Spring框架基础
Posted 专注改变人生。
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring框架基础相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、什么是spring框架
-
spring是J2EE应用程序框架,是轻量级的IoC和AOP的容器框架,主要是针对javaBean的生命周期进行管理的轻量级容器,可以单独使用,也可以和Struts框架,ibatis框架等组合使用。
二、架构概述
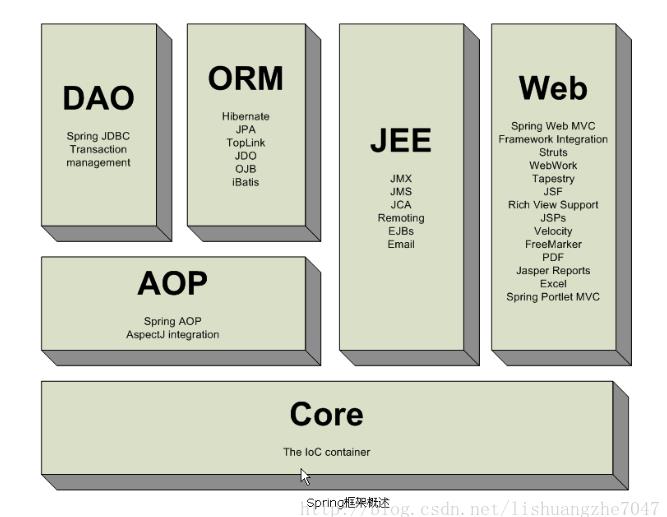
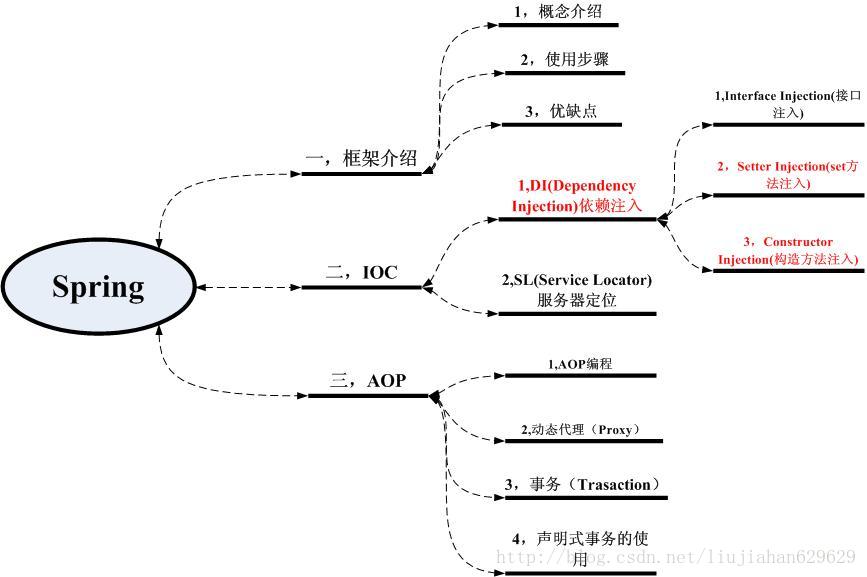
2.1 IoC(Inversion of Control) :控制反转
- 对象创建责任的反转,在spring中BeanFacotory是IoC容器的核心接口,负责实例化,定位,配置应用程序中的对象及建立这些对象间的依赖。XmlBeanFacotory实现BeanFactory接口,通过获取xml配置文件数据,组成应用对象及对象间的依赖关系。

-
spring中有三种注入方式,一种是set注入,一种是接口注入,另一种是构造方法注入。
2.1.1 第一个基于spring框架的程序(使用spring框架的ioc的优势)
- 导包,由于本例是最简单的spring的程序,所以jar包比较少。
- 创建spring的配置文件。
spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd"> <!-- 以上为头文件,必须在eclipse的xml catalog里有相应xsd文件, 有了头文件之后会有提示--> <bean class="test.Man" name="man"></bean> <!-- 创建test包里的Man类的对象,对象名为man --> </beans>
- Test.java
package test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Test test=new Test(); test.one(); test.two(); test.three(); } /** * 普通模式:哪里需要对象,就在哪个方法里new 一个类的对象然后是用。 * 存在的不足:如果有很多个类都使用一个对象,而这个对象改变了的话,就需要在很多个类里修改这个对象。 */ private void one() { PersonI man=new Man(); man.eat(); man.sleep(); } /** * 设计模式(工厂模式、门面模式): * ,优势:如果PersonI的实现类修改了,只要在工厂PersonFactory中修改相应的类即可,而这里无须修改。 */ private void two() { PersonI woman=PersonFactory.getWomen(); //工厂模式 ,优势:如果PersonI的实现类修改了,只要在工厂PersonFactory中修改相应的类即可,而这里无须修改。 woman.eat(); woman.sleep(); } /** * spring的ioc模式,将对象的实例化交给spring框架(spring容器) */ private void three() { /** * 这里的Man对象是在spring.xml中创建(new)好了 */ // ApplicationContext applicationContext=new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("src/spring.xml"); //推荐使用new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); Man man=(Man)applicationContext.getBean("man"); //getBean("man")里的man是spring.xml文件里的id或者name为man的bean man.sleep(); man.eat(); } }
- PersonFactory.java
package test; /** * 工厂模式, * @author Administrator * */ public class PersonFactory { public static PersonI getMan(){ PersonI man=new Man(); return man; } public static PersonI getWomen(){ PersonI women=new Women(); return women; } }
- PersonI.java
package test; public interface PersonI { void eat(); void sleep(); } class Man implements PersonI{ public void eat() { System.out.println("Man 中的eat方法"); } public void sleep() { System.out.println("Man 中的sleep方法"); } } class Women implements PersonI{ public void eat() { System.out.println("Women 中的eat方法"); } public void sleep() { System.out.println("Women 中的sleep方法"); } }
结果:
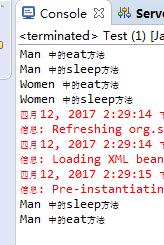

- 其中id和name标签属性都是bean的名称,区别在于id表示的bean如果这个xml被别的xml文件继承,则这个bean也可以在别的xml文件里使用。而name则不可以。
- abstract="true" 表示这个bean是抽象的,不能实例化只能被继承。
- parent="" 表示继承于某个类。
- init-method="" 表示这个bean创建的时候就调用这个方法,当然这个方法的调用会在构造方法调用之后。 destroy-method="" 表示bean销毁的时候调用这个方法,有时候不会调用。
- scope="singleton || prototype " singleton表示单例模式,对象只产生一个实例,init-method方法和destroy-method方法只执行一次。 prototype表示原型模式,每次产生一个对象,每次产生一个对象init-method方法和destroy-method方法都会执行一次。
2.2 DI:依赖注入 (三种)
- 一种是set注入,一种是接口注入,另一种是构造方法注入。
(1) set注入
(2) 构造器注入
这种方式的注入是指带有参数的构造函数注入,看下面的例子,我创建了两个成员变量SpringDao和User,但是并未设置对象的set方法,所以就不能支持第一种注入方式,
这里的注入方式是在SpringAction的构造函数中注入,也就是说在创建SpringAction对象时要将SpringDao和User两个参数值传进来:
public class SpringAction { //注入对象springDao private SpringDao springDao; private User user; public SpringAction(SpringDao springDao,User user){ this.springDao = springDao; this.user = user; System.out.println("构造方法调用springDao和user"); } public void save(){ user.setName("卡卡"); springDao.save(user); } }
在XML文件中同样不用<property>的形式,而是使用<constructor-arg>标签,ref属性同样指向其它<bean>标签的name属性:
<!--配置bean,配置后该类由spring管理--> <bean name="springAction" class="com.bless.springdemo.action.SpringAction"> <!--(2)创建构造器注入,如果主类有带参的构造方法则需添加此配置--> <constructor-arg ref="springDao" index="0"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg ref="user" index="1"></constructor-arg> </bean> <bean name="springDao" class="com.bless.springdemo.dao.impl.SpringDaoImpl"></bean> <bean name="user" class="com.bless.springdemo.vo.User"></bean>
(3) 接口注入
- Person.java
package test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Person { private Phone phone; /** * set注入 * @param phone 接口 */ public void setPhone(Phone phone) { this.phone = phone; } public void usePhone(){ this.phone.games(); } public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml"); Person person=(Person)context.getBean("person"); person.usePhone(); } }
- spring.xml
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd"> <!-- 以上为头文件,必须在eclipse的xml catalog里有相应xsd文件, 有了头文件之后会有提示--> <bean name="person" class="test.Person"> <property name="phone" ref="huawei"></property> </bean> <bean name="iPhone" class="test.iPhone"></bean> <bean name="huawei" class="test.HuaWei"></bean> </beans>
- Person类的成员属性Phone phone;是一个接口,在spring.xml实例化Person的时候,把Phone接口的实现类对象“huawei”引入到Person类中,如果要引用其他对象,只需要把ref="huawei" 即可,其他代码不用改变。
2.3 AOP面向切面编程
aop就是纵向的编程,如下图所示,业务1和业务2都需要一个共同的操作,与其往每个业务中都添加同样的代码,不如写一遍代码,让两个业务共同使用这段代码。
spring中面向切面变成的实现有两种方式,一种是动态代理,一种是CGLIB,动态代理必须要提供接口,而CGLIB实现是有继承。
(1)AOP之代理模式(proxy模式)
- 代理模式:通俗来讲,比如我们去买动车票,可以去动车站售票点买票,或者去代理点买票。通常来讲,售票点只提供售票而代理点不仅可以售票而且可以实现其他的功能。 从程序设计上讲,如果我们希望某个类不被直接使用,那么我们可以创建这个类的代理,代理并不真正实现功能,而是经过处理之后调用被代理类的功能,比如客户到代理点买票,代理点的票是从售票点买来的(相当于调用实现类的方法),可以得出: 代理应该实现一个接口(被代理类也实现这个接口),也有被代理类作为成员变量。
- 静态代理 or 动态代理
案例一: 静态代理
TicketIFC.java(售票接口)
package proxy; public interface TicketIFC { void sellTicket(); }
Ticket_station.java(实现类)
package proxy; public class Ticket_station implements TicketIFC{ public void sellTicket() { System.out.println("售票站售票"); } }
Ticket_proxy.java(代理类,实现售票接口且有实现类对象)
package proxy; public class Ticket_proxy implements TicketIFC{ private TicketIFC ticketIFC; public Ticket_proxy(TicketIFC ticketIFC){ this.ticketIFC=ticketIFC; } public void sellTicket() { this.ticketIFC.sellTicket(); } }
Test.java(测试类)
package proxy; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { TicketIFC ticketIFC=new Ticket_proxy(new Ticket_station()); ticketIFC.sellTicket(); } }
结果:
案例二:动态代理(代理类是在运行时动态产生的)
- AOP的原理就是java的动态代理机制。
- 在java的动态代理机制中,有两个重要的类或接口,一个是 InvocationHandler(Interface)、另一个则是 Proxy(Class),这一个类和接口是实现我们动态代理所必须用到的。
- 每一个动态代理类都必须要实现InvocationHandler这个接口,并且每个代理类的实例都关联到了一个handler,当我们通过代理对象调用一个方法的时候,这个方法的调用就会被转发为由InvocationHandler这个接口的 invoke 方法来进行调用。
- 代理类原则: 1.实现某一接口 2.被代理的实现类。
PersonI.java (接口)
package spring_project_01; public interface PersonI { void eat(); void sleep(); }
Man.java(实现类)
package spring_project_01; public class Man implements PersonI{ public void eat() { System.out.println("Man中的eat方法"); } public void sleep() { System.out.println("Man中的sleep方法"); } }
Women.java(实现类)
package spring_project_01; public class Women implements PersonI{ public void eat() { System.out.println("Women中的eat方法"); } public void sleep() { System.out.println("Women中的sleep方法"); } }
ProxyUtil.java(代理类创建工具)
package proxy_dynamic; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; /** * 动态创建代理类 * @author Administrator * */ public class ProxyUtil implements InvocationHandler{ private Object targetObj; public Object createProxy(Object targetObj){ this.targetObj=targetObj; //Proxy.newProxyInstance参数为被代理类的类加载器、被代理类的接口,以及一个InvocationHandler对象,表示的是当我这个动态代理对象在调用方法的时候,会关联到哪一个InvocationHandler对象上 Object proxyObj=Proxy.newProxyInstance(targetObj.getClass().getClassLoader(), targetObj.getClass().getInterfaces(), this); return proxyObj; } /** * proxy:指代我们所代理的那个真实对象 * method:指代的是我们所要调用真实对象的某个方法的Method对象 * args:指代的是调用真实对象某个方法时接受的参数 */ public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("在被代理对象方法调用前会自动调用"); System.out.println("代理对象方法调用前"); Object objectReturnValue= method.invoke(this.targetObj, args); //在代理实例上处理方法调用并返回结果。java反射机制,即用方法调用对象。 System.out.println("代理对象方法调用后"); return objectReturnValue; } }
Test.java(测试类)
package proxy_static; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { TicketIFC ticketIFC=new Ticket_proxy(new Ticket_station()); ticketIFC.sellTicket(); } }
结果:
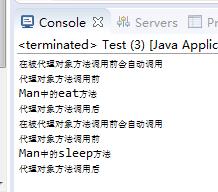
案例三:模拟事务(实物的提交和回滚都不再dao层实现,而是采用代理模式实现)
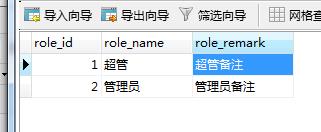
1. 数据字典:
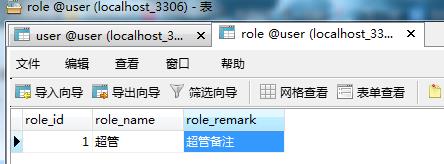
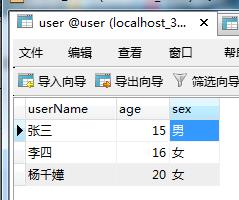
2. RoleServiceI.java(接口)
package proxy_jdbc; public interface RoleServiceI { void addRole() throws Exception; }
3. RoleServiceImpl.java(实现类,在动态代理模式下本类并不做事务的处理,把事务处理在代理类的invoke方法里处理)
package proxy_jdbc; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.Statement; public class RoleServiceImpl implements RoleServiceI{ public void addRole() throws Exception { Connection conn=null; Statement stat=null; StringBuffer SQL=new StringBuffer(); conn=DBUtil.getConn(); System.out.println("dao中的conn="+conn); stat=conn.createStatement(); /** * 插入到角色表 */ SQL.setLength(0); SQL.append("insert into role values(2,\'管理员\',\'管理员备注\')"); stat.executeUpdate(SQL.toString()); /** * 插入到用户表 */ SQL.setLength(0); SQL.append("insert into user values(\'111\',11,\'女\')"); stat.executeUpdate(SQL.toString()); DBUtil.close(null, stat, null); //这里只关闭stat流,conn流在ServiceProxyUtil.invoke方法里统一关闭。 } }
4. ServiceProxyUtil.java(动态代理生成工具):统一处理事务。
package proxy_jdbc; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * 动态代理类创建工具 * @author Administrator * */ public class ServiceProxyUtil implements InvocationHandler{ private Object targetObj; public Object createServiceProxy(Object targetObj){ this.targetObj=targetObj; Object proxy=Proxy.newProxyInstance(targetObj.getClass().getClassLoader(), targetObj.getClass().getInterfaces(), this); return proxy; } public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { /** * 在本方法里对jdbc的事务进行处理和conn流的关闭,在dao层就不用再处理了。 */ Object returnValue=null; Connection conn=null; try { conn=DBUtil.getConn(); System.out.println("proxy中的conn="+conn); conn.setAutoCommit(false); //禁止自动提交事务 returnValue=method.invoke(this.targetObj, args); //执行实现类方法 System.out.println("提交事务"); conn.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("出现异常,回滚事务"); conn.rollback(); }finally{ DBUtil.close(conn, null, null); } return returnValue; } }
5. ServiceFactory.java(静态工厂)
package proxy_jdbc; /** * 静态工厂 * @author Administrator * */ public class ServiceFactory { public static RoleServiceI getRoleServiceImpl(){ RoleServiceI roleService=new RoleServiceImpl(); return roleService; } }
6. Test.java(测试类)
package proxy_jdbc; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建动态代理创建工具 ServiceProxyUtil proxyUtil=new ServiceProxyUtil(); //用动态代理创建工具创建出一个服务层的实现类, RoleServiceI roleServiceImpl=(RoleServiceI)proxyUtil.createServiceProxy(ServiceFactory.getRoleServiceImpl()); try { roleServiceImpl.addRole(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
7. DBUtil.java
package proxy_jdbc; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; public class DBUtil { /** * ThreadLocal本地线程,类似HttpSession操作,HttpSession针对每一个用户请求,而ThreadLocal针对每一个线程。
* 这个对象用于实现当Connection创建之后除非关闭否则一直都是操作这个Connection对象 */ private static ThreadLocal<Connection> local=new ThreadLocal<Connection>(); private static final String DRIVER="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"; private static final String USER="root"; private static final String PASSWD=""; private static final String URL="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/user?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"; static{ try { Class.forName(DRIVER); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException("无法加载驱动包"); } } public static Connection getConn(){ Connection conn=null; try { if(local.get() !=null){ //如果本地线程里有值,说明这个数据库连接被创建过,所以还是使用这个连接 conn=local.get(); }else{ //如果本地线程为空,则创建一个数据库连接。 conn= DriverManager.getConnection(URL,USER,PASSWD); local.set(conn); } } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return conn; } public static void close(Connection conn,Statement stat,ResultSet rs) throws Exception{ if(conn!=null && !conn.isClosed()){ if(local.get() !=null ){ local.remove(); } conn.close(); } if(stat!=null && !stat.isClosed()){ stat.close(); } if(rs!=null && !rs.isClosed()){ rs.close(); } } }
结果:
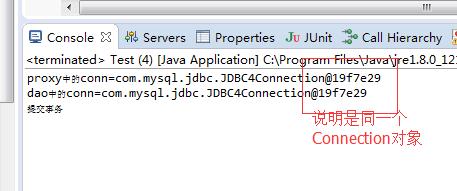
 数据已插入。
数据已插入。
- 案例三项目文件存于 --> 码云-开源中国 --> spring框架之动态代理
以上是关于Spring框架基础的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章