第五章 springboot + mybatis
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了第五章 springboot + mybatis相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
springboot集成了springJDBC与JPA,但是没有集成mybatis,所以想要使用mybatis就要自己去集成。集成方式相当简单。
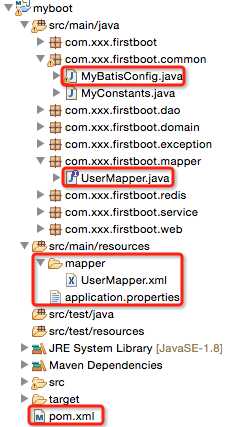
1、项目结构
2、pom.xml

<!-- 与数据库操作相关的依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 使用数据源 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.0.14</version> </dependency> <!-- mysql --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <!-- mybatis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.2.8</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>1.2.2</version> </dependency>
说明:
-
spring-boot-starter-jdbc:引入与数据库操作相关的依赖,例如daoSupport等
- druid:阿里巴巴的数据源
- mysql-connector-java:mysql连接jar,scope为runtime
- mybatis + mybatis-spring:mybatis相关jar
3、application.properties

jdbc.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://xxx:3306/mytestdb?zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 jdbc.username = root jdbc.password = vvvxxx mybatis.typeAliasesPackage=com.xxx.firstboot.domain mybatis.mapperLocations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
说明:
- mybatis.typeAliasesPackage:指定domain类的基包,即指定其在*Mapper.xml文件中可以使用简名来代替全类名(看后边的UserMapper.xml介绍)
-
mybatis.mapperLocations:指定*Mapper.xml的位置
4、com.xxx.firstboot.common.MyBatisConfig
作用:mybatis与springboot集成的入口

package com.xxx.firstboot.common; import java.util.Properties; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean; import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver; import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory; /** * springboot集成mybatis的基本入口 * 1)创建数据源 * 2)创建SqlSessionFactory */ @Configuration //该注解类似于spring配置文件 @MapperScan(basePackages="com.xxx.firstboot.mapper") public class MyBatisConfig { @Autowired private Environment env; /** * 创建数据源 * @Primary 该注解表示在同一个接口有多个实现类可以注入的时候,默认选择哪一个,而不是让@autowire注解报错 */ @Bean //@Primary public DataSource getDataSource() throws Exception{ Properties props = new Properties(); props.put("driverClassName", env.getProperty("jdbc.driverClassName")); props.put("url", env.getProperty("jdbc.url")); props.put("username", env.getProperty("jdbc.username")); props.put("password", env.getProperty("jdbc.password")); return DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(props); } /** * 根据数据源创建SqlSessionFactory */ @Bean public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource ds) throws Exception{ SqlSessionFactoryBean fb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); fb.setDataSource(ds);//指定数据源(这个必须有,否则报错) //下边两句仅仅用于*.xml文件,如果整个持久层操作不需要使用到xml文件的话(只用注解就可以搞定),则不加 fb.setTypeAliasesPackage(env.getProperty("mybatis.typeAliasesPackage"));//指定基包 fb.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(env.getProperty("mybatis.mapperLocations")));//指定xml文件位置 return fb.getObject(); } }
说明:
- 类上边添加两个
- @Configuration注解(该注解类似于spring的配置文件)
- @MapperScan注解,指定扫描的mapper接口所在的包
- 在该类中,注入了Environment实例,使用该实例可以去读取类路径下application.properties文件中的内容,读取文件内容的三种方式,见第二章 第二个spring-boot程序
- 在该类中,使用druid数据源定义了数据源Bean,spring-boot默认使用的是tomcat-jdbc数据源,这是springboot官方推荐的数据源(性能和并发性都很好)
- 根据数据源生成SqlSessionFactory
- 值得注意的是,数据源是必须指定的,否则springboot启动不了
- typeAliasesPackage和mapperLocations不是必须的,如果整个项目不需要用到*Mapper.xml来写SQL的话(即只用注解就可以搞定),那么不需要配
- @Primary注解:指定在同一个接口有多个实现类可以注入的时候,默认选择哪一个,而不是让@Autowire注解报错(一般用于多数据源的情况下)
这样之后,在项目中再使用springboot就和在ssm中(配置完成后)使用一样了。
5、com.xxx.firstboot.mapper.UserMapper

package com.xxx.firstboot.mapper; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; import com.xxx.firstboot.domain.User; public interface UserMapper { @Insert("INSERT INTO tb_user(username, password) VALUES(#{username},#{password})") public int insertUser(@Param("username") String username, @Param("password") String password); /** * 插入用户,并将主键设置到user中 * 注意:返回的是数据库影响条数,即1 */ public int insertUserWithBackId(User user); }
说明:该接口中有两个方法,
- 一个普通插入:直接用注解搞定
- 一个插入返回主键:需要使用xml来搞定

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- 指定工作空间,要与接口名相同,源代码没有去看,猜测应该是通过"这里的namespace.下边方法的id"来定位方法的 --> <mapper namespace="com.xxx.firstboot.mapper.UserMapper"> <!-- 若不需要自动返回主键,将useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"去掉即可(当然如果不需要自动返回主键,直接用注解即可) --> <insert id="insertUserWithBackId" parameterType="User" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" > <![CDATA[ INSERT INTO tb_user ( username, password ) VALUES ( #{username, jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{password, jdbcType=VARCHAR} ) ]]> </insert> </mapper>
6、com.xxx.firstboot.dao.UserDao

package com.xxx.firstboot.dao; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import com.xxx.firstboot.domain.User; import com.xxx.firstboot.mapper.UserMapper; @Repository public class UserDao { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; public int insertUser(String username, String password){ return userMapper.insertUser(username, password); } public int insertUserWithBackId(User user){ return userMapper.insertUserWithBackId(user); } }
7、com.xxx.firstboot.service.UserService

package com.xxx.firstboot.service; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import com.xxx.firstboot.dao.UserDao; import com.xxx.firstboot.domain.User; @Service public class UserService { @Autowired private UserDao userDao; public boolean addUser(String username, String password){ return userDao.insertUser(username, password)==1?true:false; } public User addUserWithBackId(String username, String password){ User user = new User(); user.setUsername(username); user.setPassword(password); userDao.insertUserWithBackId(user);//该方法后,主键已经设置到user中了 return user; } }
8、com.xxx.firstboot.controller.UserController

package com.xxx.firstboot.web; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import com.xxx.firstboot.domain.User; import com.xxx.firstboot.service.UserService; import io.swagger.annotations.Api; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponse; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponses; @RestController @RequestMapping("/user") @Api("userController相关api") public class UserController { @Autowired private UserService userService; @ApiOperation("添加用户") @ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(paramType="query",name="username",dataType="String",required=true,value="用户的姓名",defaultValue="zhaojigang"), @ApiImplicitParam(paramType="query",name="password",dataType="String",required=true,value="用户的密码",defaultValue="wangna") }) @ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"), @ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对") }) @RequestMapping(value="/addUser",method=RequestMethod.POST) public boolean addUser(@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password) { return userService.addUser(username,password); } @ApiOperation("添加用户且返回已经设置了主键的user实例") @ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(paramType="query",name="username",dataType="String",required=true,value="用户的姓名",defaultValue="zhaojigang"), @ApiImplicitParam(paramType="query",name="password",dataType="String",required=true,value="用户的密码",defaultValue="wangna") }) @ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"), @ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对") }) @RequestMapping(value="/addUserWithBackId",method=RequestMethod.POST) public User addUserWithBackId(@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password) { return userService.addUserWithBackId(username, password); } }
测试:
进入项目的pom.xml文件所在目录,执行"mvn spring-boot:run"(这是最推荐的spring-boot的运行方式),另外一种在主类上右击-->"run as"-->"java application"不常用
参考自:
http://www.111cn.net/jsp/Java/93604.htm :springboot+mybatis+多数据源
http://blog.csdn.net/xiaoyu411502/article/details/48164311:springboot+mybatis+读写分离(其实读写分离就是两个数据源对两个库进行操作)
以上是关于第五章 springboot + mybatis的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
