java集合:ArrayList
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java集合:ArrayList相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、简介。(1.8源码)
ArrayList是实现List接口的动态数组。(动态意思就是大小可变)默认初始容量为10。随着ArrayList中元素的增加,它的容量也会不断的自动增长。如果我们知道具体所需数据量,在构造ArrayList时可以给ArrayList指定一个初始容量,避免内存的浪费。
二、源码。
(1)三个构造方法。
第一个:用于初始化列表的容量。
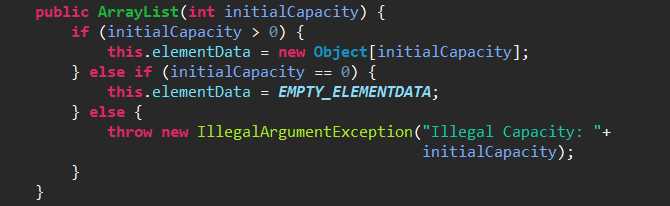
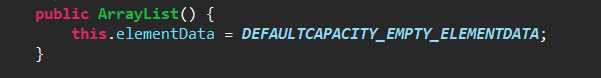
第二个:默认构造函数,初始容量为10的空列表
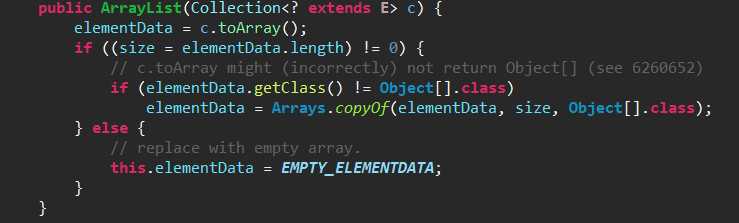
第三个:构造一个包含指定 collection 的元素的列表,这些元素是按照该 collection 的迭代器返回它们的顺序排列的
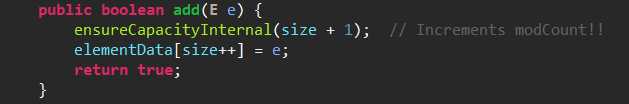
(2)新增元素的四种方法
第一个:将指定的元素添加到此列表的尾部,里边含有ensureCapacity()方法能自动检查是否需要扩容的。
第二个:将指定的元素插入此列表中的指定位置,。
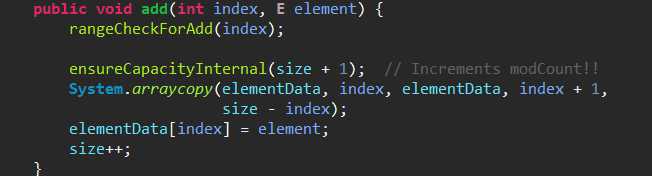
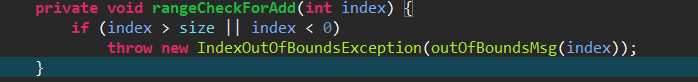
其中这个方法是用于检查索引位置是否正确。
第三个:按照指定 collection 的迭代器所返回的元素顺序,将该 collection 中的所有元素添加到此列表的尾部。
public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest,int destPos,int length) src:源数组;srcPos:源数组要复制的起始位置;dest:目的数组;destPos:目的数组放置的起始位置;length:复制的长度。
1 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { 2 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 3 int numNew = a.length; 4 ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount 5 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); 6 size += numNew; 7 return numNew != 0; 8 }
第四个:从指定的位置开始,将指定 collection 中的所有元素插入到此列表中。
1 public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { 2 rangeCheckForAdd(index); 3 4 Object[] a = c.toArray(); 5 int numNew = a.length; 6 ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount 7 8 int numMoved = size - index; 9 if (numMoved > 0) 10 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, 11 numMoved); 12 13 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); 14 size += numNew; 15 return numNew != 0; 16 }
(3)删除元素的五种方法
第一种:根据下标删除元素
1 public E remove(int index) { 2 rangeCheck(index); 3 4 modCount++; 5 E oldValue = elementData(index); 6 7 int numMoved = size - index - 1; 8 if (numMoved > 0) 9 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 10 numMoved); 11 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work 12 13 return oldValue; 14 }
第二种:删除匹配到最近的元素。注意“==”与“equals”的区别,“==”比较的是对象的引用,“equals”比较的是对象的值。什么时候应该用什么,自己看内存的存储规则。
1 public boolean remove(Object o) { 2 if (o == null) { 3 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 4 if (elementData[index] == null) { 5 fastRemove(index); 6 return true; 7 } 8 } else { 9 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 10 if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { 11 fastRemove(index); 12 return true; 13 } 14 } 15 return false; 16 }
第三种:与一类似不做解释
1 private void fastRemove(int index) { 2 modCount++; 3 int numMoved = size - index - 1; 4 if (numMoved > 0) 5 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 6 numMoved); 7 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work 8 }
第四种:删除指定范围内的一段元素
1 protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) { 2 modCount++; 3 int numMoved = size - toIndex; 4 System.arraycopy(elementData, toIndex, elementData, fromIndex, 5 numMoved); 6 7 // clear to let GC do its work 8 int newSize = size - (toIndex-fromIndex); 9 for (int i = newSize; i < size; i++) { 10 elementData[i] = null; 11 } 12 size = newSize; 13 }
第五种:原集合与给定集合比较。如果原集合与给定的集合无相同元素则原集合不改变,反之。
1 public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { 2 Objects.requireNonNull(c); 3 return batchRemove(c, false); 4 }
1 private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { 2 final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; 3 int r = 0, w = 0; 4 boolean modified = false; 5 try { 6 for (; r < size; r++) 7 if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) 8 elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; 9 } finally { 10 // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, 11 // even if c.contains() throws. 12 if (r != size) { 13 System.arraycopy(elementData, r, 14 elementData, w, 15 size - r); 16 w += size - r; 17 } 18 if (w != size) { 19 // clear to let GC do its work 20 for (int i = w; i < size; i++) 21 elementData[i] = null; 22 modCount += size - w; 23 size = w; 24 modified = true; 25 } 26 } 27 return modified; 28 }
(4)替换元素方法
1 public E set(int index, E element) { 2 rangeCheck(index); 3 4 E oldValue = elementData(index); 5 elementData[index] = element; 6 return oldValue; 7 }
(5)查找元素方法
1 public E get(int index) { 2 rangeCheck(index); 3 4 return elementData(index); 5 }
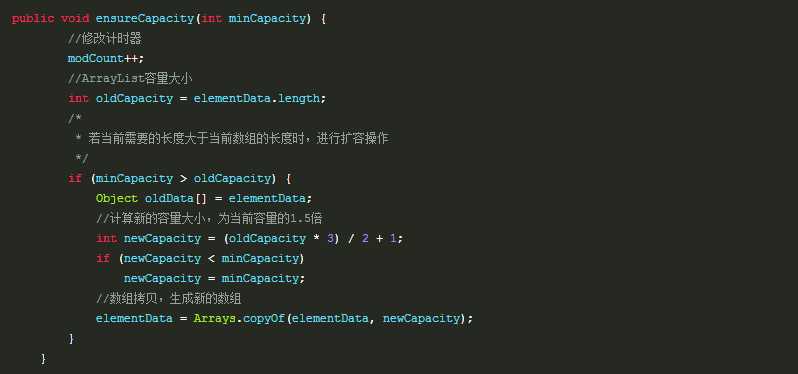
(6)关于源码扩容操作,1.8的乱。
1.8
1 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { 2 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { 3 minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); 4 } 5 6 ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); 7 } 8 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { 9 modCount++; 10 11 // overflow-conscious code 12 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) 13 grow(minCapacity); 14 } 15 private void grow(int minCapacity) { 16 // overflow-conscious code 17 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; 18 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); 19 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) 20 newCapacity = minCapacity; 21 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) 22 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); 23 // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: 24 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); 25 } 26 private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { 27 if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow 28 throw new OutOfMemoryError(); 29 return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? 30 Integer.MAX_VALUE : 31 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; 32 }
从别人博客弄来简短的
为什么每次扩容处理会是1.5倍,而不是2.5、3、4倍呢?通过google查找,发现1.5倍的扩容是最好的倍数。因为一次性扩容太大(例如2.5倍)可能会浪费更多的内存(1.5倍最多浪费33%,而2.5被最多会浪费60%,3.5倍则会浪费71%……)。但是一次性扩容太小,需要多次对数组重新分配内存,对性能消耗比较严重。所以1.5倍刚刚好,既能满足性能需求,也不会造成很大的内存消耗。
以上是关于java集合:ArrayList的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章