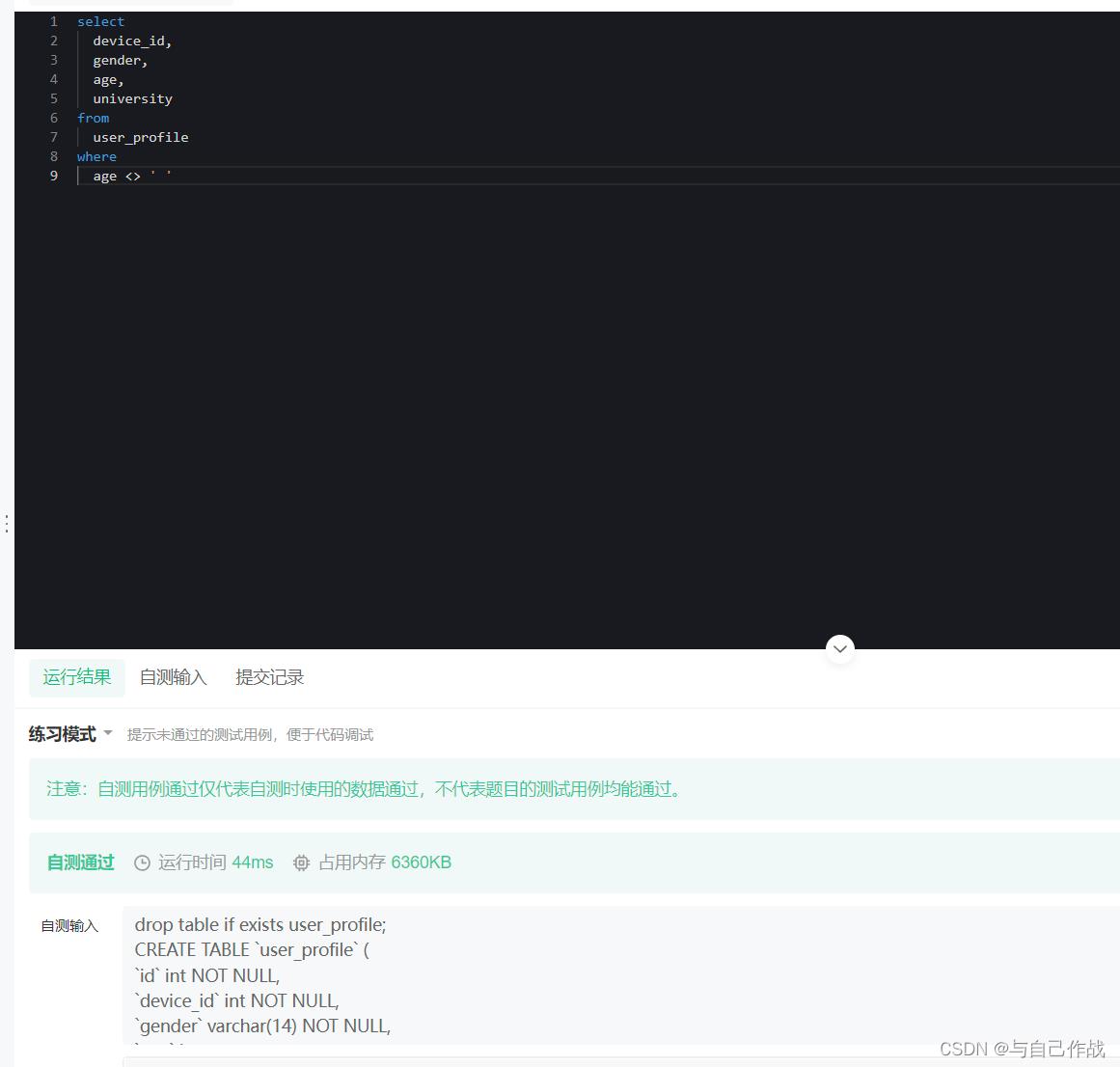
1.2.3 SQL语句 第三种方法(执行效率一般,普遍写法)
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
university
from
user_profile
where
age is not null
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
university
from
user_profile
where
age is not null
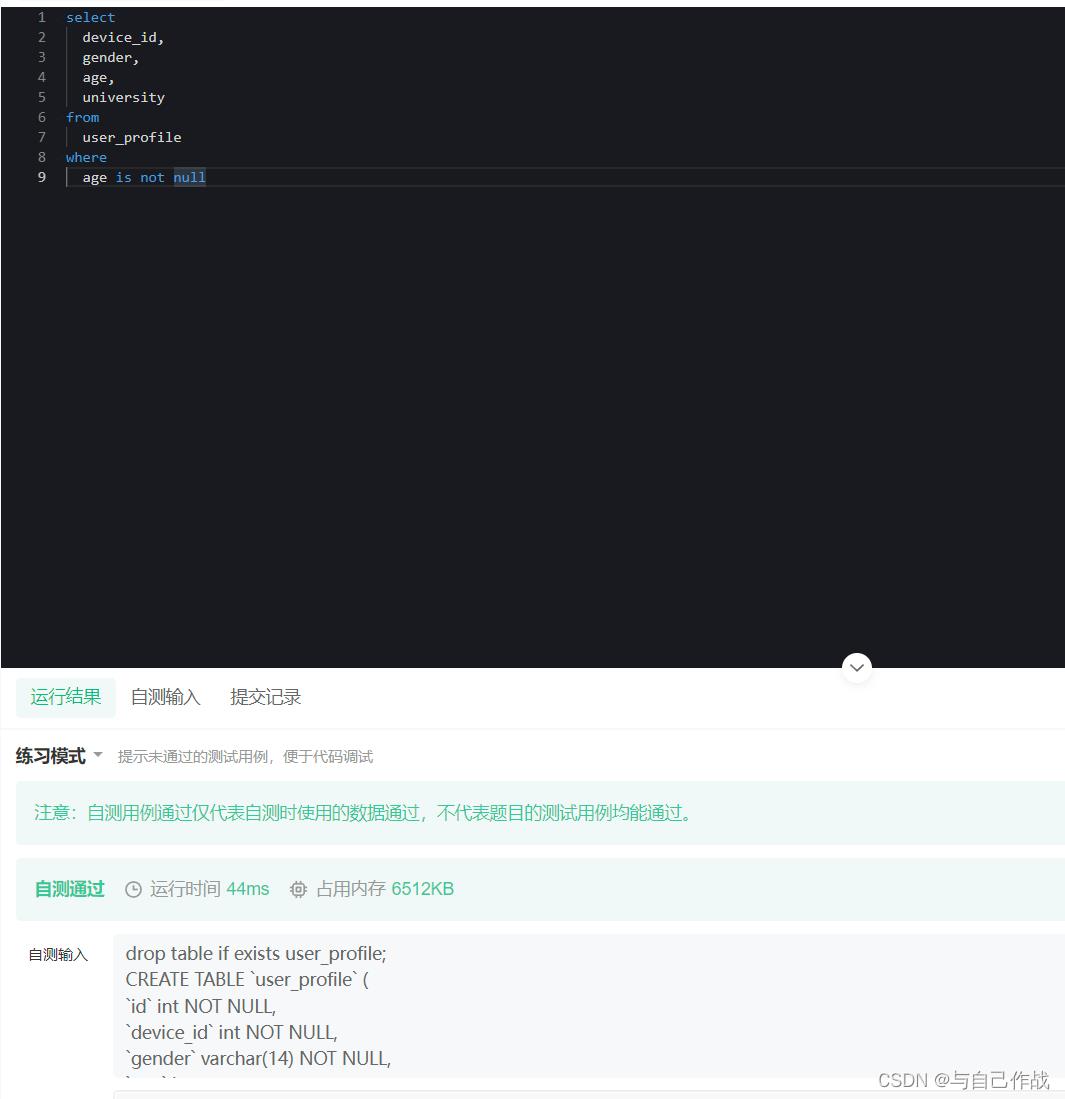
推荐刷题网站:【牛客网–SQL篇】
网址注册地址:【牛客网–注册地址】
入门sql语句-牛客刷题
基础查询
- 查询表所有列:
select * from user_profile;
- 查询表指定列数据:
select age from user_profile;
- 查询指定列并去重:
select
DISTINCT university
from
user_profile;
select university
from user_profile
group by university;
- 查询年龄数据并修改命名、输出前2条数据;
select age as new_age
from user_profile
limit 2;
条件查询
- 查询后排序
升序:
select device_id,age
from user_profile
order by age;
降序:
select device_id,age
from user_profile
order by age desc;
查询后多列升序排序:
select device_id,gpa,age
from user_profile
order by gpa,age;
查询后多列降序排序;
select device_id,gpa,age
from user_profile
order by gpa desc,age desc;
- 查询除了某大学的用户信息,过滤空值
select
device_id, university
from
user_profile
where
university != '复旦大学';
# not like '复旦大学';
# not in ('复旦大学');
- 高级操作符混合
and,or
select
device_id,gender,age,university,gpa
from
user_profile
where
gpa>3.5 and university ='山东大学'
or
gpa>3.8 and university='复旦大学';
- in,not in
select
device_id,gender,age,university,gpa
from
user_profile
where
university in ('复旦大学','北京大学','山东大学');
- 模糊查询
查看学校名称中含北京的用户
——这道题主要考察的是模糊查询 字段名 like ‘匹配内容’
_ : 下划线 代表匹配任意一个字符;
% :百分号 代表匹配0个或多个字符;
[]: 中括号 代表匹配其中的任意一个字符;
[^]: ^尖冒号 代表 非,取反的意思;不匹配中的任意一个字符。
select
device_id,age,university
from
user_profile
where
university like '%北京%';
tips:面试常问的一个问题:你了解哪些数据库优化技术?
SQL语句优化也属于数据库优化一部分,而like模糊查询会引起全表扫描,速度比较慢,应该尽量避免使用like关键字进行模糊查询。
select
device_id,age,university
from
user_profile
where
university regexp '北京';
LIKE 和 REGEXP之间的重要差别
LIKE 匹配整个列,如果被匹配的文本在列值中出现,LIKE 将不会找到它,相应的行也不会被返回(除非使用通配符)。
而 REGEXP 在列值内进行匹配,如果被匹配的文本在列值中出现,REGEXP 将会找到它,相应的行将被返回,并且 REGEXP 能匹配整个列值(与 LIKE> 相同的作用)
高级查询
- 查复旦大学学生gpa最大值
# 自己排序截取
select gpa
from user_profile
where university = '复旦大学'
order by gpa desc limit 1;
# 函数
select max(gpa)
from user_profile
where university = '复旦大学'
- 计算总数和平均值(四舍五入)
select
count(gender) as male_num,
round(avg(gpa),1) as avg_gpa
from user_profile
where gender='male';
select
gender, university,
count(device_id) as user_num,
round(avg(active_days_within_30),1) as avg_active_day,
round(avg(question_cnt),1) as avg_question_cnt
from user_profile
group by
gender,university;
题意:取出平均发贴数低于5的学校或平均回帖数小于20的学校(小数点后保留3位)
select
university,
round(avg(question_cnt), 3) as avg_question_cnt,
round(avg(answer_cnt), 3) as avg_answer_cnt
from
user_profile
group by
university
having # 聚合函数结果作为筛选条件时,不能用where,而是用having语法
avg(question_cnt) < 5
or avg(answer_cnt) < 20
- 分组排序
题意:不同大学的用户平均发帖情况,并按照平均发帖情况进行升序排列
select
university,
avg(question_cnt) as avg_question_cnt
from
user_profile
group by
university
order by
avg(question_cnt)
☆☆☆ 多表查询
题意:所有来自浙江大学的用户题目回答明细情况
- 子查询(嵌套查询、内部查询)
一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句内的查询。
第一种:创建一张临时表用,获取浙江大学device_id对用户题目回答明细进行过滤。
select
device_id,
question_id,
result
from
question_practice_detail
where device_id in
(
select device_id
from user_profile
where university ='浙江大学'
)
- 连接查询
第二种:先将两张表关联在一起,然后再筛选出浙江大学的明细数据
select
q.device_id,
q.question_id,
q.result
from
question_practice_detail q
left join user_profile u on q.device_id = u.device_id
where
university = '浙江大学'
- 连接查询——统计每个学校的答过题的用户的平均答题数
- 按每个学校统计——分组,group by
- 用户平均答题数计算:同一用户多次登录答题,需要对用户进行去重处理
- 两张表的连接处理
select
u.university,
count(q.question_id) / count(distinct q.device_id) as avg_answer_cnt
from
question_practice_detail as q
left join user_profile as u on q.device_id = u.device_id
group by
u.university;
- 连接查询——统计每个学校各难度的用户平均刷题数(三张表)
- 分组查询 group by
- 计算用户平均答题量 count(question_id)/count(disinct device_id)
- 表连接 三张表
select
university,
difficult_level,
count(q.question_id)/count(distinct q.device_id) as avg_answer_cnt
from user_profile u
join question_practice_detail q on q.device_id = u.device_id
join question_detail d on q.question_id = d.question_id
group by university, difficult_level
- 组合查询——查找山东大学或者性别为男生的信息
- 限定条件:学校为山东大学或者性别为男性的用户:university=‘山东大学’, gender=‘male’;
- 分别查看&结果不去重 :直接使用or不行,直接用union也不行,要用union all ,分别去查满足条件1的和满足条件2的,然后合在一起不去重
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
gpa
from
user_profile
where
university = '山东大学'
union all # 不去重查询方式,两个条件分别查找并都展示
select
device_id,
gender,
age,
gpa
from
user_profile
where
gender = 'male'
常用函数
- 条件函数
- 计算25岁及以上 和25岁以下 的用户数量
if语句使用:if(条件,条件真的值1,条件假的值2)
# if语句使用
select
if(age>=25, '25岁及以上','25岁以下') as age_cut,
count(distinct device_id) as number
from user_profile
group by age_cut
# case 语句格式
select
case
when age>=25 then '25岁及以上'
else '25岁以下'
end as age_cut,
count(distinct device_id) as number
from user_profile
group by age_cut
- 查看不同年龄段用户信息
# if语句格式
select
device_id,
gender,
if (
age >= 25, '25岁及以上', if (age >= 20 and age <= 24, '20-24岁', '其他')
) as age_cut
from
user_profile
# case 语句格式
# when... then...
# else...
# end as...
select
device_id,
gender,
case
when age>=25 then '25岁及以上'
when age>=20 and age <=24 then '20-24岁'
else '其他'
end as 'age_cut'
from user_profile
- 计算用户2021年8月每天的练题数量
# 使用日期函数
select
day (date) as ourday,
count(question_id) as question_cnt
from
question_practice_detail
where
month (date) = 8 and year (date) = 2021
group by ourday
# 使用正则表达式
select
day (date) as ourday,
count(question_id) as question_cnt
from
question_practice_detail
where
date regexp '2021-08'
group by ourday
- 计算用户的平均次日留存率
次日:涉及到前后两天,此处通过两个表来进行连接(自连接);
次日留存率:有前一天记录的日期统计量/所有记录的日期统计量
select
count(q2.device_id)/count(q1.device_id)
from
(select distinct device_id,date from question_practice_detail) as q1
left join
(select distinct device_id,date from question_practice_detail) as q2
on q2.device_id = q1.device_id and q2.date= date_add(q1.date, interval 1 day)
# 还可以用函数 datediff(q1.date,q2.date)=1
- 文本函数
substring_index(str,分隔符,序号)
序号为正数,表示从左往右 截取目标分隔符之前的字符串;1, 2, 3...
序号为负数,表示从右往左 截取目标分隔符之后的字符串;-1, 2, -3...
# 复习 if 和case 逻辑语句
# 复习 like 模糊查询
# 复习 regexp 正则匹配
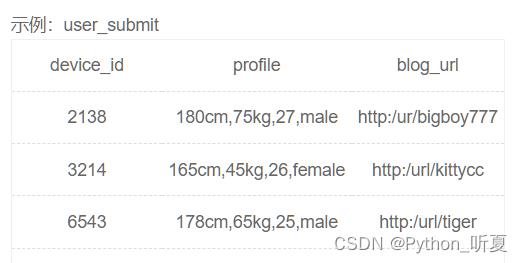
###############################################
select
if(profile regexp 'female','female','male') as 'gender',
count(device_id) as number
from user_submit
group by gender
###############################################
select
if(profile like '%female','female','male') as 'gender',
count(device_id) as number
from user_submit
group by gender
###############################################
select
case
when profile regexp 'female' then 'female'
when profile regexp 'male' then 'male'
end as 'gender',
count(device_id) as number
from user_submit
group by gender
# 新学习:字符串提取函数substring_index
select
substring_index (profile, ',', -1) as gender,
count(device_id) as number
from user_submit
group by gender
- 截取年龄
select
substring_index(substring_index(profile,',',-2),',',1) as age,
count(device_id) as number
from user_submit
group by age
- 窗口函数
row_number() over() 解析
基本功能:分组和排序功能
语法格式: row_number() over(partition by 分组列 order by 排序列)
- 找出每个学校分数最低的学生
# 方式一:通过子查询语句和连接语句
select
u2.device_id,
u1.university,
u1.gpa
from
(
select
university,
min(gpa) gpa
from
user_profile
group by
university
) as u1
left join user_profile u2 on u1.university = u2.university
and u1.gpa = u2.gpa
order by
u1.university
# 方式二:通过窗口函数
select
device_id,
university,
gpa
from (
select
device_id,
university,
gpa,
row_number() over(
partition by university order by gpa
) as rank
from user_profile
) as u_rk
where u_rk.rank =1
综合练习
select
q2.difficult_level,
sum(if (q1.result = 'right', 1, 0)) / count(result) as correct_rate # 主要看这一步统计方式
from question_practice_detail q1
left join user_profile u on q1.device_id=u.device_id # 注意此处连接的顺序
left join question_detail q2 on q2.question_id = q1.question_id
where
university = '浙江大学'
group by
difficult_level
order by
correct_rate
以上是关于牛客刷题--SQL篇SQL9查找除复旦大学的用户信息&&SQL10用where过滤空值练习的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章