XML--Java中的四种常见解析方式--dom
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了XML--Java中的四种常见解析方式--dom相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Java中常用的解析方式主要有四种:
Java 自带:Dom、Sax。
外加包:Jdom、Dom4j。
1.Dom
主要的构建方式
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder db=dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
Document dm=db.parse("rec\\\\books.xml");
其中节点类为Node 节点集合类为NodeList
attr属性集合用NamedNodeMap 通过getAttributes()实现。
NodeList booklist=dm.getElementsByTagName("book");
NodeList childnodes = book.getChildNodes();
字节点childnodes集合用getChildNodes()实现
字节点第i个通过childnodes.item(i)获得
“集合”长度用get.length()实现
节点类型有多种 通过Node.ELEMENT_NODE可以获得该节点的类型
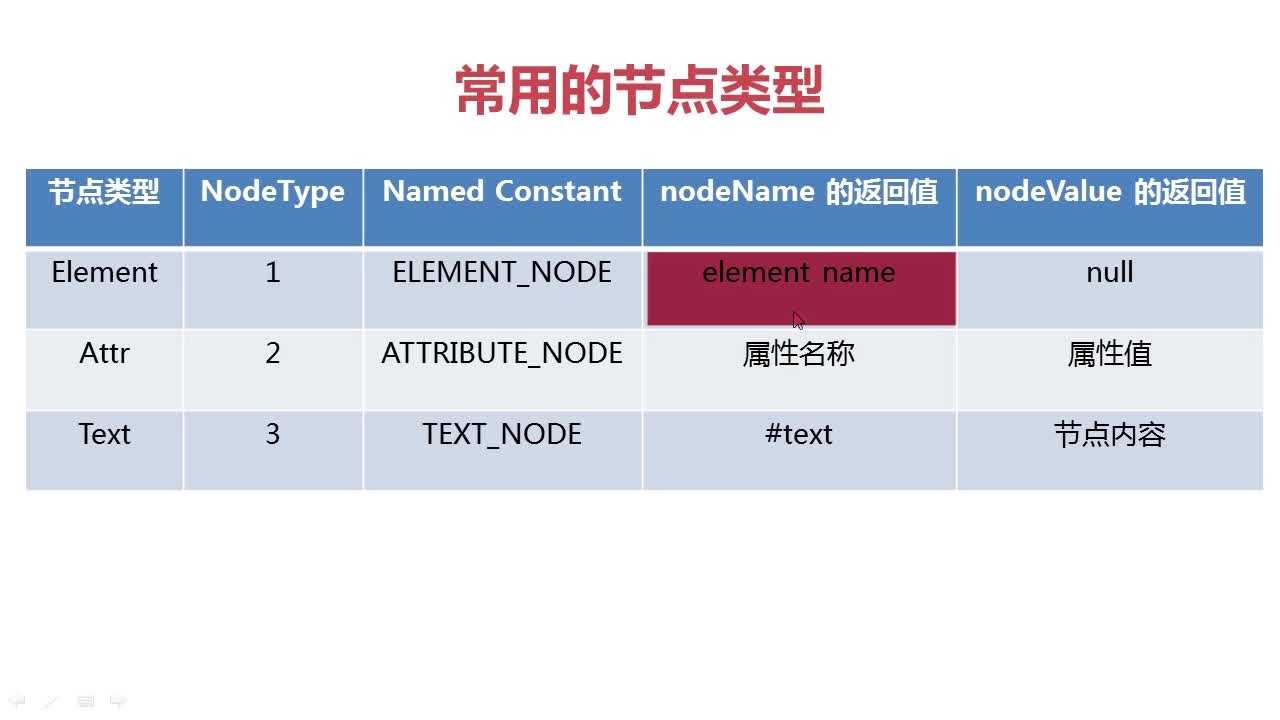
如上图如要获得<name>数据结构</name>中的文本
则需要通过childnodes.item(k).getTextContent()直接获得文本
或者通过childnodes.item(k).getFirstchild().getNodeName。(文本被视为name标签的Text类型子节点)
PS:xml空格会被视为一个text类型的节点。
例子:

public class Xmltest { public List<book> books; public Xmltest(){ this.books=new ArrayList(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Xmltest test=new Xmltest(); int i=2005; int j=i>>2; System.out.println(j); test.Jiexi(); test.foreprint(); } public void Jiexi() throws Exception{ DocumentBuilderFactory dbf=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); DocumentBuilder db=dbf.newDocumentBuilder(); Document dm=db.parse("E:\\\\books.xml");// TODO Auto-generated method stub NodeList booklist=dm.getElementsByTagName("book"); for (int i = 0; i < booklist.getLength(); i++) { book temp=new book(); Node book = booklist.item(i); NamedNodeMap attrs = book.getAttributes(); NodeList childnodes = book.getChildNodes(); for (int k = 0; k < childnodes.getLength(); k++) { if (childnodes.item(k).getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { if (childnodes.item(k).getNodeName() == "name") temp.name = childnodes.item(k).getn; if (childnodes.item(k).getNodeName() == "years") temp.years = childnodes.item(k).getTextContent(); if (childnodes.item(k).getNodeName() == "price") temp.price = childnodes.item(k).getTextContent(); } } books.add(temp); } } public void foreprint(){ for(book temp:books){ System.out.println("------------"); System.out.println("书名为:"+temp.name); System.out.println("出版年份:"+temp.years); System.out.println("价格为:"+temp.price+"元"); } } }
以上是关于XML--Java中的四种常见解析方式--dom的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
