JAVA中重写equals()方法为什么要重写hashcode()方法?
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JAVA中重写equals()方法为什么要重写hashcode()方法?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
object对象中的 public boolean equals(Object obj),对于任何非空引用值 x 和 y,当且仅当 x 和 y 引用同一个对象时,此方法才返回 true;
注意:当此方法被重写时,通常有必要重写 hashCode 方法,以维护 hashCode 方法的常规协定,该协定声明相等对象必须具有相等的哈希码。如下:
(1)当obj1.equals(obj2)为true时,obj1.hashCode() == obj2.hashCode()必须为true
(2)当obj1.hashCode() == obj2.hashCode()为false时,obj1.equals(obj2)必须为false
如果不重写equals,那么比较的将是对象的引用是否指向同一块内存地址,重写之后目的是为了比较两个对象的value值是否相等。特别指出利用equals比较八大包装对象
(如int,float等)和String类(因为该类已重写了equals和hashcode方法)对象时,默认比较的是值,在比较其它自定义对象时都是比较的引用地址
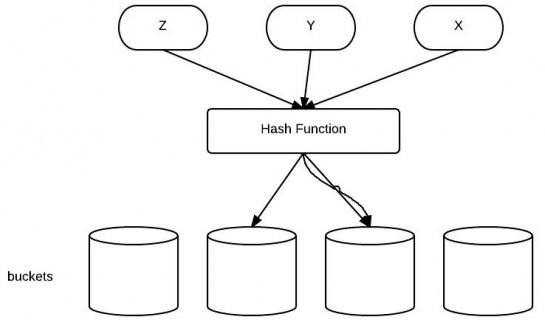
hashcode是用于散列数据的快速存取,如利用HashSet/HashMap/Hashtable类来存储数据时,都是根据存储对象的hashcode值来进行判断是否相同的。
这样如果我们对一个对象重写了euqals,意思是只要对象的成员变量值都相等那么euqals就等于true,但不重写hashcode,那么我们再new一个新的对象,
当原对象.equals(新对象)等于true时,两者的hashcode却是不一样的,由此将产生了理解的不一致,如在存储散列集合时(如Set类),将会存储了两个值一样的对象,
导致混淆,因此,就也需要重写hashcode()
举例说明:
- import java.util.*;
- public class HelloWorld {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /*
- Collection c = new HashSet();
- c.add("hello");
- c.add(new Name("f1","l1"));
- c.add(new Integer(100));
- c.remove("hello");
- c.remove(new Integer(100));
- System.out.println(c.remove(new Name("f1","l1")));
- */
- Name n1 = new Name("01");
- Name n2 = new Name("01");
- Collection c = new HashSet();
- c.add(n1);
- System.out.println("------------");
- c.add(n2);
- System.out.println("------------");
- System.out.println(n1.equals(n2));
- System.out.println("------------");
- System.out.println(n1.hashCode());
- System.out.println(n2.hashCode());
- System.out.println(c);
- }
- }
- class Name {
- private String id;
- public Name(String id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- public String toString(){
- return this.id;
- }
- public boolean equals(Object obj) {
- if (obj instanceof Name) {
- Name name = (Name) obj;
- System.out.println("equal"+ name.id);
- return (id.equals(name.id));
- }
- return super.equals(obj);
- }
- public int hashCode() {
- Name name = (Name) this;
- System.out.println("Hash" + name.id);
- return id.hashCode();
- }
- }

就这个程序进行分析,在第一次添加时,调用了hashcode()方法,将hashcode存入对象中,第二次也一样,然后对hashcode进行比较。hashcode也只用于HashSet/HashMap/Hashtable类存储数据,所以会用于比较,需要重写
总结,自定义类要重写equals方法来进行等值比较,自定义类要重写compareTo方法来进行不同对象大小的比较,重写hashcode方法为了将数据存入HashSet/HashMap/Hashtable类时进行比较
以上是关于JAVA中重写equals()方法为什么要重写hashcode()方法?的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章