electron-vue架构解析4-页面元素渲染过程分析(原)
Posted 工程师阿杜
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了electron-vue架构解析4-页面元素渲染过程分析(原)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
上一节介绍了开发环境的创建过程,这一节我们来看具体页面渲染的过程。
由于页面渲染都是在渲染进程完成的,我们就从渲染进程的配置文件来看入口在哪里。
前面介绍过,渲染进程公用了两个配置文件,一个是electron-vue/dev-client.js,他负责在界面上提示当前的编译步骤,而另一个配置文件在webpack.renderer.config.js中定义:
let rendererConfig =
...
entry:
renderer: path.join(__dirname, '../src/renderer/main.js')
,
...
也就是说,渲染进程的真正入口文件在src/renderer/main.js里面。
我们来看这个文件内容:
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
if (!process.env.IS_WEB) Vue.use(require('vue-electron'))
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue(
components: App ,
router,
template: '<App/>'
).$mount('#app')这个文件内容很简单,就是创建一个Vue对象,并将App这个Vue组件挂载到页面的app元素挂载上去。
这里的App组件根据import语句看到,他就是当前目录下的App.vue文件,由于在webpack配置的extensions字段中说明了所有vue格式文件在引用时都无需添加后缀,因此这里的import只需要使用App即可。
那么这个App组件究竟挂载到哪里的html上呢?我们还要从webpack配置说起。
渲染进程的webpack中使用了一个html-webpack-plugin的插件,可以根据模板生成首页的html:
new HtmlWebpackPlugin(
filename: 'index.html',
template: path.resolve(__dirname, '../src/index.ejs'),
minify:
collapseWhitespace: true,
removeAttributeQuotes: true,
removeComments: true
,
nodeModules: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
? path.resolve(__dirname, '../node_modules')
: false
),这说明模板就是src/index.ejs文件:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>electron-vue-framework</title>
<% if (htmlWebpackPlugin.options.nodeModules) %>
<script>
require('module').globalPaths.push('<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.nodeModules.replace(/\\\\/g, '\\\\\\\\') %>')
</script>
<% %>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'development') window.__static = require('path').join(__dirname, '/static').replace(/\\\\/g, '\\\\\\\\')
</script>
</body>
</html>这个模板会被html-webpack-plugin插件生成为index.html文件,而这个模板中就包含了唯一的
app。
也就是说,App这个Vue组件的挂载点就在生成的index.html文件上,并且是整个页面唯一的元素。
我们接下来看App这个组件的内容:
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default
name: 'electron-vue-framework'
</script>这个组件说明,内部包含一个路由控件,并且没有指定具体路由地址(那么Vue就会加载路由中的默认地址),我们来看router/index.js中为Vue定义的路由表:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router(
routes: [
path: '/',
name: 'landing-page',
component: require('@/components/LandingPage').default
,
path: '*',
redirect: '/'
]
)这说明默认路由叫做landing-page,对应的组件是LandingPage.vue,我们来看这个组件:
<template>
<div id="wrapper">
<img id="logo" src="~@/assets/logo.png" alt="electron-vue">
<main>
<div class="left-side">
<span class="title">
Welcome to your new project!
</span>
<system-information></system-information>
</div>
<div class="right-side">
<div class="doc">
<div class="title">Getting Started</div>
<p>
electron-vue comes packed with detailed documentation that covers everything from
internal configurations, using the project structure, building your application,
and so much more.
</p>
<button @click="open('https://simulatedgreg.gitbooks.io/electron-vue/content/')">Read the Docs</button><br><br>
</div>
<div class="doc">
<div class="title alt">Other Documentation</div>
<button class="alt" @click="open('https://electron.atom.io/docs/')">Electron</button>
<button class="alt" @click="open('https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/')">Vue.js</button>
</div>
</div>
</main>
</div>
</template>
<script>
...
</script>
<style>
...
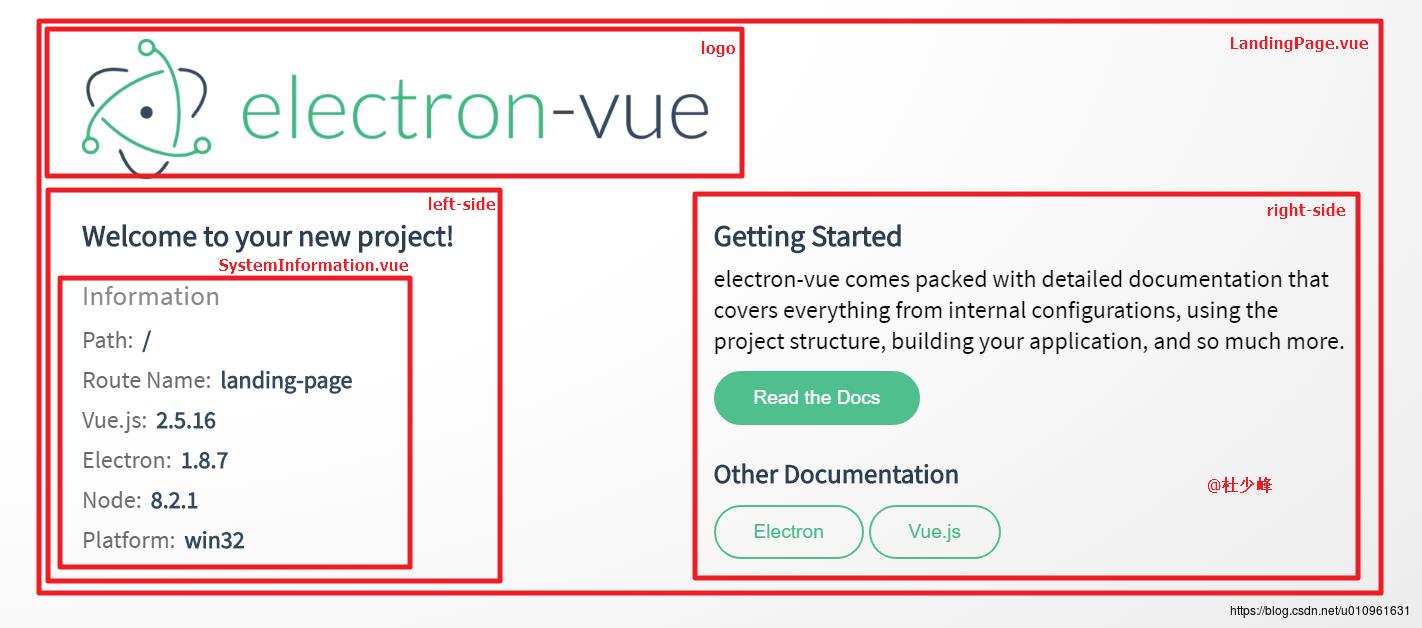
</style>这里很清晰的看到,这个页面包含了left-side和right-side两个div,分列页面左右(具体排列可以查看css中描述),左侧的布局还嵌套了一个system-information的组件,而右侧布局中就是一些文字+按钮。
而system-information的组件就是SystemInformation.vue文件,内容如下:
<template>
<div>
<div class="title">Information</div>
<div class="items">
<div class="item">
<div class="name">Path:</div>
<div class="value"> path </div>
</div>
<div class="item">
<div class="name">Route Name:</div>
<div class="value"> name </div>
</div>
<div class="item">
<div class="name">Vue.js:</div>
<div class="value"> vue </div>
</div>
<div class="item">
<div class="name">Electron:</div>
<div class="value"> electron </div>
</div>
<div class="item">
<div class="name">Node:</div>
<div class="value"> node </div>
</div>
<div class="item">
<div class="name">Platform:</div>
<div class="value"> platform </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
...
</script>
<style>
...
</style>这都是一些系统属性。
至此,我们明白了整个页面是怎么被渲染出来的。他的布局如下:
通过vue-devtools工具我们也可以看出他的渲染结构:
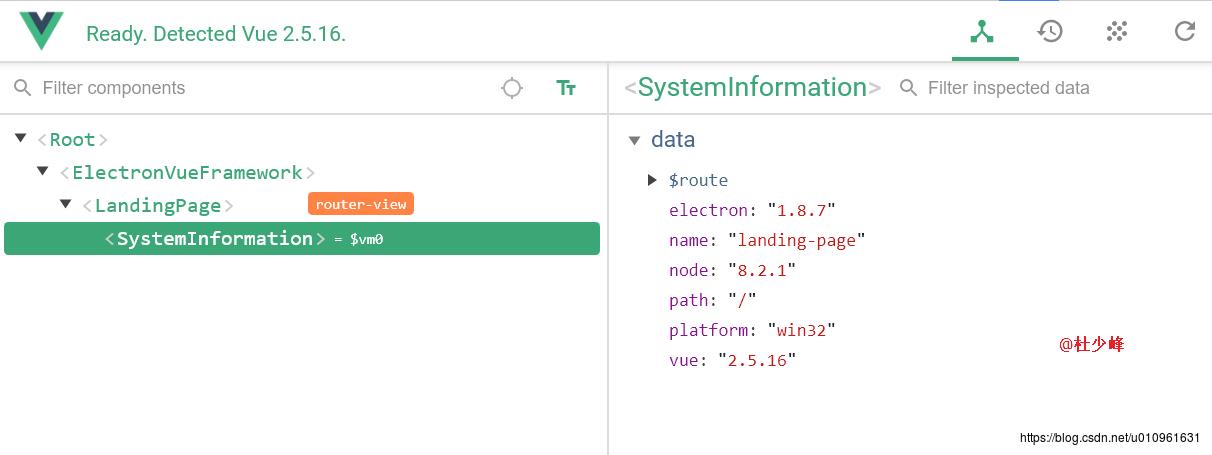
至此,整个页面的渲染过程我们就分析完了。
我们再次贴出这个系列的文章列表:
- electron-vue架构解析1-序言(原)
- electron-vue架构解析2-生产环境打包过程分析(原)
- electron-vue架构解析3-开发环境启动流程分析(原)
- electron-vue架构解析4-页面元素渲染过程分析(原)
以上是关于electron-vue架构解析4-页面元素渲染过程分析(原)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章