Spring 中使用XML配置方式和使用注解方式实现DI
Posted 刘二雄
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring 中使用XML配置方式和使用注解方式实现DI相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Spring容器给我们提供了很好的环境,我们只关注主要业务即可,其他的无需关注太多。今天刚学的DI
DI(Dependency Injection):依赖注入
使用XML配置文件完成依赖注入
1.1普通属性的注入
创建实体类:

package cn.spring.entity; import java.io.Serializable; /** * Created by accp on 2017/3/23. */ public class User implements Serializable { private String name; private String pwd; private Integer age; //带参构造 public User(String name, String pwd, Integer age) { this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; this.age = age; } public User(String name, String pwd) { this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; } public User(String name, Integer age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public User() { } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name=\'" + name + \'\\\'\' + ", pwd=\'" + pwd + \'\\\'\' + ", age=" + age + \'}\'; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } }
编写xml文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd "> <!--属性注入--> <bean id="user1" class="cn.spring.entity.User"> <property name="name" value="张三"></property> <property name="age" value="18"></property> </bean> </beans>
测试类:

@Test /*属性注入*/ public void firstTest(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user=(User)ctx.getBean("user1"); System.out.println(user); }
运行结果:
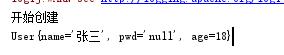
1.1.2域属性的注入
创建实体类

package cn.spring.entity; import java.io.Serializable; /** * Created by accp on 2017/3/23. */ public class User implements Serializable { private String name; private String pwd; private Integer age; private Car myCar; public User(String name, String pwd, Car myCar) { this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; this.myCar = myCar; } public User(String name, String pwd, Integer age, Car myCar) { this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; this.age = age; this.myCar = myCar; } //带参构造 public User(String name, String pwd, Integer age) { this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; this.age = age; } public User(String name, String pwd) { this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; } public User(String name, Integer age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public User() { } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name=\'" + name + \'\\\'\' + ", pwd=\'" + pwd + \'\\\'\' + ", age=" + age + ", myCar=" + myCar + \'}\'; } public Car getMyCar() { return myCar; } public void setMyCar(Car myCar) { this.myCar = myCar; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } }

package cn.spring.entity; /** * Created by accp on 2017/3/23. */ public class Car { private String color; public Car() { } public Car(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public String toString() { return "Car{" + "color=\'" + color + \'\\\'\' + \'}\'; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } }
编写xml文件

<!--域属性注入-->
<bean id="mmCar" class="cn.spring.entity.Car">
<property name="color" value="green color"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="user4" class="cn.spring.entity.User">
<property name="name" value="王小二"></property>
<property name="age" value="10"></property>
<property name="myCar" ref="mmCar"></property>
</bean>
测试类

@Test /*域属性注入*/ public void fourTest(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user=(User)ctx.getBean("user4"); System.out.println(user); }
运行结果:
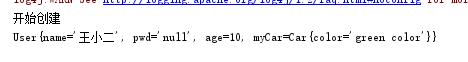
1.2构造注入
这个示例还是借用上面创建的实体类,实体类的构造已创建完成,接下来就编写xml文件
xml文件

<!--构造注入-->
<bean id="user2" class="cn.spring.entity.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="李四"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="123"></constructor-arg>
<!-- <constructor-arg index="2" value="16"></constructor-arg>-->
</bean>
编写测试类

@Test /*构造注入*/ public void secondTest(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user=(User)ctx.getBean("user2"); System.out.println(user); }
运行结果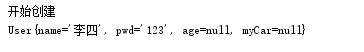
1.2.2构造注入域属性
注入域属性与普通属性注入域属性的方式是一致的,我们只需简单的更改代码即可。
xml文件编写

<!--构造注入域属性-->
<bean id="mmCar1" class="cn.spring.entity.Car">
<property name="color" value="red color"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="user5" class="cn.spring.entity.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="小二"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="6375196"></constructor-arg>
<!-- <constructor-arg index="2" value="16"></constructor-arg>-->
<constructor-arg index="2" ref="mmCar1"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
编写测试类

@Test /*构造注入域属性*/ public void fiveTest(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user=(User)ctx.getBean("user5"); System.out.println(user); }
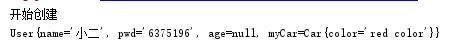
1.3使用p命名空间注入
使用p命名空间注入时,需要注意的是:需要引入

如上图所示的命名空间。
xml文件编写
<!--p空间注入 直接注入值 -->
<bean id="user3" class="cn.spring.entity.User" p:name="王五" p:age="14" p:myCar="myCar"></bean><!-- p:myCar="red"-->
还有一种方式:
<!--p空间注入 引用bean -->
<!--<bean id="user3" class="cn.spring.entity.User" p:name="王五" p:age="14" p:myCar-ref="mmCar" ></bean>-->
一共两种方式,都可以实现p命名空间的注入。
编写测试类

@Test /*p空间注入*/ public void thirdTest(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user=(User)ctx.getBean("user3"); System.out.println(user); }
运行结果

1.4集合注入
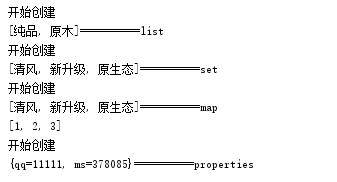
集合注入分为:array list set map properties 注入
在这里我们就不举例array的示例了,简单的把其他的实例演示一下。
创建实体类

package cn.spring.entity; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; /** * Created by accp on 2017/3/23. */ public class CollectionBean { /** * 数组 * List * Map * Set * properties * */ private List<String> list; private Set<String> set; private Map<String,String> map; private Properties properties; public Properties getProperties() { return properties; } public void setProperties(Properties properties) { this.properties = properties; } public Map<String, String> getMap() { return map; } public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) { this.map = map; } public Set<String> getSet() { return set; } public void setSet(Set<String> set) { this.set = set; } public List<String> getList() { return list; } public void setList(List<String> list) { this.list = list; } }
编写xml文件

@Test /*list集合注入*/ public void sexTest01(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)ctx.getBean("collectionBean"); System.out.println(bean.getList()); } @Test /*set集合注入*/ public void sexTest02(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //set集合 CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)ctx.getBean("collectionBean2"); System.out.println(bean.getSet()); } @Test /*map集合注入*/ public void sexTest03(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //map集合 CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)ctx.getBean("collectionBean3"); System.out.println(bean.getMap().values()); //value值 System.out.println(bean.getMap().keySet()); //key值 } @Test /*properties 注入*/ public void setTest04(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)ctx.getBean("properties"); System.out.println(bean.getProperties()); }
编写测试类

@Test /*list集合注入*/ public static void sexTest01(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)ctx.getBean("collectionBean"); System.out.println(bean.getList()+"==========list"); } @Test /*set集合注入*/ public static void sexTest02(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //set集合 CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)ctx.getBean("collectionBean2"); System.out.println(bean.getSet()+"==========set"); } @Test /*map集合注入*/ public static void sexTest03(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //map集合 CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)ctx.getBean("collectionBean3"); System.out.println(bean.getMap().values()+"==========map"); //value值 System.out.println(bean.getMap().keySet()); //key值 } @Test /*properties 注入*/ public static void sexTest04(){ ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); CollectionBean bean=(CollectionBean)ctx.getBean("properties"); System.out.println(bean.getProperties()+"==========properties"); }
运行结果
1.5使用注解的方式
使用注解方式实现值的注入需要导入命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd ">
以上的文件约束中的context为注解需要导入的命名空间。
在编写xml文件时只需要加入包扫描器即可。
xml文件编写
<!--注解配置包扫描器-->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.spring.note"></context:component-scan>
创建实体类

package cn.spring.note; import cn.spring.entity.*; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import javax.annotation.Resource; /** * Created by accp on 2017/3/23. */ //Component :不分包 //Service: biz层 //Controller: action //Repository: biz @Component("person") public class Person { @Value("张三") private String name; @Value("18")以上是关于Spring 中使用XML配置方式和使用注解方式实现DI的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
