Java IO 流
Posted Zview
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java IO 流相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
InputStream和OutputStream的对应关系如下:
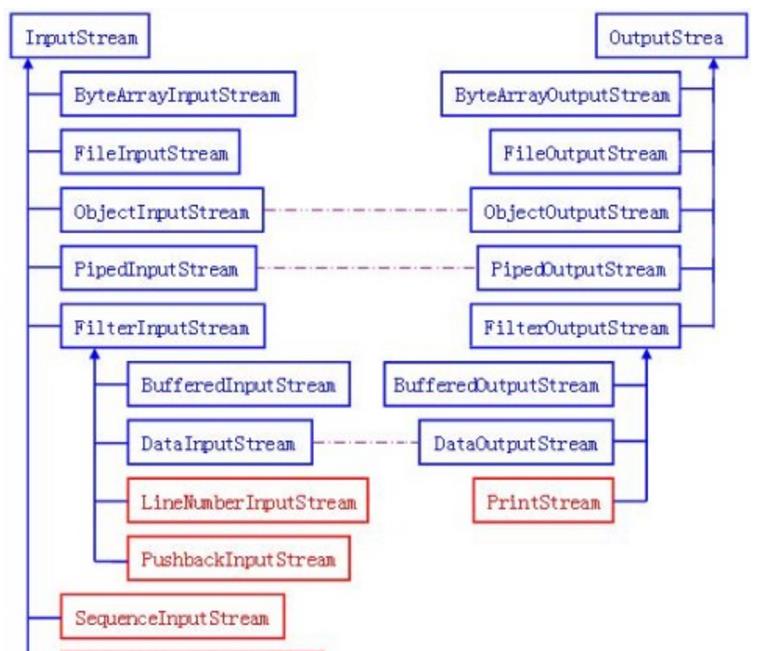
这里针对每一个类,分别做一些实例和介绍:
1、InputStream、OutputSTream
InputStream\\OutSTream是抽象类,定义了关于字节流操作的最基本的方法
InputStream: available() / read() / mark() /reset() / skip() /markSupported()/ close()
OutputStream: close() / flush() / write()
对于InputStream mark()标记当前流的位置,reset()返回到上次标记的流的位置,skip(int n)跳过n个字节
2、ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream
把Byte转换为InputStream
//构造方法,其他方法与InputStream相同
ByteArrayInputStream(byte[] buf)
ByteArrayInputStream(byte[] buf, int offset, int length)
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(ArrayLetters);
/ 从字节流中读取5个字节
for (int i=0; i<LEN; i++) {
if (bais.available() >= 0) {
int tmp = bais.read();
System.out.printf("%d : 0x%s\\n", i, Integer.toHexString(tmp));
}
}
ByteArrayOutputStream中是有一个可以随着输入增长的byte数组缓冲区的,可以用来方便的缓存数据:
主要的用到的方法是可用
通过toByteArray()得到内部的Byte数组,
通过toString将内部数据转为StringwriteTo(OutputStream out) 将内部的byte数组写入到另外一个输出流中
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f)); ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream=new ByteArrayOutputStream(); int c; while((c=bis.read())!=-1){ byteArrayOutputStream.write(c); } System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream); byte[] b=byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(); System.out.println(new String(b));
3、FileInputStream和FileOutputStream
连接地址
FileInputStream 和FileOutputStream适用于操作于任何形式的文件(因为是以字节为向导),如果想要操作文本文件,采用FileInputReader和FileOutputWriter效率更高
FileChannel getChannel() //用于在java nio中的Channel
FileDescriptor getFD() // 返回该文件的文件描述符 同时文件输入\\输出流 都可以通过FD进行构造
其他的方法与InputStream以及OutputStream的方法一样
FileDescriptor是文件描述符
就是用来描述一个文件的。
可以用来作为在多个流之间的桥梁(文件的输入输出流都可以通过FD构造,也都能生成FD对象)
FileDescriptor中有三个常量in、out、err,分别是标准输入、输出、错误的句柄
4、ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream
主要用于对象的序列化操作
Person p=new Person("lz",19); Person p1=new Person("lz1",191); try { FileOutputStream fo=new FileOutputStream("D:/ww"); ObjectOutputStream oo=new ObjectOutputStream(fo); oo.writeObject(p); oo.writeObject(p1); oo.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream("D:/ww"); ObjectInputStream oi = new ObjectInputStream(fi); Person p3=(Person) oi.readObject(); Person p4=(Person) oi.readObject(); System.out.println(p3.getName()); System.out.println(p4.getName()); } catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
5、PipedInputStream和PipedOutputStream
用于在多线程之间的单向的管道的通信,使用connect方法把两个管道给关联起来
class Sender implements Runnable{ PipedOutputStream pos=new PipedOutputStream(); public void connect(PipedInputStream pipedInputStream) throws IOException { pos.connect(pipedInputStream); } @Override public void run() { StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer("The Meaasge is:"); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { sb.append(i); try { pos.write(sb.toString().getBytes()); Thread.sleep(500); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } class Receiver implements Runnable{ PipedInputStream pis=new PipedInputStream(); public void Receiver(PipedOutputStream ops) throws IOException { pis.connect(ops); } @Override public void run() { while (true){ int num= 0; try { if((num = pis.available())>0) { byte b[] = new byte[num]; pis.read(b); System.out.println(new String(b)); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } public class _PipedStream { public static void main(String[] args) { Sender s=new Sender(); Receiver r=new Receiver(); try { s.connect(r.pis); //将两个流连接起来 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Thread t1=new Thread(s); Thread t2=new Thread(r); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
6、BufferedInputStream与BufferedOutputStream
BufferedInputStream是带缓冲区的输入流,默认缓冲区大小是8M,能够减少访问磁盘的次数,提高文件读取性能;BufferedOutputStream是带缓冲区的输出流,能够提高文件的写入效率。BufferedInputStream与BufferedOutputStream分别是FilterInputStream类和FilterOutputStream类的子类,实现了装饰设计模式。
构造方法是传入InputStream和OutPutStream,可以指定缓冲区的大小,默认的缓冲区的大小是8M
7、DataInputStream和DataOutputStram
实现了对于各种基本数据结构的读写的方法,也是装饰类
提供了回退流的机制,可以将已经读出来的byte放回去,或者将指定的内容放到流中
PushbackInputStream(InputStream inputStream) PushbackInputStream(InputStream inputStream,int numBytes) 第二种形式创建的流对象具有一个长度为numBytes的回推缓存,从而允许将多个字节回推到输入流中。 void unread(int b) void unread(byte[] buffer) void unread(byte[] buffer,int offset,int numBytes) 第一种形式回推b的低字节,这会使得后续的read()调用会把这个字节再次读取出来。第二种形式回推buffer中的字节。第三种形式回推buffer中从offset开始的numBytes个字节。
当回推缓存已满时,如果试图回推字节,就会抛出IOException异常。
想象流是一个队列,每次都是从队列头读出流数据,回退流就是往头上在写回数据,注意写回数据的长度不能大于“回推缓存”,这个回推缓存实在回退流的构造函数中定义的
将两个流合并,要合并多个流可以通过指定Enumeration<InputStream>来处理
10、PrintStream
PrintStream 是打印输出流,能够方便地打印各种数据值表示形式。
System.out就是一个PrintStream实例,使用方法类似,需注意方法append(),向流的尾部追加内容。默认情况PrintStream是自动flush的
print()和println()都是将其中参数转换成字符串之后,再写入到输入流。
以上是关于Java IO 流的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章