编码剖析Spring装配基本属性的原理
Posted 疯子加天才
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了编码剖析Spring装配基本属性的原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/52856465
上回我们已经讲到了Spring依赖注入的第一种方式,现在我们来详解第二种方式,须知这一切都是以编码剖析Spring依赖注入的原理案例为基础的。
我们将Spring的配置文件——beans.xml的内容改为:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 依赖注入的第一种方式 -->
<!--
<bean id="personDao" class="cn.itcast.dao.impl.PersonDaoBean"></bean>
<bean id="personService" class="cn.itcast.service.impl.PersonServiceBean">
<property name="personDao" ref="personDao"></property>
</bean>
-->
<!-- 依赖注入第二种方式: -->
<bean id="personService" class="cn.itcast.service.impl.PersonServiceBean">
<property name="personDao">
<bean class="cn.itcast.dao.impl.PersonDaoBean"></bean>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>这种方式是使用内部bean依赖注入,其缺点就是:该bean不能被其他bean使用。
接下来将测试类——SpringTest.java的代码改为:
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
PersonService personService = (PersonService) ctx.getBean("personService");
personService.save();
ctx.close(); // 正常关闭Spring容器
}
}测试test()方法,将发现Eclipse控制台打印: 
接下来,我们将讲解基本类型对象的依赖注入。
Spring装配基本属性
首先我们将PersonServiceBean类的代码改为:
public class PersonServiceBean implements PersonService {
private PersonDao personDao;
private String name;
private Integer id;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public PersonDao getPersonDao() {
return personDao;
}
public void setPersonDao(PersonDao personDao) {
this.personDao = personDao;
}
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("id = " + id + ", name = " + name);
personDao.add();
}
}接着我们要将Spring的配置文件的内容改为:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 依赖注入的第一种方式 -->
<!--
<bean id="personDao" class="cn.itcast.dao.impl.PersonDaoBean"></bean>
<bean id="personService" class="cn.itcast.service.impl.PersonServiceBean">
<property name="personDao" ref="personDao"></property>
</bean>
-->
<!-- 依赖注入第二种方式: -->
<bean id="personService" class="cn.itcast.service.impl.PersonServiceBean">
<property name="personDao">
<bean class="cn.itcast.dao.impl.PersonDaoBean"></bean>
</property>
<!-- 为基本类型属性注入值 -->
<property name="name" value="itcast" />
<property name="id" value="88" />
</bean>
</beans>最后测试SpringTest类的test()方法,将发现Eclipse控制台打印: 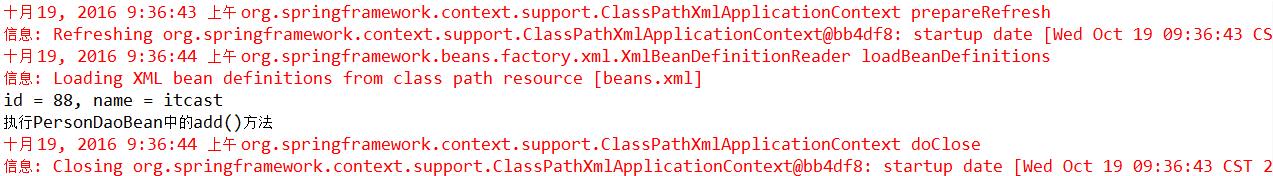
到这里,自然就会产生一个疑问——Spring内部是如何注入基本类型对象的呢?有了疑问,我们接下来就来深入剖析其中的原理。
编码剖析Spring装配基本属性的原理
我们应确保Spring的配置文件——beans.xml的内容为:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 依赖注入的第一种方式 -->
<!--
<bean id="personDao" class="cn.itcast.dao.impl.PersonDaoBean"></bean>
<bean id="personService" class="cn.itcast.service.impl.PersonServiceBean">
<property name="personDao" ref="personDao"></property>
</bean>
-->
<!-- 依赖注入第二种方式: -->
<bean id="personDao" class="cn.itcast.dao.impl.PersonDaoBean"></bean>
<bean id="personService" class="cn.itcast.service.impl.PersonServiceBean">
<property name="personDao" ref="personDao"></property>
<!-- 为基本类型属性注入值 -->
<property name="name" value="itcast" />
<property name="id" value="88" />
</bean>
</beans>对照以上Spring的配置文件的内容,我们应该修改PropertyDefinition类的代码为:
/**
* 该JavaBean专门用户存放<property ...>的信息
* @author li ayun
*
*/
public class PropertyDefinition {
private String name;
private String ref;
private String value;
public PropertyDefinition(String name, String ref, String value) {
this.name = name;
this.ref = ref;
this.value = value;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getRef() {
return ref;
}
public void setRef(String ref) {
this.ref = ref;
}
}- 1
接下来我们就要对传智播客版的Spring容器修修改改了,由于我们要将把本身为字符串的值转成相应的属性类型的值,所以就要用到commons-beanutils工具,即要将commons-beanutils-1.9.2.jar包导入到项目中去。这样,ItcastClassPathXMLApplicationContext类的代码就应该为:
/**
* 传智播客版Spring容器
* @author li ayun
*
*/
public class ItcastClassPathXMLApplicationContext {
private List<BeanDefinition> beanDefines = new ArrayList<BeanDefinition>();
private Map<String, Object> sigletons = new HashMap<String, Object>();
public ItcastClassPathXMLApplicationContext(String filename) {
this.readXML(filename);
this.instanceBeans();
this.injectObject();
}
/**
* 为bean对象的属性(依赖)注入值
*/
private void injectObject() {
for (BeanDefinition beanDefinition : beanDefines) {
Object bean = sigletons.get(beanDefinition.getId());
if (bean != null) {
try {
PropertyDescriptor[] ps = Introspector.getBeanInfo(bean.getClass()).getPropertyDescriptors();
for (PropertyDefinition propertyDefinition : beanDefinition.getPropertys()) {
for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDesc : ps) {
if (propertyDefinition.getName().equals(propertyDesc.getName())) {
Method setter = propertyDesc.getWriteMethod(); // 获取属性的setter方法,若setter方法是private的
if (setter != null) { // 最好判断有无setter方法,因为属性可以没有setter方法
Object value = null;
if (propertyDefinition.getRef() != null && !"".equals(propertyDefinition.getRef().trim()) ) {
value = sigletons.get(propertyDefinition.getRef());
} else { // 注入基本类型
value = ConvertUtils.convert(propertyDefinition.getValue(), propertyDesc.getPropertyType()); // 把本身为字符串的值转成相应的属性类型的值
}
setter.setAccessible(true); // 允许访问私有的setter方法
setter.invoke(bean, value); // 把引用对象注入到属性中
}
break;
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 完成bean的实例化
*/
private void instanceBeans() {
for (BeanDefinition beanDefinition : beanDefines) {
try {
if (beanDefinition.getClassName() != null && !"".equals(beanDefinition.getClassName().trim())) {
sigletons.put(beanDefinition.getId(), Class.forName(beanDefinition.getClassName()).newInstance());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 读取XML配置文件
* @param filename
*/
private void readXML(String filename) {
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
Document document = null;
try {
URL xmlpath = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(filename);
document = saxReader.read(xmlpath);
Map<String, String> nsMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
nsMap.put("ns", "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"); // 加入命名空间
XPath xsub = document.createXPath("//ns:beans/ns:bean"); // 创建beans/bean查询路径
xsub.setNamespaceURIs(nsMap); // 设置命名空间
List<Element> beans = xsub.selectNodes(document); // 获取文档下所有bean节点
for (Element element : beans) {
String id = element.attributeValue("id"); // 获取id属性值
String clazz = element.attributeValue("class"); // 获取class属性值
BeanDefinition beanDefine = new BeanDefinition(id, clazz);
XPath propertysub = element.createXPath("ns:property");
propertysub.setNamespaceURIs(nsMap); // 设置命名空间
List<Element> propertys = propertysub.selectNodes(element);
for (Element property : propertys) {
String propertyName = property.attributeValue("name");
String propertyRef = property.attributeValue("ref");
// System.out.println(propertyName + "=" + propertyRef); // 测试用
String propertyValue = property.attributeValue("value");
PropertyDefinition propertyDefinition = new PropertyDefinition(propertyName, propertyRef, propertyValue);
beanDefine.getPropertys().add(propertyDefinition);
}
beanDefines.add(beanDefine);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取bean实例
* @param beanName
* @return
*/
public Object getBean(String beanName) {
return this.sigletons.get(beanName);
}
}- 1
最后,我们就要对传智播客版的Spring容器测试一把了,看它是否真能如我们所想的那样完成对基本类型对象的注入。我们修改单元测试SpringTest类的代码为:
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test() {
ItcastClassPathXMLApplicationContext ctx = new ItcastClassPathXMLApplicationContext("beans.xml");
PersonService personService = (PersonService) ctx.getBean("personService");
personService.save();
}
}测试test(),可看到Eclipse控制台打印: 
这就已说明模拟Spring容器成功了,我们也对其中的原理有了更深刻的认识。如要查看源码,可点击编码剖析Spring装配基本属性的原理进行下载。
以上是关于编码剖析Spring装配基本属性的原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章