Javac语法糖之EnumSwitch
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Javac语法糖之EnumSwitch相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Enum在Java中也被当作一个类来处理,并且Enum也算是Java中的语法糖,主要通过Javac中的Lower类来处理枚举这个语法糖的。
Java7中允许在swith中使用enum类,如下:
public class TestEnumClass {
public void test() {
Color color = Color.RED;
switch (color) {
case RED:
System.out.println("red");
break;
case GREEN:
System.out.println("green");
break;
case BLUE:
System.out.println("blue");
break;
default:
System.out.println("unknow");
}
}
}
现在就来看看编译器javac是怎么对enum switch进行解语法糖的。如果要处理switch语句,肯定要调用visitSwitch()方法,具体代码如下:
public void visitSwitch(JCSwitch tree) {
Type selsuper = types.supertype(tree.selector.type);
boolean enumSwitch = selsuper != null && (tree.selector.type.tsym.flags() & ENUM) != 0;
boolean stringSwitch = selsuper != null && types.isSameType(tree.selector.type, syms.stringType);
Type target = enumSwitch ?
tree.selector.type :
(stringSwitch? syms.stringType : syms.intType);
tree.selector = translate(tree.selector, target); // Translate a single node, boxing or unboxing if needed.
tree.cases = translateCases(tree.cases); // translate a list of case parts of switch statements.
if (enumSwitch) {
result = visitEnumSwitch(tree);
} else if (stringSwitch) {
result = visitStringSwitch(tree);
} else {
result = tree;
}
}
由上可以知道,switch中使用的类型有3种,枚举类、字符串和整数类型。传入的参数tree的各种值如下截图。
下面访问的是visitEnumSwitch()方法,代码如下:
public JCTree visitEnumSwitch(JCSwitch tree) {
TypeSymbol enumSym = tree.selector.type.tsym;
EnumMapping map = mapForEnum(tree.pos(), enumSym);
make_at(tree.pos());
Symbol ordinalMethod = lookupMethod(tree.pos(),
names.ordinal,
tree.selector.type,
List.<Type>nil());
JCArrayAccess selector = make.Indexed(map.mapVar,
make.App(make.Select(tree.selector,
ordinalMethod)));
ListBuffer<JCCase> cases = new ListBuffer<JCCase>();
for (JCCase c : tree.cases) {
if (c.pat != null) {
VarSymbol label = (VarSymbol)TreeInfo.symbol(c.pat);
JCLiteral pat = map.forConstant(label);
cases.append(make.Case(pat, c.stats));
} else {
cases.append(c);
}
}
JCSwitch enumSwitch = make.Switch(selector, cases.toList());
patchTargets(enumSwitch, tree, enumSwitch);
return enumSwitch;
}
调用后的结果是生成了新的switch()语句,如下:
switch (com.test03.TestEnumClass$1.$SwitchMap$com$test03$Color[color.ordinal()]) {
case 1:
System.out.println("red");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("green");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("blue");
break;
default:
System.out.println("unknow");
}
代码调用了mapForEnum()方法,其具体的代码实现如下:
Map<TypeSymbol,EnumMapping> enumSwitchMap = new LinkedHashMap<TypeSymbol,EnumMapping>();
EnumMapping mapForEnum(DiagnosticPosition pos, TypeSymbol enumClass) {
EnumMapping map = enumSwitchMap.get(enumClass);
if (map == null)
enumSwitchMap.put(enumClass, map = new EnumMapping(pos, enumClass));
return map;
}
其中会初始化一个EnumMapping类的对象,这个类的代码如下:
/** This map gives a translation table to be used for enum switches.
*
* For each enum that appears as the type of a switch
* expression, we maintain an EnumMapping to assist in the
* translation, as exemplified by the following example:
*
* we translate
* switch(colorExpression) {
* case red: stmt1;
* case green: stmt2;
* }
* into
* switch(Outer$0.$EnumMap$Color[colorExpression.ordinal()]) {
* case 1: stmt1;
* case 2: stmt2
* }
* with the auxiliary table initialized as follows:
* class Outer$0 {
* synthetic final int[] $EnumMap$Color = new int[Color.values().length];
* static {
* try { $EnumMap$Color[red.ordinal()] = 1; } catch (NoSuchFieldError ex) {}
* try { $EnumMap$Color[green.ordinal()] = 2; } catch (NoSuchFieldError ex) {}
* }
* }
* class EnumMapping provides mapping data and support methods for this translation.
*/
class EnumMapping {
EnumMapping(DiagnosticPosition pos, TypeSymbol forEnum) {
this.forEnum = forEnum;
this.values = new LinkedHashMap<VarSymbol,Integer>();
this.pos = pos;
Name varName = names
.fromString(target.syntheticNameChar() + // 系统指定为‘$‘
"SwitchMap" +
target.syntheticNameChar() +
writer.xClassName(forEnum.type).toString()
.replace(‘/‘, ‘.‘)
.replace(‘.‘, target.syntheticNameChar()));
ClassSymbol outerCacheClass = outerCacheClass();
this.mapVar = new VarSymbol(STATIC | SYNTHETIC | FINAL,
varName,
new ArrayType(syms.intType, syms.arrayClass),
outerCacheClass);
enterSynthetic(pos, mapVar, outerCacheClass.members());
}
DiagnosticPosition pos = null;
// the next value to use
int next = 1; // 0 (unused map elements) go to the default label
// the enum for which this is a map
final TypeSymbol forEnum;
// the field containing the map
final VarSymbol mapVar;
// the mapped values
final Map<VarSymbol,Integer> values;
JCLiteral forConstant(VarSymbol v) {
Integer result = values.get(v);
if (result == null)
values.put(v, result = next++);
return make.Literal(result);
}
// generate the field initializer for the map
void translate() {
// ...
}
}
查看enumSwitchMap中的值,如下:
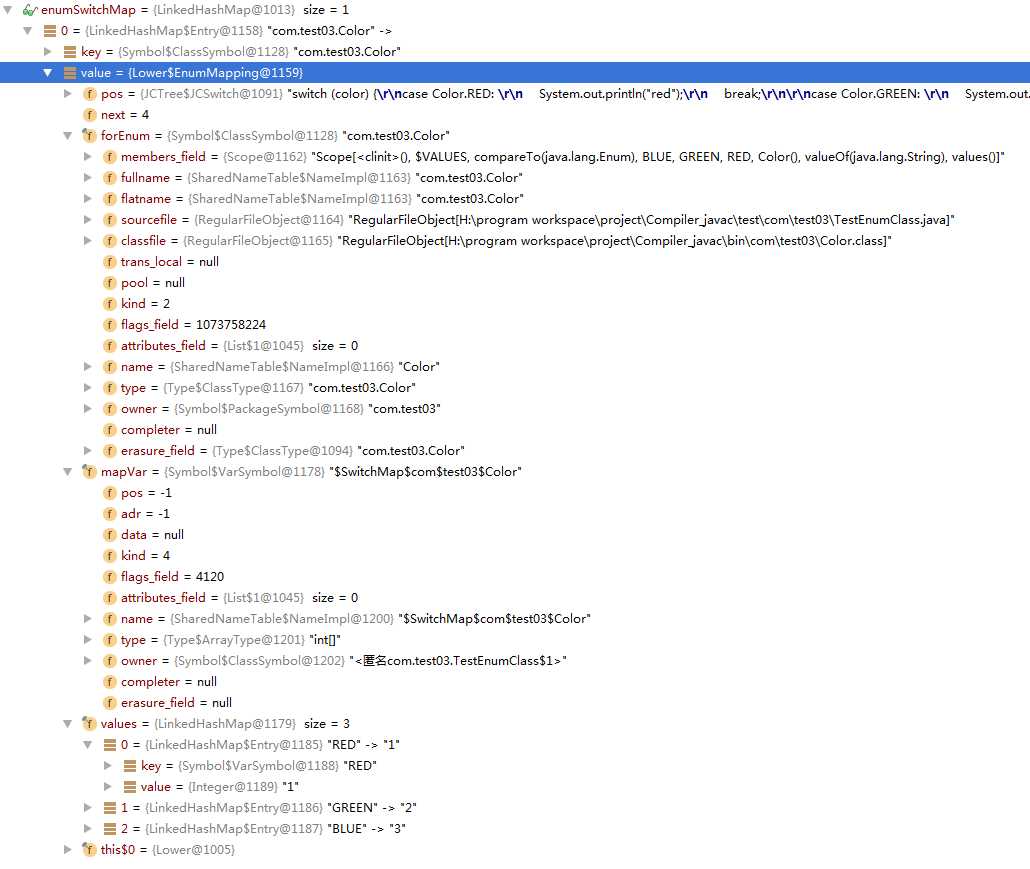
下面还需要对Color这个Enum类型进行一些处理,通过translateTopLevelClass()方法中循环调用EnumMapping中的translate()方法后,Color如下:
/*synthetic*/ class TestEnumClass$1 {
/*synthetic*/ static final int[] $SwitchMap$com$test03$Color = new int[Color.values().length];
static {
try {
com.test03.TestEnumClass$1.$SwitchMap$com$test03$Color[Color.RED.ordinal()] = 1;
} catch (NoSuchFieldError ex) {
}
try {
com.test03.TestEnumClass$1.$SwitchMap$com$test03$Color[Color.GREEN.ordinal()] = 2;
} catch (NoSuchFieldError ex) {
}
try {
com.test03.TestEnumClass$1.$SwitchMap$com$test03$Color[Color.BLUE.ordinal()] = 3;
} catch (NoSuchFieldError ex) {
}
}
}
下面继续来看switch对于字符串的处理。
The general approach used is to translate a single string switch statement into a series of two chained switch statements:
the first a synthesized statement switching on the argument string‘s hash value and
computing a string‘s position in the list of original case labels, if any, followed by a second switch on the
computed integer value. The second switch has the same code structure as the original string switch statement
except that the string case labels are replaced with positional integer constants starting at 0.
The first switch statement can be thought of as an inlined map from strings to their position in the case
label list. An alternate implementation would use an actual Map for this purpose, as done for enum switches.
With some additional effort, it would be possible to use a single switch statement on the hash code of the
argument, but care would need to be taken to preserve the proper control flow in the presence of hash
collisions and other complications, such as fallthroughs. Switch statements with one or two
alternatives could also be specially translated into if-then statements to omit the computation of the hash
code.
The generated code assumes that the hashing algorithm of String is the same in the compilation environment as
in the environment the code will run in. The string hashing algorithm in the SE JDK has been unchanged
since at least JDK 1.2. Since the algorithm has been specified since that release as well, it is very
unlikely to be changed in the future.
Different hashing algorithms, such as the length of the strings or a perfect hashing algorithm over the
particular set of case labels, could potentially be used instead of String.hashCode.
举一个具体的例子,如下:
public class TestStringSwitch {
public void test(String status) {
switch (status) {
case "killed":
case "alive":
System.out.println("killed or alive");
break;
case "sacrificed":
System.out.println("sacrificed");
break;
case "die":
System.out.println("die");
break;
default:
System.out.println("default");
break;
}
}
}
调用visitStringSwitch()方法后解语法粮的结果如下:
{
/*synthetic*/ final String s97$ = status;
/*synthetic*/ int tmp97$ = -1;
switch (s97$.hashCode()) {
case -1131353987:
if (s97$.equals("killed")) tmp97$ = 0;
break;
case 92903629:
if (s97$.equals("alive")) tmp97$ = 1;
break;
case 1585581907:
if (s97$.equals("sacrificed")) tmp97$ = 2;
break;
case 99456:
if (s97$.equals("die")) tmp97$ = 3;
break;
}
switch (tmp97$) {
case 0:
case 1:
System.out.println("killed or alive");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("sacrificed");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("die");
break;
default:
System.out.println("default");
break;
}
}
通过class进行反编译后的结果如下:
public class TestStringSwitch
{
public void test(String status)
{
String str;
switch ((str = status).hashCode())
{
case -1131353987:
if (str.equals("killed")) {
break;
}
break;
case 99456:
if (str.equals("die")) {}
break;
case 92903629:
if (str.equals("alive")) {
break;
}
break;
case 1585581907:
if (!str.equals("sacrificed"))
{
break label129;
System.out.println("killed or alive");
return;
}
else
{
System.out.println("sacrificed");
return;
System.out.println("die");
}
break;
}
label129:
System.out.println("default");
}
}
哈希函数在映射的时候可能存在冲突,多个字符串的哈希值可能是一样的,所以还要通过字符串比较来保证。
以上是关于Javac语法糖之EnumSwitch的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章