冒泡排序(java)
Posted 诺-诺
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了冒泡排序(java)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
冒泡排序的思想就是将相邻的两个元素做一次比较, 比较出如果后面元素比前面元素小就交换一次位置;
经过一趟这样的交换最大的元素就落在了最后面, 所以内层循环的边界也出来了,就是不算经排序后的最后的几个元素 ,即 n - i - 1;
而外层循环所需要比较到的位置也就是n - 2, 如果超过了则超过了边界;(其中n 是元素的总个数)
例如有这样一列数:
38、49、65、76、13、27、30、97
每趟经过排序如下:
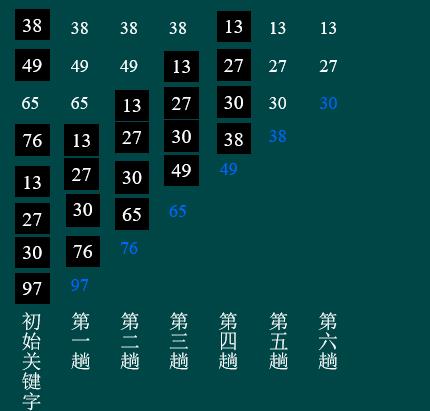
下面是冒泡排序的算法:
public class BubbleSort { public int[] sort(int[] arrays) { int temp = 0; for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length - 2; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < arrays.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (arrays[j] > arrays[j + 1]) { temp = arrays[j]; arrays[j] = arrays[j + 1]; arrays[j + 1] = temp; } } } return arrays; } }
测试类如下:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { BubbleSort bubbleSort = new BubbleSort(); int[] array = createArray(); long ct1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); int[] arrays = bubbleSort.sort(array); long ct2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); display(arrays); System.out.println("所消耗的时间:" + (ct2 - ct1)); } public static void display(int[] arrays) { System.out.println("排序后数据:"); for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) { System.out.print(arrays[i] + "\\t"); if (i % 10 == 0) { System.out.println(); } } System.out.println(); } public static int[] createArray() { int[] array = new int[10000]; System.out.println("数组中元素是:"); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { array[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 1000); System.out.print(array[i] + "\\t"); if (i % 10 == 0) { System.out.println(); } } System.out.println(); return array; } }
10000个数经过冒泡排序的时间大约是200ms,而十万个数经过排序的时间大约就是14000ms,由此可见数据量很大条件下冒泡排序的局限性;

以上是关于冒泡排序(java)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章