深度学习之手撕深度神经网络DNN代码(基于numpy)
Posted 我是管小亮
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了深度学习之手撕深度神经网络DNN代码(基于numpy)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
声明
1)本文仅供学术交流,非商用。所以每一部分具体的参考资料并没有详细对应。如果某部分不小心侵犯了大家的利益,还望海涵,并联系博主删除。
2)博主才疏学浅,文中如有不当之处,请各位指出,共同进步,谢谢。
3)此属于第一版本,若有错误,还需继续修正与增删。还望大家多多指点。大家都共享一点点,一起为祖国科研的推进添砖加瓦。
文章目录
0、前言
在之前写过一个手撕代码系列 深度学习之手撕神经网络代码(基于numpy),搭建了感知机和一个隐藏层的神经网络,理解了神经网络的基本结构和传播原理,掌握了如何从零开始手写一个神经网络。但是神经网络和深度学习之所以效果奇佳的一个原因就是,隐藏层多,网络结构深,很久之前一个小伙伴想让我写一个基于numpy的DNN,一直没填坑,今天就来写一下。
1、神经网络步骤
不知道你还记不记得搭建一个神经网络结构的步骤(深度学习之手撕神经网络代码(基于numpy)),大概是六点:
- 构建网络
- 初始化参数
- 迭代优化
- 计算损失
- 反向传播
- 更新参数
简洁地说就是三点,即构建网络、赋值参数、循环计算。
- 首先是确定准备搭建的网络结构是怎么样的(大话卷积神经网络CNN(干货满满)),比如经典的AlexNet,VGGNet等等;
- 然后是对权重w和偏置b进行参数初始化(深度学习入门笔记(十二):权重初始化),比如Xavier初始化,He初始化等等;
- 最后是迭代计算,(深度学习之手撕神经网络代码(基于numpy)),比如前向传播,反向传播等等。
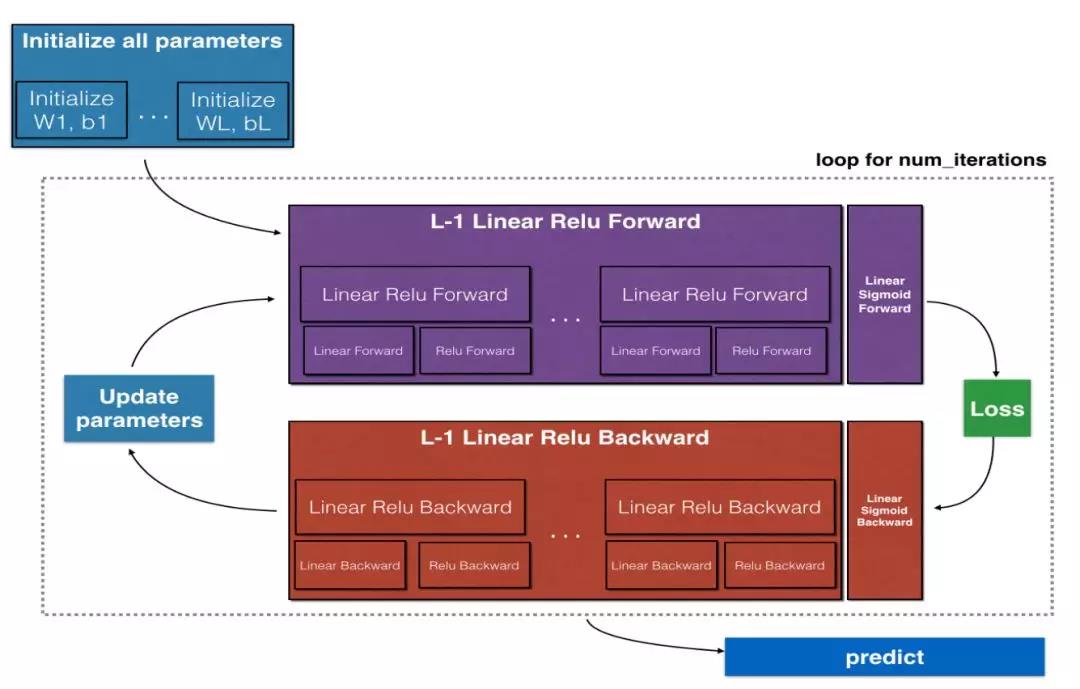
2、深度神经网络
之前写过的一些深度神经网络的理论:
需要补得童鞋可以看一下,避免后面不懂。这里就简单说两句,底层神经网络提取特征,然后接着卷积池化,再经过神经元的激活和随机失活,从而实现前行传播,计算损失函数,反向传播回调整参数,优化迭代过程。
以一个简单的手写数字识别为例,图例是整个过程:
- 端到端无中间操作,像素值即特征,转换为向量,经过深度神经网络,输出独热编码概率。

- 网络结构包括输入层,输出层和隐藏层,前向传播即,卷积池化并输出下一层,反向传播也是如此,只不过是反着的。

- 得到一张图片,提取其中的像素输入到,GPU加速训练过的神经网络中,输出结果就是分类结果。

3、初始化参数
深度神经网络的隐藏层数量用 layer_dims 表示,这样一共有多少层就不用全部写出来了,更加方便灵活:
def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims):
# 随机种子
np.random.seed(3)
parameters =
# 网络层数
L = len(layer_dims)
for l in range(1, L):
parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])*0.01
parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))
assert(parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1]))
assert(parameters['b' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], 1))
return parameters
上述代码使用的是随机数和归零操作来初始化权重 W 和偏置 b,如果想要别的初始化方式,几种常用的初始化方式的numpy写法如下:
- 截断正态分布初始化
def truncated_normal(mean, std, out_shape):
"""
Parameters
----------
mean : float or array_like of floats
The mean/center of the distribution
std : float or array_like of floats
Standard deviation (spread or "width") of the distribution.
out_shape : int or tuple of ints
Output shape. If the given shape is, e.g., ``(m, n, k)``, then
``m * n * k`` samples are drawn.
Returns
-------
samples : :py:class:`ndarray <numpy.ndarray>` of shape `out_shape`
Samples from the truncated normal distribution parameterized by `mean`
and `std`.
"""
samples = np.random.normal(loc=mean, scale=std, size=out_shape)
reject = np.logical_or(samples >= mean + 2 * std, samples <= mean - 2 * std)
while any(reject.flatten()):
resamples = np.random.normal(loc=mean, scale=std, size=reject.sum())
samples[reject] = resamples
reject = np.logical_or(samples >= mean + 2 * std, samples <= mean - 2 * std)
return samples
- He正态分布初始化
def he_normal(weight_shape):
"""
Parameters
----------
weight_shape : tuple
The dimensions of the weight matrix/volume.
Returns
-------
W : :py:class:`ndarray <numpy.ndarray>` of shape `weight_shape`
The initialized weights.
"""
fan_in, fan_out = calc_fan(weight_shape)
std = np.sqrt(2 / fan_in)
return truncated_normal(0, std, weight_shape)
- Glorot正态分布初始化(Xavier)
def glorot_normal(weight_shape, gain=1.0):
"""
Parameters
----------
weight_shape : tuple
The dimensions of the weight matrix/volume.
Returns
-------
W : :py:class:`ndarray <numpy.ndarray>` of shape `weight_shape`
The initialized weights.
"""
fan_in, fan_out = calc_fan(weight_shape)
std = gain * np.sqrt(2 / (fan_in + fan_out))
return truncated_normal(0, std, weight_shape)
这三个初始化方式可自行调用,这里就按照最简单的讲解了。
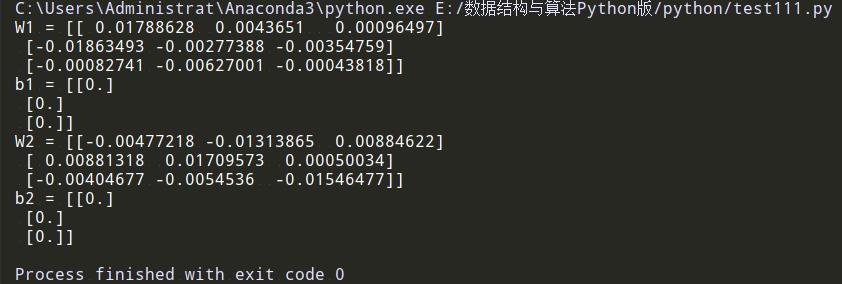
小应用
假设一个输入层大小 3 ,隐藏层大小 3,输出层大小 3 的深度神经网络,然后调用参数初始化函数,输入参数 [3,3,3,输出如下:
parameters = initialize_parameters_deep([3,3,3])
print("W1 = " + str(parameters["W1"]))
print("b1 = " + str(parameters["b1"]))
print("W2 = " + str(parameters["W2"]))
print("b2 = " + str(parameters["b2"]))
4、激活函数
除了经常使用的 sigmoid 激活函数,就是 ReLU 激活函数了,有 Leaky RELU,ELU,SELU,Softplus 等等。
wikipedia列出来的这些函数:

几种常用的激活函数的numpy写法如下:
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
import numpy as np
class ActivationBase(ABC):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
def __call__(self, z):
if z.ndim == 1:
z = z.reshape(1, -1)
return self.fn(z)
@abstractmethod
def fn(self, z):
raise NotImplementedError
@abstractmethod
def grad(self, x, **kwargs):
raise NotImplementedError
class Sigmoid(ActivationBase):
def __init__(self):
"""
A logistic sigmoid activation function.
"""
super().__init__()
def __str__(self):
return "Sigmoid"
def fn(self, z):
"""
Evaluate the logistic sigmoid, :math:`\\sigma`, on the elements of input `z`.
"""
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def grad(self, x):
"""
Evaluate the first derivative of the logistic sigmoid on the elements of `x`.
"""
fn_x = self.fn(x)
return fn_x * (1 - fn_x)
def grad2(self, x):
"""
Evaluate the second derivative of the logistic sigmoid on the elements of `x`.
"""
fn_x = self.fn_x
return fn_x * (1 - fn_x) * (1 - 2 * fn_x)
class ReLU(ActivationBase):
"""
A rectified linear activation function.
"""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def __str__(self):
return "ReLU"
def fn(self, z):
"""
Evaulate the ReLU function on the elements of input `z`.
"""
return np.clip(z, 0, np.inf)
def grad(self, x):
"""
Evaulate the first derivative of the ReLU function on the elements of input `x`.
"""
return (x > 0).astype(int)
def grad2(self, x):
"""
Evaulate the second derivative of the ReLU function on the elements of input `x`.
"""
return np.zeros_like(x)
class LeakyReLU(ActivationBase):
"""
'Leaky' version of a rectified linear unit (ReLU).
"""
def __init__(self, alpha=0.3):
self.alpha = alpha
super().__init__()
def __str__(self):
return "Leaky ReLU(alpha=)".format(self.alpha)
def fn(self, z):
"""
Evaluate the leaky ReLU function on the elements of input `z`.
"""
_z = z.copy()
_z[z < 0] = _z[z < 0] * self.alpha
return _z
def grad(self, x):
"""
Evaluate the first derivative of the leaky ReLU function on the elements
of input `x`.
"""
out = np.ones_like(x)
out[x < 0] *= self.alpha
return out
def grad2(self, x):
"""
Evaluate the second derivative of the leaky ReLU function on the elements of input `x`.
"""
return np.zeros_like(x)
class ELU(ActivationBase):
def __init__(self, alpha=1.0):
"""
An exponential linear unit (ELU).
-----
Parameters
----------
alpha : float
Slope of negative segment. Default is 1.
"""
self.alpha = alpha
super().__init__()
def __str__(self):
return "ELU(alpha=)".format(self.alpha)
def fn(self, z):
"""
Evaluate the ELU activation on the elements of input `z`.
"""
# z if z > 0 else alpha * (e^z - 1)
return np.where(z > 0, z, self.alpha * (np.exp(z) - 1))
def grad(self, x):
"""
Evaluate the first derivative of the ELU activation on the elements
of input `x`.
"""
# 1 if x > 0 else alpha * e^(z)
return np.where(x > 0, np.ones_like(x), self.alpha * np.exp(x))
def grad2(self, x):
"""
Evaluate the second derivative of the ELU activation on the elements
of input `x`.
"""
# 0 if x > 0 else alpha * e^(z)
return np.where(x >= 0, np.zeros_like(x), self.alpha * np.exp(x))
class SELU(ActivationBase):
"""
A scaled exponential linear unit (SELU).
"""
def __init__(self):
self.alpha = 1.6732632423543772848170429916717
self.scale = 1.0507009873554804934193349852946
self.elu = ELU(alpha=self.alpha)
super().__init__()
def __str__(self):
return "SELU"
def fn(self, z):
"""
Evaluate the SELU activation on the elements of input `z`.
"""
return self.scale * self.elu.fn(z)
def grad(self, x):
"""
Evaluate the first derivative of the SELU activation on the elements
of input `x`.
"""
return np.where(
x >= 0, np.ones_like(x) * self.scale, np.exp(x) * self.alpha * self.scale
)
def grad2(self, x):
"""
Evaluate the second derivative of the SELU activation on the elements
of input `x`.
"""
return np.where(x > 0, np.zeros_like(x), np.exp(x) * self.alpha * self.scale)
class SoftPlus(ActivationBase):
def __init__(self):
"""
A softplus activation function.
"""
super().__init__()
def __str__(self):
return "SoftPlus"
def fn(self, z):
"""
Evaluate the softplus activation on the elements of input `z`.
"""
return np.log(np.exp(z) + 1)
def grad(self, x):
"""
Evaluate the first derivative of the softplus activation on the elements
of input `x`.
"""
exp_x = np.exp(x)
return exp_x / (exp_x + 1)
def grad2(self, x):
"""
Evaluate the second derivative of the softplus activation on the elements
of input `x`.
"""
exp_x = np.exp(x)
return exp_x / ((exp_x + 1) ** 2)
5、前向传播
我们这里仅仅使用 sigmoid 和 relu 两种激活函数进行前向传播,代码如下:
def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation):
if activation == "sigmoid":
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = sigmoid(Z)
elif activation == "relu":
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = relu(Z)
assert (A.shape == (W.shape[0], A_prev.shape[1]))
cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache)
return A, cache
A_prev 是前一步前向计算的结果,W 和 b 分别对应权重和偏置,中间有一个激活函数判断。如果你想更换激活函数,直接替换即可。
对于某一层的前向传播过程如下:
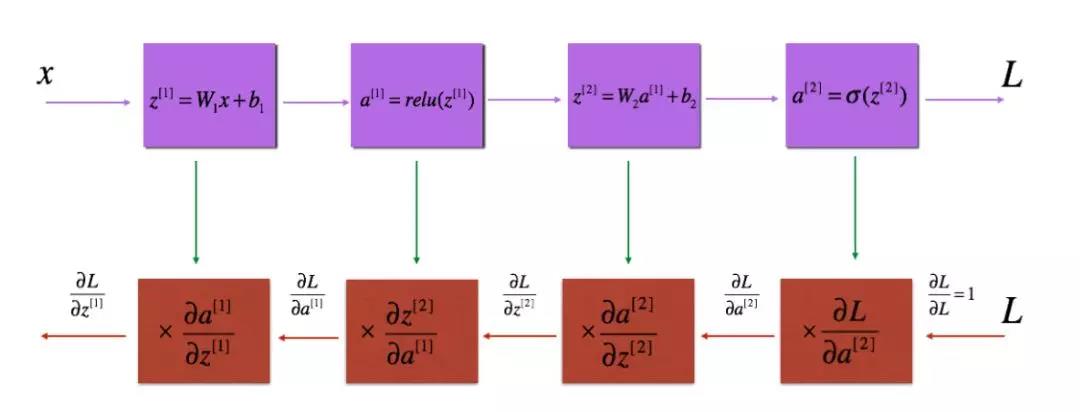
实现过程如下:
def L_model_forward(X, parameters):
caches = []
A = X
网络层数
L = len(parameters) // 2
# 实现[LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1)
for l in range(1, L):
A_prev = A
A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters["W"+str(l)], parameters["b"+str(l)], "relu")
caches.append(cache)
# 实现LINEAR -> SIGMOID
AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters["W"+str(L)], parameters["b"+str(L)], "sigmoid")
caches.append(cache)
assert(AL.shape == (1,X.shape[1]))
return AL, caches
6、计算损失
通过前向传播得到结果之后,根据结果去计算损失函数大小。
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
import numpy as np
import numbers
def is_binary(x):
"""Return True if array `x` consists only of binary values"""
msg = "Matrix must be binary"
assert np.array_equal(x, x.astype(bool)), msg
return True
def is_stochastic(X):
"""True if `X` contains probabilities that sum to 1 along the columns"""
msg = "Array should be stochastic along the columns"
assert len(X[X < 0]) == len(X[X > 1]) == 0, msg
assert np.allclose(np.sum(X, axis=1), np.ones(X.shape[0])), msg
return True
class OptimizerInitializer(object):
def __init__(self, param=None):
"""
A class for initializing optimizers. Valid inputs are:
(a) __str__ representations of `OptimizerBase` instances
(b) `OptimizerBase` instances
(c) Parameter dicts (e.g., as produced via the `summary` method in
`LayerBase` instances)
If `param` is `None`, return the SGD optimizer with default parameters.
"""
self.param = param
def __call__(self):
param = self.param
if param is None:
opt = SGD()
elif isinstance(param, OptimizerBase):
opt = param
elif isinstance(param, str):
opt = self.init_from_str()
elif isinstance(param, dict):
opt = self.init_from_dict()
return opt
def init_from_str(self):
r = r"([a-zA-Z]*)=([^,)]*)"
opt_str = se以上是关于深度学习之手撕深度神经网络DNN代码(基于numpy)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章