java集合类源码分析之Map
Posted Wilange
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java集合类源码分析之Map相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
java集合中Map接口的实现类有HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap和TreeMap,与List不同的是Map并不是继承自Collection接口。可以这样来理解它:
- Map提供key到value的映射,一个Map中不能包含相同的key,每个key只能映射一个 value。
- Map接口提供3种集合的视图,Map的内容可以被当作一组key集合,一组value集合,或者一组key-value映射
1.HashMap
- HashMap的基本实现为一个链表数组(Entry<K, V>[ ]),即存放链表的数组,数组中的每个元素都是一个链表的头结点,而链表中的基本数据类型是一个静态内部类(Node)的对象,这些对象都具有相同的hash(key)值,所以是一种无序存储。

1 static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { 2 final int hash; 3 final K key; 4 V value; 5 Node<K,V> next; 6 7 Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { 8 this.hash = hash; 9 this.key = key; 10 this.value = value; 11 this.next = next; 12 } 13 14 public final K getKey() { return key; } 15 public final V getValue() { return value; } 16 public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } 17 18 public final int hashCode() { 19 return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); 20 } 21 22 public final V setValue(V newValue) { 23 V oldValue = value; 24 value = newValue; 25 return oldValue; 26 } 27 28 public final boolean equals(Object o) { 29 if (o == this) 30 return true; 31 if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { 32 Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; 33 if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && 34 Objects.equals(value, e.getValue())) 35 return true; 36 } 37 return false; 38 } 39 }
-
HashMap 的实例有两个参数影响其性能:初始容量(默认16) 和加载因子(默认0.75)。容量是哈希表中桶的数量,初始容量只是哈希表在创建时的容量。加载因子是描述哈希表在扩容之前可以达到多满的一种度量。当哈希表中的条目数超出了加载因子与当前容量的乘积时,则要对该哈希表进行rehash 操作(即重建内部数据结构),从而哈希表将具有大约两倍的桶数。因此,HashMap的容量并不等于能够存储的对象的个数。
-
因此,在创建实例的时候我们要按照自己的需求来设置这两个值,当空间大而对查询效率要求高的时候可以将初始容量设置的大一些,而加载因子小一些这样的话查询效率高,但空间利用率不高,而当空间比较小而效率要求不是很高的时候可以将初始容量设置小一些而加载因子设置大一些,这样查询速度会慢一些而空间利用率会高一些。
- 按照key关键字的哈希值和buckets数组的长度取模(hash(key)%length)查找桶的位置,如果key的哈希值相同,Hash冲突(指向了同一个桶)则每次新添加的作为头节点,而最先添加的在表尾。
(参考文章:http://blog.csdn.net/qh_java/article/details/46404439)
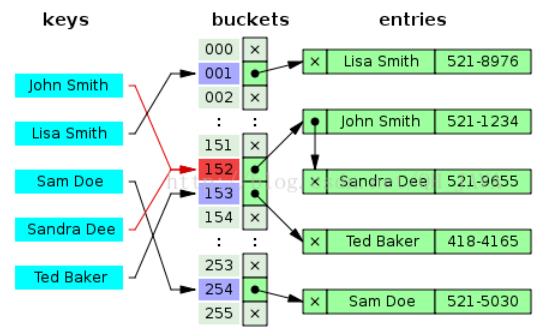
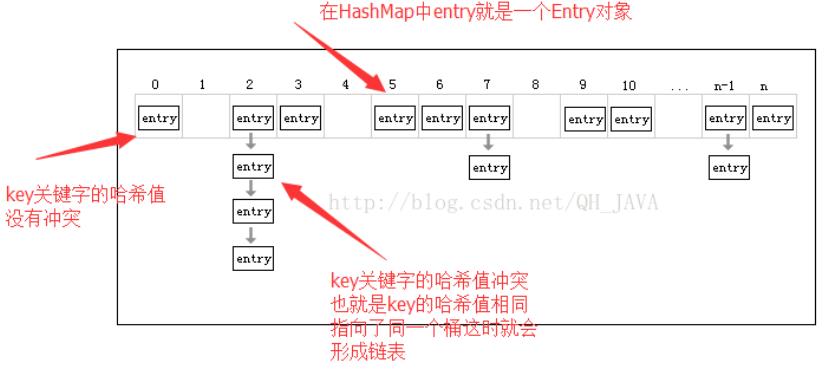
图片来源:http://blog.csdn.net/qh_java/article/details/46404439
下面通过源码来进行分析,了解HashMap的一些基本用法:
- 构造器(四种)
1.HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) 第一个参数为初始容量,第二个参数为加载因子
2.HashMap(int initialCapacity) 只初始化容量,加载因子为默认值0.75
3. HashMap() 空的构造器,加载因子为默认值0.75
4.HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) 初始化HashMap中的元素,加载因子默认0.75
- 插入元素
1.put(K key, V value) 插入单个map元素
2. putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) 插入一个map集合

1 //hashMap默认按key的哈希值存储,所以是一种无序存储 2 hashMap.put("A", 100); 3 hashMap.put("B", 120); 4 hashMap.put("C", 105); 5 for(String key: hashMap.keySet()){ 6 System.out.print(key+":"+hashMap.get(key)+", "); 7 }//A:100, B:120, C:105,
这里解释一下HashMap集合key值唯一的实现方法:在插入元素时,调用的是putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true)方法,这个方法先要检查原有HashMap集合中是否包含了将要插入的key值,若有,则用新的value值覆盖旧的值并返回旧的value值,完成插入操作;否则直接插入新的键值对并返回null,完成插入操作。
- 查找元素
1.get(Object key) 按key值查找相应的value值
2.containsKey(Object key) 查找map中是否含有指定的key
3.containsValue(Object value) 查找map中是否含有指定的value

1 System.out.println(hashMap.get("A"));//100 2 System.out.println(hashMap.containsKey("A"));//true 3 System.out.println(hashMap.containsValue(100));//true
- 修改元素
1.put(K key, V value) 找到key值相同的value,用新的value值进行覆盖

1 hashMap.put("A", 500); 2 System.out.println(hashMap.get("A"));//500
- 删除元素
1.remove(Object key) 按key查找,将相应的key-value对删除,并返回删除的value值
2.clear() 清空所有元素

1 System.out.println(hashMap.size());//4 2 hashMap.remove("D"); 3 System.out.println(hashMap.containsKey("D"));//false 4 System.out.println(hashMap.size());//3
2.TreeMap
- TreeMap的基本实现是一棵红黑二叉树,按照key值以二叉树的结构进行存储,即当前节点的值大于或等于左孩子节点的值而小于或等于右孩子节点的值,所以TreeMap是一种按key排序的有序存储结构。数据存储的基本形式是一个Entry<K, V>对象,而Entry是TreeMap的一个静态内部类。

1 static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { 2 K key; 3 V value; 4 Entry<K,V> left; 5 Entry<K,V> right; 6 Entry<K,V> parent; 7 boolean color = BLACK; 8 9 /** 10 * Make a new cell with given key, value, and parent, and with 11 * {@code null} child links, and BLACK color. 12 */ 13 Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) { 14 this.key = key; 15 this.value = value; 16 this.parent = parent; 17 } 18 19 /** 20 * Returns the key. 21 * 22 * @return the key 23 */ 24 public K getKey() { 25 return key; 26 } 27 28 /** 29 * Returns the value associated with the key. 30 * 31 * @return the value associated with the key 32 */ 33 public V getValue() { 34 return value; 35 } 36 37 /** 38 * Replaces the value currently associated with the key with the given 39 * value. 40 * 41 * @return the value associated with the key before this method was 42 * called 43 */ 44 public V setValue(V value) { 45 V oldValue = this.value; 46 this.value = value; 47 return oldValue; 48 } 49 50 public boolean equals(Object o) { 51 if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) 52 return false; 53 Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; 54 55 return valEquals(key,e.getKey()) && valEquals(value,e.getValue()); 56 } 57 58 public int hashCode() { 59 int keyHash = (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode()); 60 int valueHash = (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); 61 return keyHash ^ valueHash; 62 } 63 64 public String toString() { 65 return key + "=" + value; 66 } 67 }
(关于红黑二叉树的算法和基本操作可以参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3245399.html)
- 构造器(四种)
1.TreeMap() 空的构造器,采用默认的比较器(按key值升序排列)
2.TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) 参数为自定义的比较器,常用于实现降序排列
3.TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) 参数为一个map子集,用于初始化TreeMap对象,采用默认比较器
4.TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) 参数为一个SortedMap集合,用于初始化TreeMap对象,采用参数自带的比较器
应用示例:

1 //采用默认比较器按key值升序排列,进行存储 2 Map<String, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<String, Integer>(); 3 treeMap.put("B", 120); 4 treeMap.put("C", 105); 5 treeMap.put("A", 100); 6 for(String key: treeMap.keySet()){ 7 System.out.print(key+":"+treeMap.get(key)+", "); 8 } //A:100, B:120, C:105, 9 }

1 //自定义比较器,实现降序存储 2 Map<String, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<String, Integer>(new Comparator<String>() { 3 @Override 4 public int compare(String o1, String o2) { 5 // return 0; 默认升序 6 return o2.compareTo(o1); //降序 7 } 8 }); 9 treeMap.put("B", 120); 10 treeMap.put("C", 105); 11 treeMap.put("A", 100); 12 for(String key: treeMap.keySet()){ 13 System.out.print(key+":"+treeMap.get(key)+", "); 14 } //C:105, B:120, A:100,

1 //初始化TreeMap对象,采用默认比较器进行排序 2 Map<String, Integer> subMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); 3 subMap.put("B", 100); 4 subMap.put("A", 120); 5 subMap.put("C", 105); 6 subMap.put("D", 200); 7 for(String key: subMap.keySet()){ 8 System.out.print(key+":"+subMap.get(key)+", "); 9 } //D:200, A:120, B:100, C:105, 10 11 System.out.println(); 12 13 Map<String, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<String, Integer>(subMap); 14 for(String key: treeMap.keySet()){ 15 System.out.print(key+":"+treeMap.get(key)+", "); 16 } //A:120, B:100, C:105, D:200,

1 //初始化TreeMap对象,采用参数自带的比较器 2 //注意:此处参数必须为SortedMap接口的实现类,否则将采用默认比较器 3 SortedMap<String, Integer> subMap = new TreeMap<String, Integer>(new Comparator<String>() { 4 5 @Override 6 public int compare(String o1, String o2) { 7 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 8 return o2.compareTo(o1); 9 } 10 }); 11 subMap.put("B", 100); 12 subMap.put("F", 120); 13 subMap.put("D", 105); 14 for(String key: subMap.keySet()){ 15 System.out.print(key+":"+subMap.get(key)+", "); 16 } //F:120, D:105, B:100, 17 18 System.out.println(); 19 20 Map<String, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<String, Integer>(subMap); 21 for(String key: treeMap.keySet()){ 22 System.out.print(key+":"+treeMap.get(key)+", "); 23 } //F:120, D:105, B:100, 24 25 System.out.println(); 26 27 treeMap.put("A", 200); 28 treeMap.put("C", 300); 29 treeMap.put("E", 400); 30 for(String key: treeMap.keySet()){ 31 System.out.print(key+":"+treeMap.get(key)+", "); 32 } //F:120, E:400, D:105, C:300, B:100, A:200,
- 插入元素
1.put(K key, V value) 插入一个key-value对,并调整二叉树结构
2.putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map) 插入一个Map子集
由于红黑二叉树的结构限制,每次插入元素时都需要调整树的结构以保证插入后任然是一颗红黑二叉树,至于红黑二叉树的维持算法此处不做详细介绍,关于TreeMap集合实现key值唯一的方法与HashMap基本相同。
- 查询元素
1.get(Object key) 按照指定的key值查找相对应的value值

1 treeMap.put("A", 200); 2 treeMap.put("C", 300); 3 treeMap.put("E", 400); 4 for(String key: treeMap.keySet()){ 5 System.out.print(key+":"+treeMap.get(key)+", "); 6 } //F:120, E:400, D:105, C:300, B:100, A:200, 7 8 System.out.println(treeMap.get("A"));//200
- 修改元素
1.put(K key, V value) 根据key值查找相对应的value值,并用新的value值覆盖

1 treeMap.put("A",500); 2 System.out.println(treeMap.get("A"));//500
- 删除元素
1.remove(Object key) 按key值删除相对应的键值对,并返回删除的value值
2.clear() 清空所有元素
3.Hashtable
HashMap和Hashtable类似,但是Hashtable是线程安全的(同步机制,原因类似于StringBuffer类和Vector类),并且不允许空的键(key)和值(value)。
以上是关于java集合类源码分析之Map的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
