java:Hibernate框架(环境搭建,Hibernate.cfg.xml中属性含义,Hibernate常用API对象,HibernteUitl,对象生命周期图,数据对象的三种状态)
Posted 咫尺天涯是路人丶
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java:Hibernate框架(环境搭建,Hibernate.cfg.xml中属性含义,Hibernate常用API对象,HibernteUitl,对象生命周期图,数据对象的三种状态)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.环境搭建:
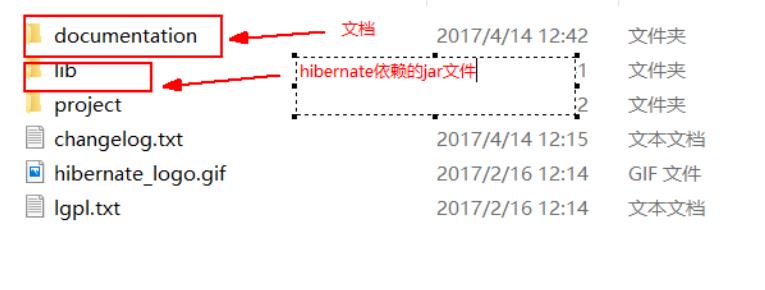
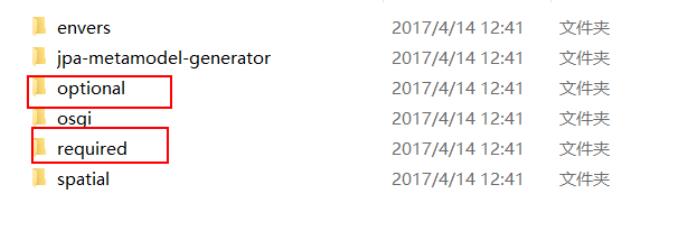
三个准备+7个步骤
准备1:新建项目并添加hibernate依赖的jar文件
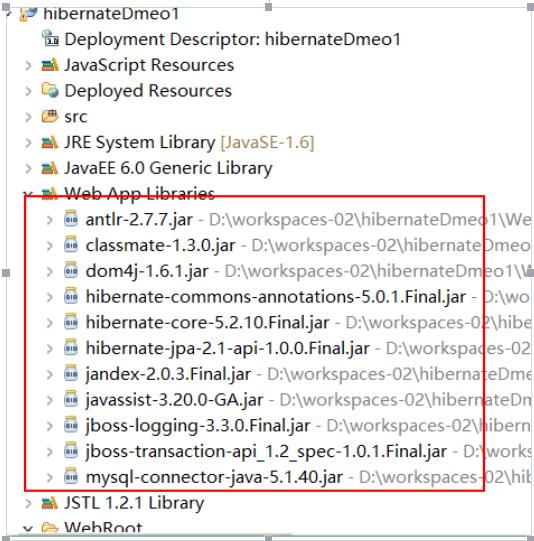
准备2:在classpath下(src目录下)新建hibernate的配置文件:hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!--驱动名称,URL,用户名,密码 --> <property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/struts2</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property> <property name="hibernate.connection.password">root</property> <!--方言 --> <property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect</property> <!-- 输出SQL语句 --> <property name="show_sql">true</property> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
准备3:新建实体类和映射文件xxx.hbm.xml(将实体类与数据库中表建立映射关联)
Userinfo.java
package cn.zzsxt.entity; public class Userinfo { private int userId; private String userName; private String userPass; public int getUserId() { return userId; } public void setUserId(int userId) { this.userId = userId; } public String getUserName() { return userName; } public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } public String getUserPass() { return userPass; } public void setUserPass(String userPass) { this.userPass = userPass; } }
Userinfo.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <!-- class name="实体类的全限定类名" table="表名" 如果table缺省情况下默认使用实体类的简单类名 --> <class name="cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo" table="userinfo"> <!-- id name="实体类中属性名称" column="表中的主键" type="数据类型" --> <id name="userId" column="userId" type="java.lang.Integer"> <!-- 主键的生成策略:native(主键自增),increment:主键自增,assigned:手工指定 --> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <!-- property name="实体类的属性名" column="表中字段名" --> <property name="userName" column="userName" type="java.lang.String"></property> <property name="userPass" column="userPass" type="java.lang.String"></property> </class>
</hibernate-mapping>
注意:将映射文件应该在hibernate.cfg.xml中引入,否则将抛出异常
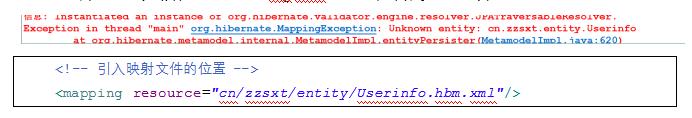
七个步骤:
public static void main(String[] args) { //步骤1:创建Configuration对象,调用configure()解析hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件 Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure(); //步骤2:创建SessionFactory,解析映射文件xxx.hbm.xml SessionFactory sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory(); //步骤3:创建Session,类似jdbc中Connection Session session = sf.openSession(); //步骤4:开启事务 Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); //步骤5:执行持久化操作 Userinfo user = new Userinfo(); user.setUserName("test"); user.setUserPass("test"); session.save(user); //步骤6:提交事务 tx.commit(); //步骤7:关闭session session.close(); }

2.Hibernate.cfg.xml中重要属性的含义?
问答互动:前面已经配置好了Hibernate.cfg.xml,那么每个属性具体含义是什么?
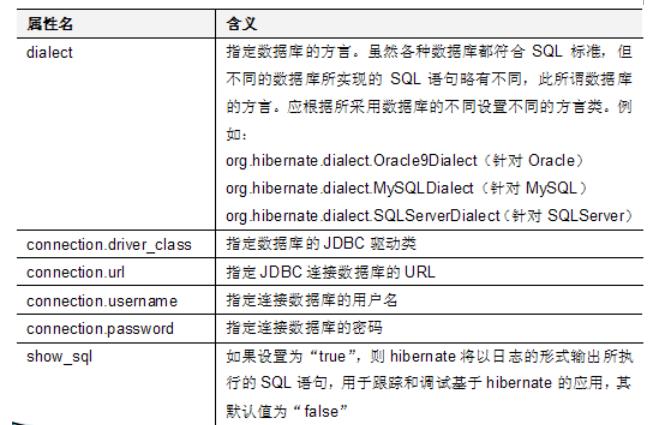
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory> <!--驱动名称,URL,用户名,密码 --> <property name="connection.driver_class"> com.mysql.jdbc.Driver </property> <property name="connection.url"> jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate3 </property> <property name="connection.username">root</property> <property name="connection.password">root</property> <!--方言 --> <property name="hibernate.dialect"> org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect </property> <!-- 输出SQL语句 --> <property name="show_sql">true</property> <!-- 格式化SQL语句 --> <property name="format_sql">true</property> <!-- 根据映射文件生产表: create:创建(不推荐:先删除原有表,重新创建表,原有数据丢失) update:创建+更新记录(推荐,会保存原有数据) --> <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> <!-- 引入映射文件的位置 --> <mapping resource="cn/zzsxt/entity/Userinfo.hbm.xml" /> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
3.*.hbm.xml中重要属性的含义?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 一个映射文件中可以配置多个实体类与表的映射关系. 为了便于管理,建议每个文件只配置一个实体类与表的映射关系 --> <!-- hibernate-mapping标签: 此标签代表一个Hibernate映射.是映射文件的根标签. 属性: package: 可选属性,用于配置当前配置文件中,描述的实体类的默认包名. --> <hibernate-mapping package="cn.zzsxt.entity"> <!-- class标签: 此标签用于描述一个实体类与表的映射信息 属性: name: 可选属性,用于配置实体类的全命名,如果在hibernate-mapping中配置了包名,可省略包名. table:可选属性,用于配置与实体类对应的数据库表,如果表面与类名一致,可以省略. --> <class name="Userinfo" table="userinfo"> <!-- id标签: 此标签用于描述类中的主键属性.此属性对应数据库表中的主键字段. 在数据库设计范式中,明确定义了一个数据的唯一标识即为主键. 所以在Hibernate设计中,建议为类定义主键属性,也称为OID. 属性: name: 可选属性,配置类中的属性名,注意,这里的属性指property,而不是field. column:可选属性,配置与此属性对应的数据库表中的字段名,如果字段名与属性名一致,可以省略. length:可选属性,代表数据库中此字段的字段长度,不建议配置,Hibernate会自动识别数据库表的字段长度 type: 可选属性,代表当前数据的类型,此属性的数据值可用java标准类名或Hibernate框架定义类型赋值. 不推荐配置,Hibernate会自动识别类中属性的具体类型和表中字段的数据类型进行合适的匹配. --> <id name="userId" column="userId" type="java.lang.Integer"> <!-- generator标签: 此标签用于描述主键生成策略,即当进行数据新增的时候,数据的主键数据如何生产.常见策略如下: increment 用于为long, short或者int类型生成唯一标识.只有在没有其他进程往 同一张表中插入数据时才能使用. 在集群下不要使用。. identity 对DB2, MySQL, MS SQL Server, Sybase和HypersonicSQL 的内置标识字段提供支持. 返回的标识符是long, short或者int类型. native 本地化策略,根据底层数据库的能力选择identity, sequence或者hilo中的一个. 如果是mysql,native和identity是一样的,默认使用主键自增 如果是Oracle,native和sequence是一样的, 默认使用命名为hibernate_sequence的序列 sequence 在DB2,PostgreSQL, Oracle, SAP DB, McKoi中使用序列(sequence), 而在Interbase中使用生成器(generator).返回的标识符是long, short或者 int类型的. 配置方式如下: <generator class="sequence"> <param name="sequence">sequenceName</param> </generator> assigned 让应用程序在save()之前为对象分配一个标示符.这是 <generator>元素没有指定时 的默认生成策略. --> <generator class="native"></generator> </id> <!-- propety标签: 此标签用于描述类中的属性与数据库表中字段的对应关系. 属性: name: 可选属性,配置类中的属性名,注意,这里的属性指property,而不是field. column:可选属性,配置与此属性对应的数据库表中的字段名,如果字段名与属性名一致,可以省略. length:可选属性,代表数据库中此字段的字段长度,不建议配置,Hibernate会自动识别数据库表的字段长度 type: 可选属性,代表当前数据的类型,此属性的数据值可用java标准类名或Hibernate框架定义类型赋值. 不推荐配置,Hibernate会自动识别类中属性的具体类型和表中字段的数据类型进行合适的匹配. --> <property name="userName" column="userName" type="java.lang.String" length="20"></property> <property name="userPass" column="userPass" type="java.lang.String" length="20"></property> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
4.Hibernate常用API对象


5.HibernteUitl.java
public class HibernateUtil { private static SessionFactory sessionFactory; private static ThreadLocal<Session> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Session>(); private static Session session; static{ Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure(); sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(); } public static Session getSession(){ session = threadLocal.get(); if(session!=null){ return session; } session = sessionFactory.openSession(); threadLocal.set(session); return session; } }
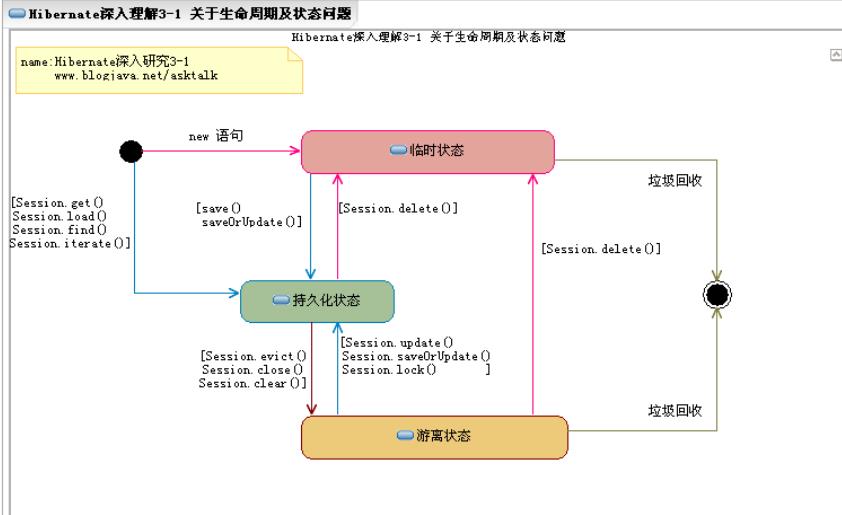
6.对象生命周期图
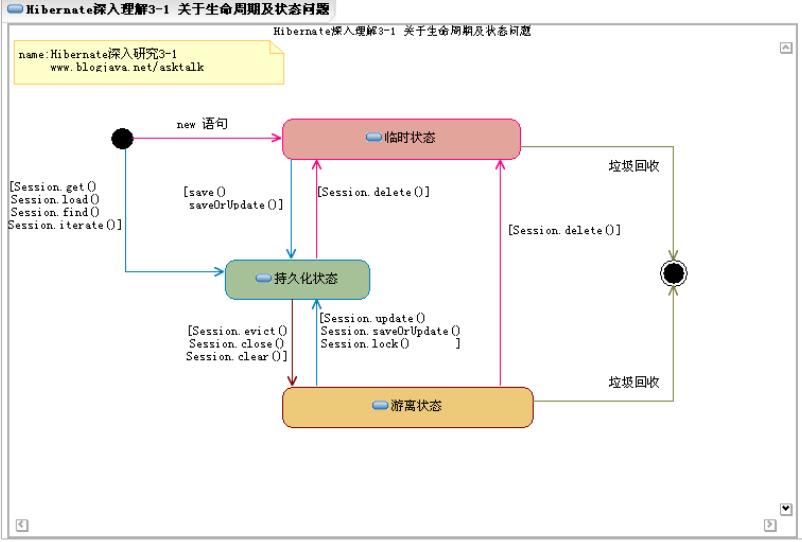
7.数据对象的三种状态
1.临时状态/瞬时状态
代表当前数据对象只在内存中存在,对象的主键属性无数据或数据无效.
临时状态对象的出现: 可能是新创建的对象,可能是被删除的持久状态或游离状态的数据对象.
2.持久状态
代表当前数据对象在内存中存在,且在数据库对应表中有相应的记录与之完全对应.
此状态下的数据对象被Session所管理.
此状态下的数据对象一定存在主键属性数据.
持久状态对象的出现: 可能是从数据库中查询对象时,临时状态对象被保存时,游离状态对象被更新或锁定时.
3.游离状态
代表当前数据对象在内存中存在,且在数据库对应表中有相应的记录.
此状态下的数据对象不被Session管理.
此状态下的数据对象一定存在主键属性数据.
游离状态对象的出现: 可能是被Session清理(clear/evict)时,或Session被关闭时.

8.增删查改:
TestSave:
package cn.zzsxt.test; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo; public class TestSave { public static void main(String[] args) { //步骤1:创建Configuration对象,调用configure()解析hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件 Configuration cfg = new Configuration(); //步骤2:创建SessionFactory,解析映射文件xxx.hbm.xml SessionFactory sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory(); //步骤3:创建Session,类似jdbc中Connection Session session = sf.openSession(); //步骤4:开启事务 Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); //步骤5:执行持久化操作 Userinfo user = new Userinfo(); user.setUserName("test"); user.setUserPass("test"); session.save(user); //步骤6:提交事务 tx.commit(); //步骤7:关闭session session.close(); } }
TestDelete:
package cn.zzsxt.test; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo; public class TestDelete { public static void main(String[] args) { Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure(); SessionFactory sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory(); Session session = sf.openSession(); //开启事务,应为hibernat默认没有开启事务,必须手工开启事务和提交事务,否则更改的数据无法保存至数据库中,查询可以不开启或提交事务 Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); //查询编号为17的用户信息 Userinfo user = session.get(Userinfo.class, 17); //删除用户信息 session.delete(user); tx.commit(); session.close(); } }
TestGetAll:
package cn.zzsxt.test; import java.util.List; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import org.hibernate.query.Query; import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo; public class TestGetAll { public static void main(String[] args) { Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure(); SessionFactory sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory(); Session session = sf.openSession(); //创建Query对象,用于执行查询HQL(Hiberante Query Language)语句 //String sql = select * from userinfo String hql="from Userinfo"; Query query = session.createQuery(hql); List<Userinfo> list = query.list(); for (Userinfo userinfo : list) { System.out.println(userinfo); } session.close(); } }
TestGetById:
package cn.zzsxt.test; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo; public class TestGetById { public static void main(String[] args) { Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure(); SessionFactory sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory(); Session session = sf.openSession(); //开启事务,应为hibernat默认没有开启事务,必须手工开启事务和提交事务,否则更改的数据无法保存至数据库中,查询可以不开启或提交事务 // Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); Userinfo user = session.get(Userinfo.class, 17); System.out.println(user); // tx.commit(); session.close(); } }
TestUpdate:
package cn.zzsxt.test; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; import cn.zzsxt.entity.Userinfo; public class TestUpdate { public static void main(String[] args) { Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure(); SessionFactory sf = cfg.buildSessionFactory(); Session session = sf.openSession(); //开启事务,应为hibernat默认没有开启事务,必须手工开启事务和提交事务,否则更改的数据无法保存至数据库中,查询可以不开启或提交事务 Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction(); //查询编号为17的用户信息 Userinfo user = session.get(Userinfo.class, 17); //修改用户信息 user.setUserName("test2"); user.setUserPass("test2"); // session.update(user); //savaOrUpdate()===>save()+update() session.saveOrUpdate(user); tx.commit(); session.close(); } }
以上是关于java:Hibernate框架(环境搭建,Hibernate.cfg.xml中属性含义,Hibernate常用API对象,HibernteUitl,对象生命周期图,数据对象的三种状态)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章