双向循环链表list_head WRITE_ONCE READ_ONCE 函数的分析与使用
Posted papaofdoudou
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了双向循环链表list_head WRITE_ONCE READ_ONCE 函数的分析与使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在Linux内核中,为了提供统一的链表操作,减少结构体的额外开支,内核提供了 list.h 文件,在源码中的路径为 include/linux/list.h。
list.h内嵌到不同的object中,配合container_of宏,为各种类型的object提供了"变身"的能力,程序中可以非常方便的根据list地址,将list_head对象强制cast为包含其的目标对象,过程有点类似于C++中的父类到子类的强制转化,这种转换当然是有前提的,对于CPP来说,由于转换后内存或扩张,你的对象得真的是一个子类对象才能保证转换的安全性,同样道理list_head也需要保证被转换的list真的在目标对象之中才可以.
READ_ONCE/WRITE_ONCE:
从linux 4.4版本开始,list的实现变得复杂了一些,主要是WRITE_ONCE/READ_ONCE的引入,将平凡的读取和写入操作变得麻烦了不少.
下载LINUX源码仓库,发现主要相关的提交有三个:1658d35ead5d8,1c97be677f72b,和d679ae94fdd5d.



上面的代码是初始化一个双向循环链表 ,将list中的两个指针 next 和 prev 都指向 自己,也就是 list , 那为什么不直接赋值呢?查以前版本的内核代码,发现 linux4.4 以下的版本都是直接赋值的,linux4.5以上的版本都进行了优化。

那我们进行思考以下两个问题:
1、内核出于什么原因进行优化呢? 它和直接赋值有什么区别?
2、我们什么时候要使用 WRITE_ONCE/READ_ONCE?
先看看它的定义:
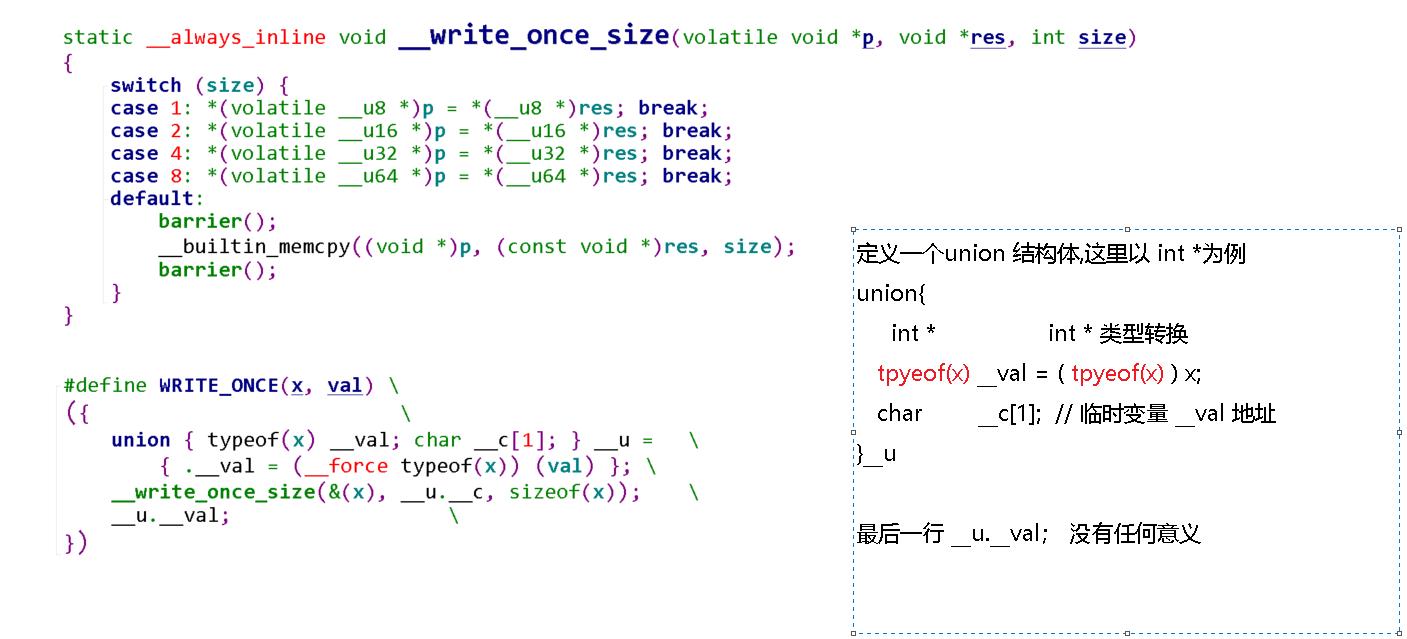
为什么要用READ_ONCE()和WRITE_ONCE()这两个宏呢? 这里起到关键作用的就是 volatile ,它主要告诉编译器:
1、声明这个变量很重要,不要把它当成一个普通的变量,做出错误的优化。
2、保证 CPU 每次都从内存重新读取变量的值,而不是用寄存器中暂存的值。
因为在 多线程/多核 环境中,不会被当前线程修改的变量,可能会被其他的线程修改,从内存读才可靠。
还有一部分原因是,这两个宏可以作为标记,提醒编程人员这里面是一个多核/多线程共享的变量,必要的时候应该加互斥锁来保护。在多核多线程编程时,要注意共享变量的使用,要保证是 volatile的.
/* SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0 */
#ifndef _BR_LIST_H
#define _BR_LIST_H
#define br_barrier() __asm__ __volatile__("": : :"memory")
#define br_smp_read_barrier_depends() do while (0)
#define BR_LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x100)
#define BR_LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x200)
#define br_container_of(ptr, type, member) ( \\
const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \\
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );)
#define __BR_READ_ONCE_SIZE \\
( \\
switch (size) \\
case 1: *(__u8 *)res = *(volatile __u8 *)p; break; \\
case 2: *(__u16 *)res = *(volatile __u16 *)p; break; \\
case 4: *(__u32 *)res = *(volatile __u32 *)p; break; \\
case 8: *(__u64 *)res = *(volatile __u64 *)p; break; \\
default: \\
br_barrier(); \\
__builtin_memcpy((void *)res, (const void *)p, size); \\
br_barrier(); \\
\\
)
static __always_inline
void __br_read_once_size(const volatile void *p, void *res, int size)
__BR_READ_ONCE_SIZE;
static __no_kasan_or_inline
void __br_read_once_size_nocheck(const volatile void *p, void *res, int size)
__BR_READ_ONCE_SIZE;
static __always_inline void __br_write_once_size(volatile void *p, void *res, int size)
switch (size)
case 1: *(volatile __u8 *)p = *(__u8 *)res; break;
case 2: *(volatile __u16 *)p = *(__u16 *)res; break;
case 4: *(volatile __u32 *)p = *(__u32 *)res; break;
case 8: *(volatile __u64 *)p = *(__u64 *)res; break;
default:
br_barrier();
__builtin_memcpy((void *)p, (const void *)res, size);
br_barrier();
#define __BR_READ_ONCE(x, check) \\
( \\
union typeof(x) __val; char __c[1]; __u; \\
if (check) \\
__br_read_once_size(&(x), __u.__c, sizeof(x)); \\
else \\
__br_read_once_size_nocheck(&(x), __u.__c, sizeof(x)); \\
br_smp_read_barrier_depends(); /* Enforce dependency ordering from x */ \\
__u.__val; \\
)
#define BR_READ_ONCE(x) __BR_READ_ONCE(x, 1)
#define BR_WRITE_ONCE(x, val) \\
( \\
union typeof(x) __val; char __c[1]; __u = \\
.__val = (__force typeof(x)) (val) ; \\
__br_write_once_size(&(x), __u.__c, sizeof(x)); \\
__u.__val; \\
)
struct br_list_head
struct br_list_head *next, *prev;
;
struct br_hlist_head
struct br_hlist_node *first;
;
struct br_hlist_node
struct br_hlist_node *next, **pprev;
;
/*
* Simple doubly linked list implementation.
*
* Some of the internal functions ("__xxx") are useful when
* manipulating whole lists rather than single entries, as
* sometimes we already know the next/prev entries and we can
* generate better code by using them directly rather than
* using the generic single-entry routines.
*/
#define BR_LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) &(name), &(name)
#define BR_LIST_HEAD(name) \\
struct br_list_head name = BR_LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
static inline void BR_INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct br_list_head *list)
BR_WRITE_ONCE(list->next, list);
list->prev = list;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LIST
extern bool __br_list_add_valid(struct br_list_head *new,
struct br_list_head *prev,
struct br_list_head *next);
extern bool __br_list_del_entry_valid(struct br_list_head *entry);
#else
static inline bool __br_list_add_valid(struct br_list_head *new,
struct br_list_head *prev,
struct br_list_head *next)
return true;
static inline bool __br_list_del_entry_valid(struct br_list_head *entry)
return true;
#endif
/*
* Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __br_list_add(struct br_list_head *new,
struct br_list_head *prev,
struct br_list_head *next)
if (!__br_list_add_valid(new, prev, next))
return;
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
BR_WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, new);
/**
* br_list_add - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it after
*
* Insert a new entry after the specified head.
* This is good for implementing stacks.
*/
static inline void br_list_add(struct br_list_head *new, struct br_list_head *head)
__br_list_add(new, head, head->next);
/**
* br_list_add_tail - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it before
*
* Insert a new entry before the specified head.
* This is useful for implementing queues.
*/
static inline void br_list_add_tail(struct br_list_head *new, struct br_list_head *head)
__br_list_add(new, head->prev, head);
/*
* Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries
* point to each other.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __br_list_del(struct br_list_head * prev, struct br_list_head * next)
next->prev = prev;
BR_WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, next);
/*
* Delete a list entry and clear the 'prev' pointer.
*
* This is a special-purpose list clearing method used in the networking code
* for lists allocated as per-cpu, where we don't want to incur the extra
* BR_WRITE_ONCE() overhead of a regular br_list_del_init(). The code that uses this
* needs to check the node 'prev' pointer instead of calling br_list_empty().
*/
static inline void __br_list_del_clearprev(struct br_list_head *entry)
__br_list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->prev = NULL;
/**
* br_list_del - deletes entry from list.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
* Note: br_list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is
* in an undefined state.
*/
static inline void __br_list_del_entry(struct br_list_head *entry)
if (!__br_list_del_entry_valid(entry))
return;
__br_list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
static inline void br_list_del(struct br_list_head *entry)
__br_list_del_entry(entry);
entry->next = BR_LIST_POISON1;
entry->prev = BR_LIST_POISON2;
/**
* br_list_replace - replace old entry by new one
* @old : the element to be replaced
* @new : the new element to insert
*
* If @old was empty, it will be overwritten.
*/
static inline void br_list_replace(struct br_list_head *old,
struct br_list_head *new)
new->next = old->next;
new->next->prev = new;
new->prev = old->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
static inline void br_list_replace_init(struct br_list_head *old,
struct br_list_head *new)
br_list_replace(old, new);
BR_INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
/**
* br_list_swap - replace entry1 with entry2 and re-add entry1 at entry2's position
* @entry1: the location to place entry2
* @entry2: the location to place entry1
*/
static inline void br_list_swap(struct br_list_head *entry1,
struct br_list_head *entry2)
struct br_list_head *pos = entry2->prev;
br_list_del(entry2);
br_list_replace(entry1, entry2);
if (pos == entry1)
pos = entry2;
br_list_add(entry1, pos);
/**
* br_list_del_init - deletes entry from list and reinitialize it.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
*/
static inline void br_list_del_init(struct br_list_head *entry)
__br_list_del_entry(entry);
BR_INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
/**
* br_list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will precede our entry
*/
static inline void br_list_move(struct br_list_head *list, struct br_list_head *head)
__br_list_del_entry(list);
br_list_add(list, head);
/**
* br_list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail
* @list: the entry to move
* @head: the head that will follow our entry
*/
static inline void br_list_move_tail(struct br_list_head *list,
struct br_list_head *head)
__br_list_del_entry(list);
br_list_add_tail(list, head);
/**
* br_list_bulk_move_tail - move a subsection of a list to its tail
* @head: the head that will follow our entry
* @first: first entry to move
* @last: last entry to move, can be the same as first
*
* Move all entries between @first and including @last before @head.
* All three entries must belong to the same linked list.
*/
static inline void br_list_bulk_move_tail(struct br_list_head *head,
struct br_list_head *first,
struct br_list_head *last)
first->prev->next = last->next;
last->next->prev = first->prev;
head->prev->next = first;
first->prev = head->prev;
last->next = head;
head->prev = last;
/**
* br_list_is_first -- tests whether @list is the first entry in list @head
* @list: the entry to test
* @head: the head of the list
*/
static inline int br_list_is_first(const struct br_list_head *list,
const struct br_list_head *head)
return list->prev == head;
/**
* br_list_is_last - tests whether @list is the last entry in list @head
* @list: the entry to test
* @head: the head of the list
*/
static inline int br_list_is_last(const struct br_list_head *list,
const struct br_list_head *head)
return list->next == head;
/**
* br_list_empty - tests whether a list is empty
* @head: the list to test.
*/
static inline int br_list_empty(const struct br_list_head *head)
return BR_READ_ONCE(head->next) == head;
/**
* br_list_empty_careful - tests whether a list is empty and not being modified
* @head: the list to test
*
* Description:
* tests whether a list is empty _and_ checks that no other CPU might be
* in the process of modifying either member (next or prev)
*
* NOTE: using br_list_empty_careful() without synchronization
* can only be safe if the only activity that can happen
* to the list entry is br_list_del_init(). Eg. it cannot be used
* if another CPU could re-br_list_add() it.
*/
static inline int br_list_empty_careful(const struct br_list_head *head)
struct br_list_head *next = head->next;
return (next == head) && (next == head->prev);
/**
* br_list_rotate_left - rotate the list to the left
* @head: the head of the list
*/
static inline void br_list_rotate_left(struct br_list_head *head)
struct br_list_head *first;
if (!br_list_empty(head))
first = head->next;
br_list_move_tail(first, head);
/**
* br_list_rotate_to_front() - Rotate list to specific item.
* @list: The desired new front of the list.
* @head: The head of the list.
*
* Rotates list so that @list becomes the new front of the list.
*/
static inline void br_list_rotate_to_front(struct br_list_head *list,
struct br_list_head *head)
/*
* Deletes the list head from the list denoted by @head and
* places it as the tail of @list, this effectively rotates the
* list so that @list is at the front.
*/
br_list_move_tail(head, list);
/**
* br_list_is_singular - tests whether a list has just one entry.
* @head: the list to test.
*/
static inline int br_list_is_singular(const struct br_list_head *head)
return !br_list_empty(head) && (head->next == head->prev);
static inline void __br_list_cut_position(struct br_list_head *list,
struct br_list_head *head, struct br_list_head *entry)
struct br_list_head *new_first = entry->next;
list->next = head->next;
list->next->prev = list;
list->prev = entry;
entry->next = list;
head->next = new_first;
new_first->prev = head;
/**
* br_list_cut_position - cut a list into two
* @list: a new list to add all removed entries
* @head: a list with entries
* @entry: an entry within head, could be the head itself
* and if so we won't cut the list
*
* This helper moves the initial part of @head, up to and
* including @entry, from @head to @list. You should
* pass on @entry an element you know is on @head. @list
* should be an empty list or a list you do not care about
* losing its data.
*
*/
static inline void br_list_cut_position(struct br_list_head *list,
struct br_list_head *head, struct br_list_head *entry)
if (br_list_empty(head))
return;
if (br_list_is_singular(head) &&
(head->next != entry && head != entry))
return;
if (entry == head)
BR_INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
else
__br_list_cut_position(list, head, entry);
/**
* br_list_cut_before - cut a list into two, before given entry
* @list: a new list to add all removed entries
* @head: a list with entries
* @entry: an entry within head, could be the head itself
*
* This helper moves the initial part of @head, up to but
* excluding @entry, from @head to @list. You should pass
* in @entry an element you know is on @head. @list should
* be an empty list or a list you do not care about losing
* its data.
* If @entry == @head, all entries on @head are moved to
* @list.
*/
static inline void br_list_cut_before(struct br_list_head *list,
struct br_list_head *head,
struct br_list_head *entry)
if (head->next == entry)
BR_INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
return;
list->next = head->next;
list->next->prev = list;
list->prev = entry->prev;
list->prev->next = list;
head->next = entry;
entry->prev = head;
static inline void __br_list_splice(const struct br_list_head *list,
struct br_list_head *prev,
struct br_list_head *next)
struct br_list_head *first = list->next;
struct br_list_head *last = list->prev;
first->prev = prev;
prev->next = first;
last->next = next;
next->prev = last;
/**
* list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void br_list_splice(const struct br_list_head *list,
struct br_list_head *head)
if (!br_list_empty(list))
__br_list_splice(list, head, head->next);
/**
* br_list_splice_tail - join two lists, each list being a queue
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void br_list_splice_tail(struct br_list_head *list,
struct br_list_head *head)
if (!br_list_empty(list))
__br_list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
/**
* br_list_splice_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list.
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void br_list_splice_init(struct br_list_head *list,
struct br_list_head *head)
if (!br_list_empty(list))
__br_list_splice(list, head, head->next);
BR_INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
/**
* br_list_splice_tail_init - join two lists and reinitialise the emptied list
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*
* Each of the lists is a queue.
* The list at @list is reinitialised
*/
static inline void br_list_splice_tail_init(struct br_list_head *list,
struct br_list_head *head)
if (!br_list_empty(list))
__br_list_splice(list, head->prev, head);
BR_INIT_LIST_HEAD(list);
/**
* br_list_entry - get the struct for this entry
* @ptr: the &struct br_list_head pointer.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*/
#define br_list_entry(ptr, type, member) \\
br_container_of(ptr, type, member)
/**
* br_list_first_entry - get the first element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* Note, that list is expected to be not empty.
*/
#define br_list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \\
br_list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)
/**
* br_list_last_entry - get the last element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* Note, that list is expected to be not empty.
*/
#define br_list_last_entry(ptr, type, member) \\
br_list_entry((ptr)->prev, type, member)
/**
* br_list_first_entry_or_null - get the first element from a list
* @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* Note that if the list is empty, it returns NULL.
*/
#define br_list_first_entry_or_null(ptr, type, member) ( \\
struct br_list_head *head__ = (ptr); \\
struct br_list_head *pos__ = BR_READ_ONCE(head__->next); \\
pos__ != head__ ? br_list_entry(pos__, type, member) : NULL; \\
)
/**
* br_list_next_entry - get the next element in list
* @pos: the type * to cursor
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*/
#define br_list_next_entry(pos, member) \\
br_list_entry((pos)->member.next, typeof(*(pos)), member)
/**
* br_list_prev_entry - get the prev element in list
* @pos: the type * to cursor
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*/
#define br_list_prev_entry(pos, member) \\
br_list_entry((pos)->member.prev, typeof(*(pos)), member)
/**
* br_list_for_each - iterate over a list
* @pos: the &struct br_list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define br_list_for_each(pos, head) \\
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
/**
* br_list_for_each_prev - iterate over a list backwards
* @pos: the &struct br_list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_prev(pos, head) \\
for (pos = (head)->prev; pos != (head); pos = pos->prev)
/**
* br_list_for_each_safe - iterate over a list safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the &struct br_list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct br_list_head to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \\
for (pos = (head)->next, n = pos->next; pos != (head); \\
pos = n, n = pos->next)
/**
* br_list_for_each_prev_safe - iterate over a list backwards safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the &struct br_list_head to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct br_list_head to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_prev_safe(pos, n, head) \\
for (pos = (head)->prev, n = pos->prev; \\
pos != (head); \\
pos = n, n = pos->prev)
/**
* br_list_entry_is_head - test if the entry points to the head of the list
* @pos: the type * to cursor
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*/
#define br_list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member) \\
(&pos->member == (head))
/**
* br_list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \\
for (pos = br_list_first_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member); \\
!br_list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \\
pos = br_list_next_entry(pos, member))
/**
* br_list_for_each_entry_reverse - iterate backwards over list of given type.
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_entry_reverse(pos, head, member) \\
for (pos = br_list_last_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member); \\
!br_list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \\
pos = br_list_prev_entry(pos, member))
/**
* br_list_prepare_entry - prepare a pos entry for use in br_list_for_each_entry_continue()
* @pos: the type * to use as a start point
* @head: the head of the list
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* Prepares a pos entry for use as a start point in br_list_for_each_entry_continue().
*/
#define br_list_prepare_entry(pos, head, member) \\
((pos) ? : br_list_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member))
/**
* br_list_for_each_entry_continue - continue iteration over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* Continue to iterate over list of given type, continuing after
* the current position.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_entry_continue(pos, head, member) \\
for (pos = br_list_next_entry(pos, member); \\
!br_list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \\
pos = br_list_next_entry(pos, member))
/**
* br_list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse - iterate backwards from the given point
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* Start to iterate over list of given type backwards, continuing after
* the current position.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_entry_continue_reverse(pos, head, member) \\
for (pos = br_list_prev_entry(pos, member); \\
!br_list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \\
pos = br_list_prev_entry(pos, member))
/**
* br_list_for_each_entry_from - iterate over list of given type from the current point
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type, continuing from current position.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_entry_from(pos, head, member) \\
for (; !br_list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \\
pos = br_list_next_entry(pos, member))
/**
* br_list_for_each_entry_from_reverse - iterate backwards over list of given type
* from the current point
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* Iterate backwards over list of given type, continuing from current position.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_entry_from_reverse(pos, head, member) \\
for (; !br_list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \\
pos = br_list_prev_entry(pos, member))
/**
* br_list_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \\
for (pos = br_list_first_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member), \\
n = br_list_next_entry(pos, member); \\
!br_list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \\
pos = n, n = br_list_next_entry(n, member))
/**
* br_list_for_each_entry_safe_continue - continue list iteration safe against removal
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type, continuing after current point,
* safe against removal of list entry.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_entry_safe_continue(pos, n, head, member) \\
for (pos = br_list_next_entry(pos, member), \\
n = br_list_next_entry(pos, member); \\
!br_list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \\
pos = n, n = br_list_next_entry(n, member))
/**
* br_list_for_each_entry_safe_from - iterate over list from current point safe against removal
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* Iterate over list of given type from current point, safe against
* removal of list entry.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_entry_safe_from(pos, n, head, member) \\
for (n = br_list_next_entry(pos, member); \\
!br_list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \\
pos = n, n = br_list_next_entry(n, member))
/**
* br_list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse - iterate backwards over list safe against removal
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another type * to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* Iterate backwards over list of given type, safe against removal
* of list entry.
*/
#define br_list_for_each_entry_safe_reverse(pos, n, head, member) \\
for (pos = br_list_last_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member), \\
n = br_list_prev_entry(pos, member); \\
!br_list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \\
pos = n, n = br_list_prev_entry(n, member))
/**
* br_list_safe_reset_next - reset a stale br_list_for_each_entry_safe loop
* @pos: the loop cursor used in the br_list_for_each_entry_safe loop
* @n: temporary storage used in br_list_for_each_entry_safe
* @member: the name of the br_list_head within the struct.
*
* br_list_safe_reset_next is not safe to use in general if the list may be
* modified concurrently (eg. the lock is dropped in the loop body). An
* exception to this is if the cursor element (pos) is pinned in the list,
* and br_list_safe_reset_next is called after re-taking the lock and before
* completing the current iteration of the loop body.
*/
#define br_list_safe_reset_next(pos, n, member) \\
n = br_list_next_entry(pos, member)
/*
* Double linked lists with a single pointer list head.
* Mostly useful for hash tables where the two pointer list head is
* too wasteful.
* You lose the ability to access the tail in O(1).
*/
#define BR_HLIST_HEAD_INIT .first = NULL
#define BR_HLIST_HEAD(name) struct br_hlist_head name = .first = NULL
#define BR_INIT_HLIST_HEAD(ptr) ((ptr)->first = NULL)
static inline void BR_INIT_HLIST_NODE(struct br_hlist_node *h)
h->next = NULL;
h->pprev = NULL;
static inline int br_hlist_unhashed(const struct br_hlist_node *h)
return !h->pprev;
static inline int br_hlist_empty(const struct br_hlist_head *h)
return !BR_READ_ONCE(h->first);
static inline void __br_hlist_del(struct br_hlist_node *n)
struct br_hlist_node *next = n->next;
struct br_hlist_node **pprev = n->pprev;
BR_WRITE_ONCE(*pprev, next);
if (next)
next->pprev = pprev;
static inline void br_hlist_del(struct br_hlist_node *n)
__br_hlist_del(n);
n->next = BR_LIST_POISON1;
n->pprev = BR_LIST_POISON2;
static inline void br_hlist_del_init(struct br_hlist_node *n)
if (!br_hlist_unhashed(n))
__br_hlist_del(n);
BR_INIT_HLIST_NODE(n);
static inline void br_hlist_add_head(struct br_hlist_node *n, struct br_hlist_head *h)
struct br_hlist_node *first = h->first;
n->next = first;
if (first)
first->pprev = &n->next;
BR_WRITE_ONCE(h->first, n);
n->pprev = &h->first;
/* next must be != NULL */
static inline void br_hlist_add_before(struct br_hlist_node *n,
struct br_hlist_node *next)
n->pprev = next->pprev;
n->next = next;
next->pprev = &n->next;
BR_WRITE_ONCE(*(n->pprev), n);
static inline void br_hlist_add_behind(struct br_hlist_node *n,
struct br_hlist_node *prev)
n->next = prev->next;
prev->next = n;
n->pprev = &prev->next;
if (n->next)
n->next->pprev = &n->next;
/* after that we'll appear to be on some hlist and br_hlist_del will work */
static inline void br_hlist_add_fake(struct br_hlist_node *n)
n->pprev = &n->next;
static inline bool br_hlist_fake(struct br_hlist_node *h)
return h->pprev == &h->next;
/*
* Check whether the node is the only node of the head without
* accessing head:
*/
static inline bool
br_hlist_is_singular_node(struct br_hlist_node *n, struct br_hlist_head *h)
return !n->next && n->pprev == &h->first;
/*
* Move a list from one list head to another. Fixup the pprev
* reference of the first entry if it exists.
*/
static inline void br_hlist_move_list(struct br_hlist_head *old,
struct br_hlist_head *new)
new->first = old->first;
if (new->first)
new->first->pprev = &new->first;
old->first = NULL;
#define br_hlist_entry(ptr, type, member) br_container_of(ptr,type,member)
#define br_hlist_for_each(pos, head) \\
for (pos = (head)->first; pos ; pos = pos->next)
#define br_hlist_for_each_safe(pos, n, head) \\
for (pos = (head)->first; pos && ( n = pos->next; 1; ); \\
pos = n)
#define br_hlist_entry_safe(ptr, type, member) \\
( typeof(ptr) ____ptr = (ptr); \\
____ptr ? br_hlist_entry(____ptr, type, member) : NULL; \\
)
/**
* br_hlist_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_hlist_node within the struct.
*/
#define br_hlist_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \\
for (pos = br_hlist_entry_safe((head)->first, typeof(*(pos)), member);\\
pos; \\
pos = br_hlist_entry_safe((pos)->member.next, typeof(*(pos)), member))
/**
* br_hlist_for_each_entry_continue - iterate over a hlist continuing after current point
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @member: the name of the br_hlist_node within the struct.
*/
#define br_hlist_for_each_entry_continue(pos, member) \\
for (pos = br_hlist_entry_safe((pos)->member.next, typeof(*(pos)), member);\\
pos; \\
pos = br_hlist_entry_safe((pos)->member.next, typeof(*(pos)), member))
/**
* br_hlist_for_each_entry_from - iterate over a hlist continuing from current point
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @member: the name of the br_hlist_node within the struct.
*/
#define br_hlist_for_each_entry_from(pos, member) \\
for (; pos; \\
pos = br_hlist_entry_safe((pos)->member.next, typeof(*(pos)), member))
/**
* br_hlist_for_each_entry_safe - iterate over list of given type safe against removal of list entry
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @n: another &struct br_hlist_node to use as temporary storage
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the br_hlist_node within the struct.
*/
#define br_hlist_for_each_entry_safe(pos, n, head, member) \\
for (pos = br_hlist_entry_safe((head)->first, typeof(*pos), member);\\
pos && ( n = pos->member.next; 1; ); \\
pos = br_hlist_entry_safe(n, typeof(*pos), member))
#endif结束
以上是关于双向循环链表list_head WRITE_ONCE READ_ONCE 函数的分析与使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章