Java集合系列三Vector-Stack解析
Posted wlrhnh
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java集合系列三Vector-Stack解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
2017-07-29 12:59:14
一、简介
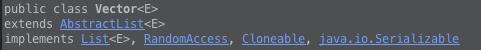
1、Vector继承关系
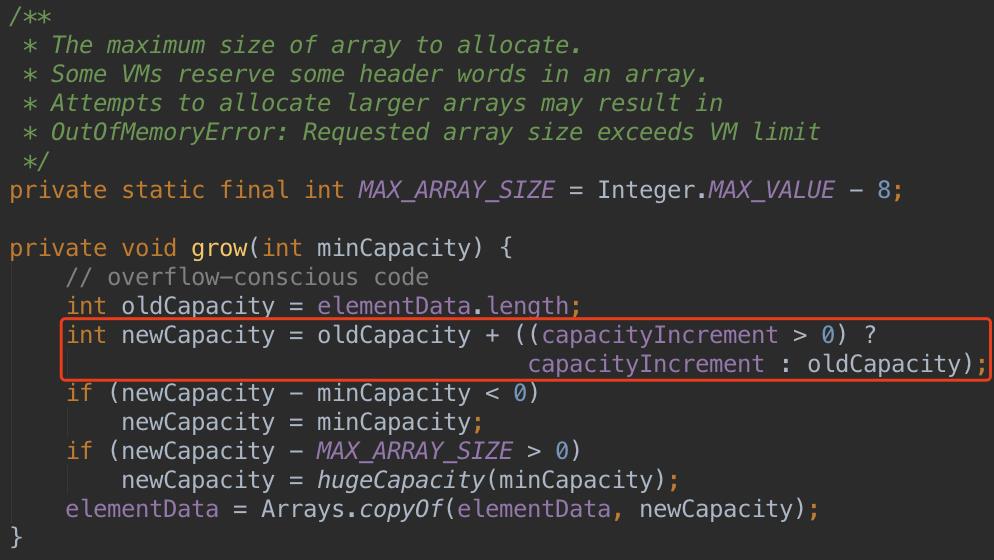
2、Vector类扩容
Vector类的实现和ArrayList极其相似,都使用数组存储元素,但是扩容策略不一样,ArrayList基本是按照1.5倍的思路扩容,Vector是按照创建Vector对象时设置的capacityIncrement值递增的,如果该值没有设置或者为0,则直接Double,如下:

3、Vector的线程安全性
Vector号称是线程安全的,它的安全性来自于几乎给每个方法都添加了synchronized关键字,由于锁对象是当前对象,只要有一个线程在执行某一个加锁的方法,也就是获得到当前对象这个锁对象,其他线程基本都不能再使用这个Vector对象了...这是一种很残暴的设计,估计这可能是synchronized刚出来之时,JDK团队的一时兴奋之作吧~
举几个例子:
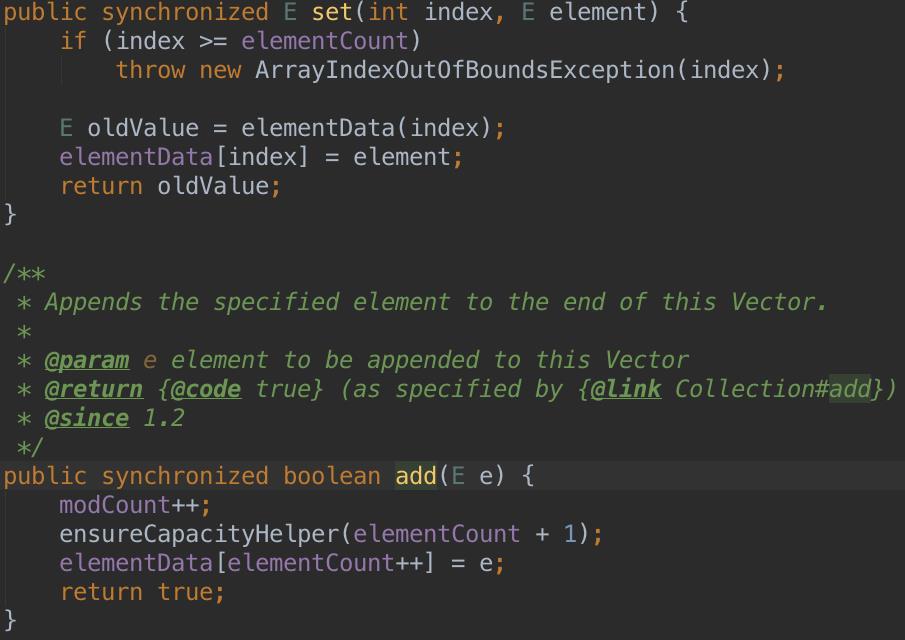
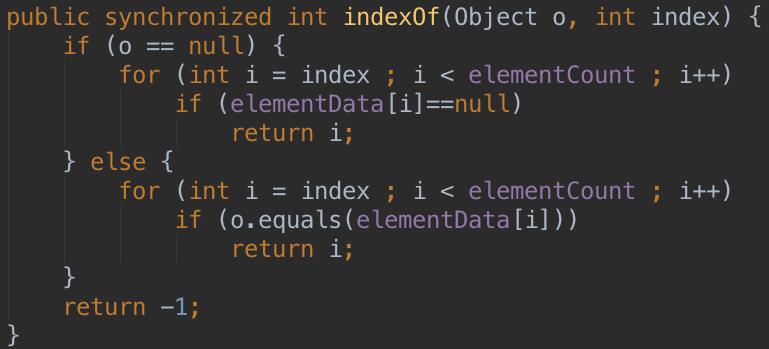
即便是有一些方法没有直接加synchronized关键字,至少它所调用的方法都是加了的。
4、Stack
Stack继承自Vector,提供了pop、push、peek、search等栈的特殊操作,源码如下:

1 package java.util; 2 3 /** 4 * The <code>Stack</code> class represents a last-in-first-out 5 * (LIFO) stack of objects. It extends class <tt>Vector</tt> with five 6 * operations that allow a vector to be treated as a stack. The usual 7 * <tt>push</tt> and <tt>pop</tt> operations are provided, as well as a 8 * method to <tt>peek</tt> at the top item on the stack, a method to test 9 * for whether the stack is <tt>empty</tt>, and a method to <tt>search</tt> 10 * the stack for an item and discover how far it is from the top. 11 * <p> 12 * When a stack is first created, it contains no items. 13 * 14 * <p>A more complete and consistent set of LIFO stack operations is 15 * provided by the {@link Deque} interface and its implementations, which 16 * should be used in preference to this class. For example: 17 * <pre> {@code 18 * Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();}</pre> 19 * 20 * @author Jonathan Payne 21 * @since JDK1.0 22 */ 23 public 24 class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> { 25 /** 26 * Creates an empty Stack. 27 */ 28 public Stack() { 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * Pushes an item onto the top of this stack. This has exactly 33 * the same effect as: 34 * <blockquote><pre> 35 * addElement(item)</pre></blockquote> 36 * 37 * @param item the item to be pushed onto this stack. 38 * @return the <code>item</code> argument. 39 * @see java.util.Vector#addElement 40 */ 41 public E push(E item) { 42 addElement(item); 43 44 return item; 45 } 46 47 /** 48 * Removes the object at the top of this stack and returns that 49 * object as the value of this function. 50 * 51 * @return The object at the top of this stack (the last item 52 * of the <tt>Vector</tt> object). 53 * @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty. 54 */ 55 public synchronized E pop() { 56 E obj; 57 int len = size(); 58 59 obj = peek(); 60 removeElementAt(len - 1); 61 62 return obj; 63 } 64 65 /** 66 * Looks at the object at the top of this stack without removing it 67 * from the stack. 68 * 69 * @return the object at the top of this stack (the last item 70 * of the <tt>Vector</tt> object). 71 * @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty. 72 */ 73 public synchronized E peek() { 74 int len = size(); 75 76 if (len == 0) 77 throw new EmptyStackException(); 78 return elementAt(len - 1); 79 } 80 81 /** 82 * Tests if this stack is empty. 83 * 84 * @return <code>true</code> if and only if this stack contains 85 * no items; <code>false</code> otherwise. 86 */ 87 public boolean empty() { 88 return size() == 0; 89 } 90 91 /** 92 * Returns the 1-based position where an object is on this stack. 93 * If the object <tt>o</tt> occurs as an item in this stack, this 94 * method returns the distance from the top of the stack of the 95 * occurrence nearest the top of the stack; the topmost item on the 96 * stack is considered to be at distance <tt>1</tt>. The <tt>equals</tt> 97 * method is used to compare <tt>o</tt> to the 98 * items in this stack. 99 * 100 * @param o the desired object. 101 * @return the 1-based position from the top of the stack where 102 * the object is located; the return value <code>-1</code> 103 * indicates that the object is not on the stack. 104 */ 105 public synchronized int search(Object o) { 106 int i = lastIndexOf(o); 107 108 if (i >= 0) { 109 return size() - i; 110 } 111 return -1; 112 } 113 114 /** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */ 115 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1224463164541339165L; 116 }
5、结尾
Vector和ArrayList的异同:
1、扩容策略不同;
2、线程安全的;
3、提供了一些独特的如removeElement()之类的方法;
4、其他方法的实现与ArrayList几乎是一致的,毕竟都是对数组的操作;
5、忽略这个类即可;
以上是关于Java集合系列三Vector-Stack解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
