jenkins实战安装java maven项目
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了jenkins实战安装java maven项目相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、构建配置搭建
1、创建一个新的项目,选择maven来操作
2、要想构建maven项目,代码库中必须要有一个maven
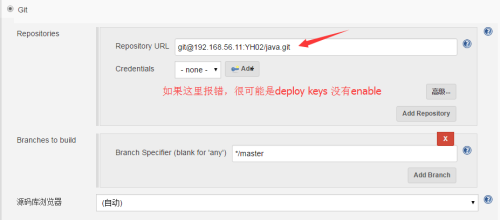
3、把maven压缩包,解压到一个目录,在当前目录下使用git上传到gitlab项目库
git init git add . git commit -m "maven" git remote add origin [email protected]:YH02/java.git git push origin master
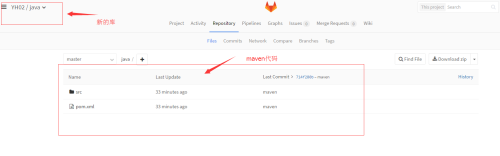
4、在gitlab上面新构建一个项目(例子java)并上传maven项目代码
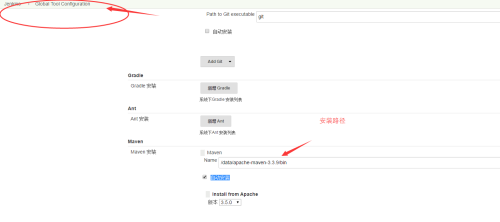
(1)maven可以在jenkin的系统设置里面的全局工具设置选项里面有manven安装
(2)手动安装maven
apache-maven-3.3.9-bin.tar.gz# 把包上传到jenkins服务器 [[email protected] ~]# tar xf apache-maven-3.3.9-bin.tar.gz -C /data/ [[email protected] ~]# ll /data/ total 0 drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 92 May 14 21:40 apache-maven-3.3.9 [[email protected] ~]# export PATH=$PATH:/data/apache-maven-3.3.9/bin #增加环境变量,可以写到bashrc里面 [[email protected] ~]# mvn -v Apache Maven 3.3.9 (bb52d8502b132ec0a5a3f4c09453c07478323dc5; 2015-11-11T00:41:47+08:00) Maven home: /data/apache-maven-3.3.9 Java version: 1.8.0_131, vendor: Oracle Corporation Java home: /usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.131-2.b11.el7_3.x86_64/jre Default locale: en_US, platform encoding: UTF-8 OS name: "linux", version: "3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64", arch: "amd64", family: "unix"
(3)在jenkins里面填入manve的安装路径
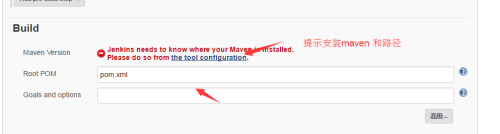
5、SRC是核心文件,pom文件是开发提供
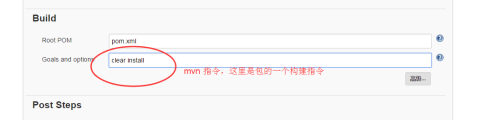
6、保存 开始构建
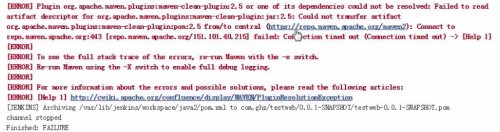
报错:
maven库不能连接,由于是国外的服务器,这里我们将配置成国内的服务器
编辑maven的配置文件
[[email protected] ~]# cd /data/apache-maven-3.3.9/ [[email protected] /data/apache-maven-3.3.9]# cd conf/ [[email protected] /data/apache-maven-3.3.9/conf]# ll total 16 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 36 Nov 11 2015 logging -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 10216 Nov 11 2015 settings.xml -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3649 Nov 11 2015 toolchains.xml [[email protected] /data/apache-maven-3.3.9/conf]# cp settings.xml settings.xml.bak [[email protected] /data/apache-maven-3.3.9/conf]# vim settings.xml [[email protected] /data/apache-maven-3.3.9/conf]# vim settings.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd"> <mirrors> <mirror> <id>yxyc</id> <mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf> <url> #镜像库 </mirror> </mirrors> <profiles> <profile> <id>default</id> <repositories> <repository> <id>public</id> <url> #本地库 <releases> <enabled>true</enabled> </releases>
查看修改了那些东西
[[email protected] /data/apache-maven-3.3.9/conf]# diff settings.xml settings.xml.bak 1a2,45 > > <!-- > Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one > or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file > distributed with this work for additional information > regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file > to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the > "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance > with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at > > http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 > > Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, > software distributed under the License is distributed on an > "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY > KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the > specific language governing permissions and limitations > under the License. > --> > > <!-- > | This is the configuration file for Maven. It can be specified at two levels: > | > | 1. User Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for a single user, > | and is normally provided in ${user.home}/.m2/settings.xml. > | > | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: > | > | -s /path/to/user/settings.xml > | > | 2. Global Level. This settings.xml file provides configuration for all Maven > | users on a machine (assuming they‘re all using the same Maven > | installation). It‘s normally provided in > | ${maven.home}/conf/settings.xml. > | > | NOTE: This location can be overridden with the CLI option: > | > | -gs /path/to/global/settings.xml > | > | The sections in this sample file are intended to give you a running start at > | getting the most out of your Maven installation. Where appropriate, the default > | values (values used when the setting is not specified) are provided. > | > |--> 5,31c49,256 < <mirrors> < <mirror> < <id>baijia</id> < <mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf> < <url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url> < </mirror> < </mirrors> < <profiles> < <profile> < <id>default</id> < <repositories> < <repository> < <id>public</id> < <url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url> < <releases> < <enabled>true</enabled> < </releases> < <snapshots> < <enabled>true</enabled> < </snapshots> < </repository> < </repositories> < </profile> < </profiles> < <activeProfiles> < <activeProfile>default</activeProfile> < </activeProfiles> --- > <!-- localRepository > | The path to the local repository maven will use to store artifacts. > | > | Default: ${user.home}/.m2/repository > <localRepository>/path/to/local/repo</localRepository> > --> > > <!-- interactiveMode > | This will determine whether maven prompts you when it needs input. If set to false, > | maven will use a sensible default value, perhaps based on some other setting, for > | the parameter in question. > | > | Default: true > <interactiveMode>true</interactiveMode> > --> > > <!-- offline > | Determines whether maven should attempt to connect to the network when executing a build. > | This will have an effect on artifact downloads, artifact deployment, and others. > | > | Default: false > <offline>false</offline> > --> > > <!-- pluginGroups > | This is a list of additional group identifiers that will be searched when resolving plugins by their prefix, i.e. > | when invoking a command line like "mvn prefix:goal". Maven will automatically add the group identifiers > | "org.apache.maven.plugins" and "org.codehaus.mojo" if these are not already contained in the list. > |--> > <pluginGroups> > <!-- pluginGroup > | Specifies a further group identifier to use for plugin lookup. > <pluginGroup>com.your.plugins</pluginGroup> > --> > </pluginGroups> > > <!-- proxies > | This is a list of proxies which can be used on this machine to connect to the network. > | Unless otherwise specified (by system property or command-line switch), the first proxy > | specification in this list marked as active will be used. > |--> > <proxies> > <!-- proxy > | Specification for one proxy, to be used in connecting to the network. > | > <proxy> > <id>optional</id> > <active>true</active> > <protocol>http</protocol> > <username>proxyuser</username> > <password>proxypass</password> > <host>proxy.host.net</host> > <port>80</port> > <nonProxyHosts>local.net|some.host.com</nonProxyHosts> > </proxy> > --> > </proxies> > > <!-- servers > | This is a list of authentication profiles, keyed by the server-id used within the system. > | Authentication profiles can be used whenever maven must make a connection to a remote server. > |--> > <servers> > <!-- server > | Specifies the authentication information to use when connecting to a particular server, identified by > | a unique name within the system (referred to by the ‘id‘ attribute below). > | > | NOTE: You should either specify username/password OR privateKey/passphrase, since these pairings are > | used together. > | > <server> > <id>deploymentRepo</id> > <username>repouser</username> > <password>repopwd</password> > </server> > --> > > <!-- Another sample, using keys to authenticate. > <server> > <id>siteServer</id> > <privateKey>/path/to/private/key</privateKey> > <passphrase>optional; leave empty if not used.</passphrase> > </server> > --> > </servers> > > <!-- mirrors > | This is a list of mirrors to be used in downloading artifacts from remote repositories. > | > | It works like this: a POM may declare a repository to use in resolving certain artifacts. > | However, this repository may have problems with heavy traffic at times, so people have mirrored > | it to several places. > | > | That repository definition will have a unique id, so we can create a mirror reference for that > | repository, to be used as an alternate download site. The mirror site will be the preferred > | server for that repository. > |--> > <mirrors> > <!-- mirror > | Specifies a repository mirror site to use instead of a given repository. The repository that > | this mirror serves has an ID that matches the mirrorOf element of this mirror. IDs are used > | for inheritance and direct lookup purposes, and must be unique across the set of mirrors. > | > <mirror> > <id>mirrorId</id> > <mirrorOf>repositoryId</mirrorOf> > <name>Human Readable Name for this Mirror.</name> > <url>http://my.repository.com/repo/path</url> > </mirror> > --> > </mirrors> > > <!-- profiles > | This is a list of profiles which can be activated in a variety of ways, and which can modify > | the build process. Profiles provided in the settings.xml are intended to provide local machine- > | specific paths and repository locations which allow the build to work in the local environment. > | > | For example, if you have an integration testing plugin - like cactus - that needs to know where > | your Tomcat instance is installed, you can provide a variable here such that the variable is > | dereferenced during the build process to configure the cactus plugin. > | > | As noted above, profiles can be activated in a variety of ways. One way - the activeProfiles > | section of this document (settings.xml) - will be discussed later. Another way essentially > | relies on the detection of a system property, either matching a particular value for the property, > | or merely testing its existence. Profiles can also be activated by JDK version prefix, where a > | value of ‘1.4‘ might activate a profile when the build is executed on a JDK version of ‘1.4.2_07‘. > | Finally, the list of active profiles can be specified directly from the command line. > | > | NOTE: For profiles defined in the settings.xml, you are restricted to specifying only artifact > | repositories, plugin repositories, and free-form properties to be used as configuration > | variables for plugins in the POM. > | > |--> > <profiles> > <!-- profile > | Specifies a set of introductions to the build process, to be activated using one or more of the > | mechanisms described above. For inheritance purposes, and to activate profiles via <activatedProfiles/> > | or the command line, profiles have to have an ID that is unique. > | > | An encouraged best practice for profile identification is to use a consistent naming convention > | for profiles, such as ‘env-dev‘, ‘env-test‘, ‘env-production‘, ‘user-jdcasey‘, ‘user-brett‘, etc. > | This will make it more intuitive to understand what the set of introduced profiles is attempting > | to accomplish, particularly when you only have a list of profile id‘s for debug. > | > | This profile example uses the JDK version to trigger activation, and provides a JDK-specific repo. > <profile> > <id>jdk-1.4</id> > > <activation> > <jdk>1.4</jdk> > </activation> > > <repositories> > <repository> > <id>jdk14</id> > <name>Repository for JDK 1.4 builds</name> > <url>http://www.myhost.com/maven/jdk14</url> > <layout>default</layout> > <snapshotPolicy>always</snapshotPolicy> > </repository> > </repositories> > </profile> > --> > > <!-- > | Here is another profile, activated by the system property ‘target-env‘ with a value of ‘dev‘, > | which provides a specific path to the Tomcat instance. To use this, your plugin configuration > | might hypothetically look like: > | > | ... > | <plugin> > | <groupId>org.myco.myplugins</groupId> > | <artifactId>myplugin</artifactId> > | > | <configuration> > | <tomcatLocation>${tomcatPath}</tomcatLocation> > | </configuration> > | </plugin> > | ... > | > | NOTE: If you just wanted to inject this configuration whenever someone set ‘target-env‘ to > | anything, you could just leave off the <value/> inside the activation-property. > | > <profile> > <id>env-dev</id> > > <activation> > <property> > <name>target-env</name> > <value>dev</value> > </property> > </activation> > > <properties> > <tomcatPath>/path/to/tomcat/instance</tomcatPath> > </properties> > </profile> > --> > </profiles> > > <!-- activeProfiles > | List of profiles that are active for all builds. > | > <activeProfiles> > <activeProfile>alwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile> > <activeProfile>anotherAlwaysActiveProfile</activeProfile> > </activeProfiles> > -->
二、部署
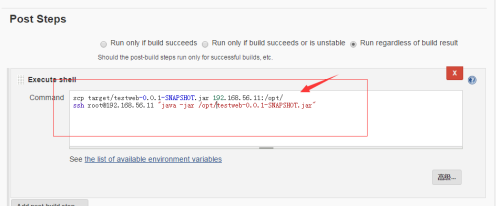
上面的构建完毕后,接下来是部署了。
我们要在java1上配置里面,写入新的内容,来完成构建完毕后,自动部署的功能!!!
jenkins 打包完毕后,文件会生成到这个目录
[[email protected] ~]# cd /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/ java/ java1/ php/ php-deploy/ [[email protected] ~]# cd /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/java1/ builds/ lastStable/ modules/ workspace/ config.xml lastSuccessful/ nextBuildNumber [[email protected] ~]# cd /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/java1/workspace/ [[email protected] /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/java1/workspace]# ll total 8 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1574 May 14 22:13 pom.xml drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 28 May 14 22:13 src drwxr-xr-x 7 root root 4096 May 14 22:25 target [[email protected] /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/java1/workspace]# cd target/ [[email protected] /var/lib/jenkins/jobs/java1/workspace/target]# ll total 8 drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 16 May 14 22:23 classes drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 27 May 14 22:24 maven-archiver drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 34 May 14 22:23 maven-status -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2435 May 14 22:24 original-testweb-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 79 May 14 22:23 surefire-reports drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 16 May 14 22:23 test-classes -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2662 May 14 22:25 testweb-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
三 maven下载的jar包存放在那里了
在家目录下面有一个.m2文件,下载的jar包都会保存在本地这里
[[email protected] ~]# cd .m2/ [[email protected] ~/.m2]# ll total 4 drwxr-xr-x 13 root root 4096 May 14 22:24 repository [[email protected] ~/.m2]# cd repository/ [[email protected] ~/.m2/repository]# ll total 0 drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 66 May 14 22:24 asm drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 37 May 14 22:21 backport-util-concurrent drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 24 May 14 22:19 classworlds drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 29 May 14 22:25 com drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 24 May 14 22:19 commons-cli drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 25 May 14 22:24 commons-lang drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 32 May 14 22:21 commons-logging drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 17 May 14 22:24 jdom drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 18 May 14 22:18 junit drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 18 May 14 22:21 log4j drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 61 May 14 22:21 org
本文出自 “圈中一鸟” 博客,谢绝转载!
以上是关于jenkins实战安装java maven项目的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
docker与jenkins的自动化CI/CD流水线实战(svn)
使用Jenkins自动编译我的 java 项目 git maven jenkins
Jenkins+Gradle+Sonar进行Java项目代码分析