SimHash算法原理与应用(Java版)
Posted 好好生活_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SimHash算法原理与应用(Java版)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
引言
项目中原使用的文本对比算法是使用MD5 Hash的方法。MD5 Hash算法简单来说是指对于任何长度的文本都可生成一段128bit长度的字符串,相同文本生成的Hash字符串是相同的,因此可用来比较文本是否相同。
但这种传统的Hash算法,对于文本的查找效率是很低的,另外文本间的相似度计算是很困难,因为即使改动文本的一个字符,得到的Hash结果也是完全不同的。因此在新项目中考虑用新的算法去做,对此作了一些技术调研,也收获了一些更好的方法。接下来会在系列博客中总结一些成果。
简要介绍
通过引言,我们已经知道传统Hash的局限性,因此,接下来引入一个名词“局部敏感哈希”。
与传统的Hash不同,局部敏感哈希是一种解决在海量的高维数据集中查找与查询数据点(query data point)近似最相邻的某个或某些数据点的方法。常用的方法包括:欧式距离、余弦距离、海明距离、Jaccard相似度等。本篇博客将介绍的SimHash算法就属于一种局部敏感哈希算法,利用海明距离比较内容之间的相似度。
SimHash是Google用来处理海量文本去重的算法。主要思想是降维,将高维的特征向量转化为一个f位的指纹,通过算出两个指纹的海明距离来确定文本的相似度,海明距离越小,相似度越低。
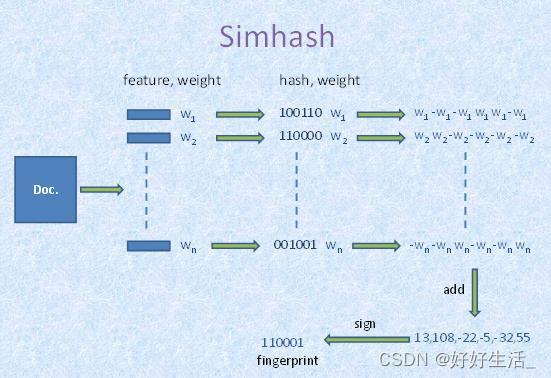
计算原理
- 分词:将处理后的文本(去除特殊字符等)进行分词,可为分词设置权重,得到分词向量
- 计算:通过Hash函数计算每个分词向量的Hash值,值为二进制串
- 加权:计算权重向量=每个分词的hash*该词对应的权重weight
- 合并:将所有分词的权重向量累加,得到一个新的权重向量
- 降维:对上述合并后得到的权重向量,大于0的位置为1,小于等于0的位置为0,从而得到文本的simHash值
核心代码
1. 文本处理,过滤特殊标签,符号统一为半角比较
/**
* 全角转半角
*
* @param text
* @return
*/
public static String toDBC(String text)
char chars[] = text.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++)
if (chars[i] == '\\u3000')
chars[i] = ' ';
else if (chars[i] > '\\uFF00' && chars[i] < '\\uFF5F')
chars[i] = (char) (chars[i] - 65248);
return new String(chars);
/**
* 去除特殊符号
* @param text 文本内容
* @return
*/
private String clearCharacters(String text)
// 将内容转换为小写
text = StringUtils.lowerCase(text);
// 过来html标签
text = Jsoup.clean(text, Whitelist.none());
// 过滤特殊字符
String[] strings = " ", "\\n", "\\r", "\\t", "\\\\r", "\\\\n", "\\\\t", " ", "&", "<", ">", """, "&qpos;";
for (String string : strings)
text = text.replaceAll(string, "");
//符号转换
text = toDBC(text);
//去空格
text = StringUtils.deleteWhitespace(text);
return text;
2. 文本分词,配置分词权重,计算每个分词的Hash值,合并分词向量,得到Hash值
/**
* 计算分词Hash,合并分词向量,得到文本Hash
* @param word
* @return
*/
public BigInteger simHash()
// 对内容进行分词处理
List<Term> terms = StandardTokenizer.segment(this.text);
// 配置词性权重
Map<String, Integer> weightMap = new HashMap<>(16, 0.75F);
weightMap.put("n", 1);
// 设置停用词
Map<String, String> stopMap = new HashMap<>(16, 0.75F);
stopMap.put("w", "");
// 设置超频词上线
Integer overCount = 5;
// 设置分词统计量
Map<String, Integer> wordMap = new HashMap<>(16, 0.75F);
for (Term term : terms)
// 获取分词字符串
String word = term.word;
// 获取分词词性
String nature = term.nature.toString();
// 过滤超频词
if (wordMap.containsKey(word))
Integer count = wordMap.get(word);
if (count > overCount)
continue;
else
wordMap.put(word, count + 1);
else
wordMap.put(word, 1);
// 过滤停用词
if (stopMap.containsKey(nature))
continue;
// 计算单个分词的Hash值
BigInteger wordHash = this.countHash(word);
for (int i = 0; i < this.hashCount; i++)
// 向量位移
BigInteger bitMask = new BigInteger("1").shiftLeft(i);
// 对每个分词hash后的列进行判断,例如:1000...1,则数组的第一位和末尾一位加1,中间的62位减一,也就是,逢1加1,逢0减1,一直到把所有的分词hash列全部判断完
// 设置初始权重
Integer weight = 1;
if (weightMap.containsKey(nature))
weight = weightMap.get(nature);
// 计算所有分词的向量
if (wordHash.and(bitMask).signum() != 0)
hashArray[i] += weight;
else
hashArray[i] -= weight;
// 生成指纹
BigInteger fingerPrint = new BigInteger("0");
for (int i = 0; i < this.hashCount; i++)
if (hashArray[i] >= 0)
fingerPrint = fingerPrint.add(new BigInteger("1").shiftLeft(i));
return fingerPrint;
/**
* 计算每个分词的Hash
* @param word
* @return
*/
private BigInteger countHash(String word)
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(word))
// 如果分词为null,则默认hash为0
return new BigInteger("0");
else
// 分词补位,如果过短会导致Hash算法失败
while (word.length() < SimHashUtil.WORD_MIN_LENGTH)
word = word + word.charAt(0);
// 分词位运算
char[] wordArray = word.toCharArray();
BigInteger x = BigInteger.valueOf(wordArray[0] << 7);
BigInteger m = new BigInteger("1000003");
// 初始桶pow运算
BigInteger mask = new BigInteger("2").pow(this.hashCount).subtract(new BigInteger("1"));
for (char item : wordArray)
BigInteger temp = BigInteger.valueOf(item);
x = x.multiply(m).xor(temp).and(mask);
x = x.xor(new BigInteger(String.valueOf(word.length())));
if (x.equals(ILLEGAL_X))
x = new BigInteger("-2");
return x;
3. 获取文本的海明距离
private int getHammingDistance(SimHashUtil simHashUtil)
// 求差集
BigInteger subtract = new BigInteger("1").shiftLeft(this.hashCount).subtract(new BigInteger("1"));
// 求异或
BigInteger xor = this.bigSimHash.xor(simHashUtil.bigSimHash).and(subtract);
int total = 0;
while (xor.signum() != 0)
total += 1;
xor = xor.and(xor.subtract(new BigInteger("1")));
return total;
4. 文本间海明距离的比较
public Double getSimilar(SimHashUtil simHashUtil)
// 获取海明距离
Double hammingDistance = (double) this.getHammingDistance(simHashUtil);
// 求得海明距离百分比
Double scale = (1 - hammingDistance / this.hashCount) * 100;
Double formatScale = Double.parseDouble(String.format("%.2f", scale));
return formatScale;
测试结果
对于任意一些文本,测试结果如下:

通过多次测试结果发现,该算法对于语意相同、文本较小差异的调整,比如文字顺序的修改、个别字的增加删减,得到的相似度结果都是百分之百。因此更适用于文本比较结果不要求每一个字符都精确完全相同的场景。
参考资料
以上是关于SimHash算法原理与应用(Java版)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章