Java 多线程与锁
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java 多线程与锁相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
多线程
线程和进程的区别
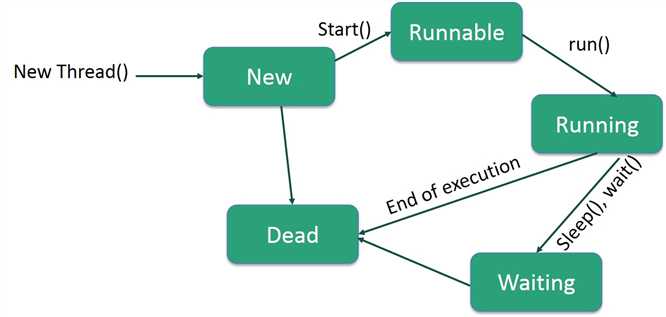
创建线程
- 通过实现Runnable 接口
1 class RunnableDemo implements Runnable{ 2 private Thread t; // create a thread 3 private String threadName; 4 5 RunnableDemo(String name){ 6 threadName = name; 7 System.out.println("Creating " + threadName); 8 try{ 9 for(int i = 3; i > 0; i--){ 10 System.out.println("Thread: " + threadName + ", " + i); 11 // wait for a while. 12 Thread.sleep(50); 13 } 14 }catch (InterruptedException e){ 15 System.out.println("Thread " + threadName +" interrupted"); 16 } 17 System.out.println("Thread “ + threadName + " exiting."); 18 } 19 20 21 public void start(){ 22 System.out.println("Starting ” + threadName); 23 if( t == null){ 24 t = new Thread(this, threadName); 25 t.start(); 26 } 27 } 28 29 public class TestThread{ 30 public static void main(String[] args){ 31 RunnableDemo R1 = new RunnableDemo("Thread-1"); 32 R1.start(); 33 34 RunnableDemo R2 = new RunnableDemo("Thread-2"); 35 R2.start(); 36 } 37 }
When an object implementing interface Runnable is used to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object‘s run method to be called in that separately executing thread.
- 通过继承Thread类
class ThreadDemo extends Thread { private Thread t; private String threadName; ThreadDemo( String name) { threadName = name; System.out.println("Creating " + threadName ); } public void run() { System.out.println("Running " + threadName ); try { for(int i = 4; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println("Thread: " + threadName + ", " + i); // Let the thread sleep for a while. Thread.sleep(50); } }catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Thread " + threadName + " interrupted."); } System.out.println("Thread " + threadName + " exiting."); } public void start () { System.out.println("Starting " + threadName ); if (t == null) { t = new Thread (this, threadName); t.start (); } } } public class TestThread { public static void main(String args[]) { ThreadDemo T1 = new ThreadDemo( "Thread-1"); T1.start(); ThreadDemo T2 = new ThreadDemo( "Thread-2"); T2.start(); } }
java.lang.Thread
public class Thread extends Object implements Runnable
锁
同步
参考:
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/java/java_multithreading.htm
http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/Runnable.html
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/Thread.html
以上是关于Java 多线程与锁的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章