Spring Data JPA 实例查询
Posted 如莲家园
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring Data JPA 实例查询相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、相关接口方法
public interface QueryByExampleExecutor<T> {
<S extends T> S findOne(Example<S> example); //根据“实例”查找一个对象。
<S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example); //根据“实例”查找一批对象
<S extends T> Iterable<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Sort sort); //根据“实例”查找一批对象,且排序
<S extends T> Page<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Pageable pageable); //根据“实例”查找一批对象,且排序和分页
<S extends T> long count(Example<S> example); //根据“实例”查找,返回符合条件的对象个数
<S extends T> boolean exists(Example<S> example); //根据“实例”判断是否有符合条件的对象
}
@NoRepositoryBean public interface JpaRepository<T, ID extends Serializable>
extends PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID>, QueryByExampleExecutor<T> {
......
@Override
<S extends T> List<S> findAll(Example<S> example); //根据实例查询
@Override
<S extends T> List<S> findAll(Example<S> example, Sort sort);//根据实例查询,并排序。
}
二、快速入门
/** * 客户 */ @Entity @Table(name = "demo_lx_Customer") public class Customer extends BaseBo { private String name; //姓名 private String sex; //性别 private int age; //年龄 private String address; //地址 private boolean focus ; //是否重点关注 private Date addTime; //创建时间 private String remark; //备注 @ManyToOne private CustomerType customerType; //客户类型 ...... }
/**
* 客户类型
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "demo_lx_CustomerType")
public class CustomerType extends BaseBo
{
private String code; //编号
private String name; //名称
private String remark; //备注
......
}
2、模拟数据

3、查询
现在要查询:地址是“郑州市”,姓“刘”的客户,可以这样来写:
//创建查询条件数据对象 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setName("刘"); customer.setAddress("河南省郑州市"); //创建匹配器,即如何使用查询条件 ExampleMatcher matcher = ExampleMatcher.matching() //构建对象 .withMatcher("name", GenericPropertyMatchers.startsWith()) //姓名采用“开始匹配”的方式查询 .withIgnorePaths("focus"); //忽略属性:是否关注。因为是基本类型,需要忽略掉 //创建实例 Example<Customer> ex = Example.of(customer, matcher); //查询 List<Customer> ls = dao.findAll(ex); //输出结果 System.out.println("数量:"+ls.size()); for (Customer bo:ls) { System.out.println(bo.getName()); }
数量:1
刘芳
三、认识“实例查询”
1、概念定义:
上面例子中,是这样创建“实例”的:Example<Customer> ex = Example.of(customer, matcher);我们看到,Example对象,由customer和matcher共同创建,为讲解方便,我们先来明确一些定义。
A、实体对象:在持久化框架中与Table对应的域对象,一个对象代表数据库表中的一条记录,如上例中Customer对象。在构建查询条件时,一个实体对象代表的是查询条件中的“数值”部分。如:要查询姓“刘”的客户,实体对象只能存储条件值“刘”。
B、匹配器:ExampleMatcher对象,它是匹配“实体对象”的,表示了如何使用“实体对象”中的“值”进行查询,它代表的是“查询方式”,解释了如何去查的问题。如:要查询姓“刘”的客户,即姓名以“刘”开头的客户,该对象就表示了“以某某开头的”这个查询方式,如上例中:withMatcher("name", GenericPropertyMatchers.startsWith())
C、实例:即Example对象,代表的是完整的查询条件。由实体对象(查询条件值)和匹配器(查询方式)共同创建。
再来理解“实例查询”,顾名思义,就是通过一个例子来查询。要查询的是Customer对象,查询条件也是一个Customer对象,通过一个现有的客户对象作为例子,查询和这个例子相匹配的对象。
2、特点及约束(局限性):
1、支持动态查询。即支持查询条件个数不固定的情况,如:客户列表中有多个过滤条件,用户使用时在“地址”查询框中输入了值,就需要按地址进行过滤,如果没有输入值,就忽略这个过滤条件。对应的实现是,在构建查询条件Customer对象时,将address属性值置具体的条件值或置为null。
2、不支持过滤条件分组。即不支持过滤条件用 or(或) 来连接,所有的过滤查件,都是简单一层的用 and(并且) 连接。
3、仅支持字符串的开始/包含/结束/正则表达式匹配 和 其他属性类型的精确匹配。查询时,对一个要进行匹配的属性(如:姓名 name),只能传入一个过滤条件值,如以Customer为例,要查询姓“刘”的客户,“刘”这个条件值就存储在表示条件对象的Customer对象的name属性中,针对于“姓名”的过滤也只有这么一个存储过滤值的位置,没办法同时传入两个过滤值。正是由于这个限制,有些查询是没办法支持的,例如要查询某个时间段内添加的客户,对应的属性是 addTime,需要传入“开始时间”和“结束时间”两个条件值,而这种查询方式没有存两个值的位置,所以就没办法完成这样的查询。
四、重点理解ExampleMatcher
1、需要考虑的因素
public class ExampleMatcher { NullHandler nullHandler; //Null值处理方式 StringMatcher defaultStringMatcher; //默认字符串匹配方式 boolean defaultIgnoreCase; //默认大小写忽略方式 PropertySpecifiers propertySpecifiers; //各属性特定查询方式 Set<String> ignoredPaths; //忽略属性列表 ...... }
(1)nullHandler:Null值处理方式,枚举类型,有2个可选值,INCLUDE(包括),IGNORE(忽略)。标识作为条件的实体对象中,一个属性值(条件值)为Null是,是否参与过滤。当该选项值是INCLUDE时,表示仍参与过滤,会匹配数据库表中该字段值是Null的记录;若为IGNORE值,表示不参与过滤。
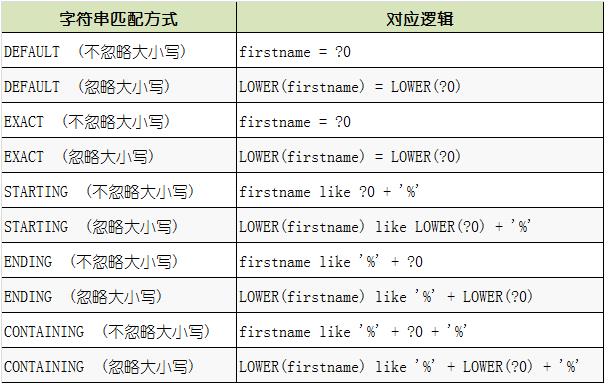
在ExampleMatcher中定义了一系列方式,用于设置这5项设置值,所有的设置方法均返回 ExampleMatcher 对象,所以支持链式编程配置。
(1)创建一个默认的 ExampleMatcher 对象。
定义:
public static ExampleMatcher matching()
默认配置如下:
A、nullHandler:IGNORE。Null值处理方式:忽略
B、defaultStringMatcher:DEFAULT。默认字符串匹配方式:默认(相等)
C、defaultIgnoreCase:false。默认大小写忽略方式:不忽略
D、propertySpecifiers:空。各属性特定查询方式,空。
E、ignoredPaths:空列表。忽略属性列表,空列表。
(2)改变Null值处理方式。
定义:
public ExampleMatcher withNullHandler(NullHandler nullHandler)
public ExampleMatcher withIncludeNullValues()
public ExampleMatcher withIgnoreNullValues()
产生效果:
改变配置项nullHandler,分别设为:指定值、INCLUDE(包括)、IGNORE(忽略)。
(3)改变默认字符串匹配方式。
定义:
public ExampleMatcher withStringMatcher(StringMatcher defaultStringMatcher)
产生效果:
改变配置项defaultStringMatcher,设为指定值。
(4)改变默认大小写忽略方式。
定义:
public ExampleMatcher withIgnoreCase()
public ExampleMatcher withIgnoreCase(boolean defaultIgnoreCase)
产生效果:
改变配置项defaultIgnoreCase,分别设为:true,指定值。
(5)向“忽略属性列表”中添加属性。
定义:
public ExampleMatcher withIgnorePaths(String... ignoredPaths)
产生效果:
改变配置项ignoredPaths,向列表中添加一个或多个属性。
(6)配置属性特定查询方式
一个属性的特定查询方式,包含了3个信息:字符串匹配方式、大小写忽略方式、属性转换器,存储在 propertySpecifiers 中,操作时用 GenericPropertyMatcher 类来传递配置信息。有4个方法来改变配置,这4个方法操作时,内部均采用增量改变的方式,即如果没有为属性定义“特定查询方式”,则会定义一个,并根据传进来的“非空信息”进行配置,如果已经定义有,则会根据传进来的“非空信息”进行更新。如果一个“特定查询方式”中的“字符串匹配方式、大小写忽略方式”没有设置值,查询时则采用ExampleMatcher中的默认配置。
A、自定义类的方式。
定义:
public ExampleMatcher withMatcher(String propertyPath, MatcherConfigurer<GenericPropertyMatcher> matcherConfigurer)
产生效果:
向 propertySpecifiers 中增加或更新属性“特定查询方式”的配置。
参数说明:
propertyPath:要配置特定查询的属性名。
matcherConfigurer:自定义类对象。自定义类需要实现MatcherConfigurer接口,在接口的 configureMatcher() 实现方法中指定相关配置。
B、直接传入通用属性查询对象方式。
定义:
public ExampleMatcher withMatcher(String propertyPath, GenericPropertyMatcher genericPropertyMatcher)
产生效果:
向 propertySpecifiers 中增加或更新属性“特定查询方式”的配置。
参数说明:
propertyPath:要配置特定查询的属性名。
genericPropertyMatcher:直接传入一个通用查询对象。 ExampleMatcher.GenericPropertyMatchers工具类中提供了常用对象创建的静态方法,所有方法均返回 GenericPropertyMatcher 对象,所以支持链式编程配置。
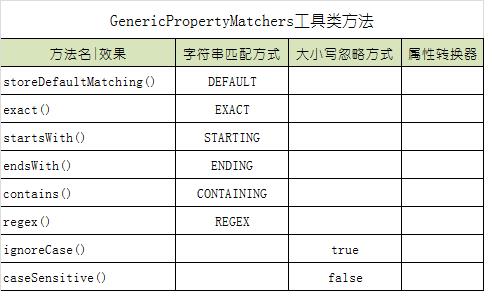
另外:GenericPropertyMatcher 类本身也提供了诸多方法,用于改变相关配置项。
C、改变的大小写忽略方式
定义:
public ExampleMatcher withIgnoreCase(String... propertyPaths)
产生效果:
向 propertySpecifiers 中增加或更新属性“特定查询方式”中的“大小写忽略方式”配置。。
D、设置属性转换器
定义:
public ExampleMatcher withTransformer(String propertyPath, PropertyValueTransformer propertyValueTransformer)
向 propertySpecifiers 中增加或更新属性“特定查询方式”中的“属性转换器”配置。
五、常用情况说明
1、关于基本数据类型。
实体对象中,避免使用基本数据类型,采用包装器类型。如果已经采用了基本类型,
而这个属性查询时不需要进行过滤,则把它添加到忽略列表(ignoredPaths)中。
2、Null值处理方式。
默认值是 IGNORE(忽略),即当条件值为null时,则忽略此过滤条件,一般业务也是采用这种方式就可满足。当需要查询数据库表中属性为null的记录时,可将值设为INCLUDE,这时,对于不需要参与查询的属性,都必须添加到忽略列表(ignoredPaths)中,否则会出现查不到数据的情况。
3、默认配置、特殊配置。
默认创建匹配器时,字符串采用的是精确匹配、不忽略大小写,可以通过操作方法改变这种默认匹配,以满足大多数查询条件的需要,如将“字符串匹配方式”改为CONTAINING(包含,模糊匹配),这是比较常用的情况。对于个别属性需要特定的查询方式,可以通过配置“属性特定查询方式”来满足要求。
4、非字符串属性
如约束中所谈,非字符串属性均采用精确匹配,即等于。
5、忽略大小写的问题。
忽略大小的生效与否,是依赖于数据库的。例如 mysql 数据库中,默认创建表结构时,字段是已经忽略大小写的,所以这个配置与否,都是忽略的。如果业务需要严格区分大小写,可以改变数据库表结构属性来实现,具体可百度。
六、常用查询示例
以“快速入门”中的实体对象和模拟数据为例,列一些常用查询,方便开发时参考。
1、无匹配器的情况
要求:查询地址是“河南省郑州市”,且重点关注的客户。
说明:对于默认匹配器满足条件时,则不需要创建匹配器。
//创建查询条件数据对象 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setAddress("河南省郑州市"); customer.setFocus(true); //创建实例 Example<Customer> ex = Example.of(customer); //查询 List<Customer> ls = dao.findAll(ex); //输出结果 System.out.println("数量:"+ls.size()); for (Customer bo:ls) { System.out.println(bo.getName()); }
输出结果:
数量:4
李明
刘芳
zhang ming
ZHANG SAN
2、通用情况
要求:根据姓名、地址、备注进行模糊查询,忽略大小写,地址要求开始匹配。
说明:这是通用情况,主要演示改变默认字符串匹配方式、改变默认大小写忽略方式、属性特定查询方式配置、忽略属性列表配置。
//创建查询条件数据对象 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setName("zhang"); customer.setAddress("河南省"); customer.setRemark("BB"); //创建匹配器,即如何使用查询条件 ExampleMatcher matcher = ExampleMatcher.matching() //构建对象 .withStringMatcher(StringMatcher.CONTAINING) //改变默认字符串匹配方式:模糊查询 .withIgnoreCase(true) //改变默认大小写忽略方式:忽略大小写 .withMatcher("address", GenericPropertyMatchers.startsWith()) //地址采用“开始匹配”的方式查询 .withIgnorePaths("focus"); //忽略属性:是否关注。因为是基本类型,需要忽略掉 //创建实例 Example<Customer> ex = Example.of(customer, matcher); //查询 List<Customer> ls = dao.findAll(ex); //输出结果 System.out.println("数量:"+ls.size()); for (Customer bo:ls) { System.out.println(bo.getName()); }
输出结果:
数量:2
zhang ming
ZHANG SAN
3、多级查询
要求:查询所有潜在客户
说明:主要演示多层级属性查询
//创建查询条件数据对象 CustomerType type = new CustomerType(); type.setCode("01"); //编号01代表潜在客户 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setCustomerType(type); //创建匹配器,即如何使用查询条件 ExampleMatcher matcher = ExampleMatcher.matching() //构建对象 .withIgnorePaths("focus"); //忽略属性:是否关注。因为是基本类型,需要忽略掉 //创建实例 Example<Customer> ex = Example.of(customer, matcher); //查询 List<Customer> ls = dao.findAll(ex); //输出结果 System.out.println("数量:"+ls.size()); for (Customer bo:ls) { System.out.println(bo.getName()); }
输出结果:
数量:4
李明
李莉
张强
ZHANG SAN
4、查询Null值
要求:地址是null的客户
说明:主要演示改变“Null值处理方式”
//创建查询条件数据对象 Customer customer = new Customer(); //创建匹配器,即如何使用查询条件 ExampleMatcher matcher = ExampleMatcher.matching() //构建对象 .withIncludeNullValues() //改变“Null值处理方式”:包括 .withIgnorePaths("id","name","sex","age","focus","addTime","remark","customerType"); //忽略其他属性 //创建实例 Example<Customer> ex = Example.of(customer, matcher); //查询 List<Customer> ls = dao.findAll(ex); //输出结果 System.out.println("数量:"+ls.size()); for (Customer bo:ls) { System.out.println(bo.getName()); }
输出结果:
数量:2
张强
刘明
七、写在最后
以上是关于Spring Data JPA 实例查询的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章