Android A/B system - bootctrl
Posted Dufre.WC
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android A/B system - bootctrl相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
android A/B system系列
Achitecture
在Android A/B System概述中有讲到A升B的一个例子。下面这张图是想说明两个问题:
- 启动的时候是如何知道要从A启动还是B启动?
- 升级的时候是如何要更新A还是B?
图中有两个流程,和涉及的一些模块:
模块:
- bootloader:启动的早期阶段,叫preloader/lk都行
- misc:单独的一块分区,存放启动的信息,也是今天研究的重点
- update_verifier:当前slot启动成功,会将当前的slot设置为successful,表示这个slot是可以成功启动的
- update_engine:Android负责升级流程的守护进程
- bootctrl HAL:google规定的HAL,各个IC厂商有自己的底层实现,是获取misc信息的软件接口
流程:
- boot flow
- get active slot:读misc的信息,从而知道当前要从slot A启动还是slot B启动
- mark slot successful:启动成功的时候,标记当前slot为successful
- update flow
- trigger update and read update package
- get current slot:获取当前slot,假设当前slot为A,那么要更新slot B;当前为B,那么要更新slot A
- write data to another slot:更新
- set active slot:更新完成以后,切换slot,则下次启动从更新的slot启动

misc
关于misc分区的内容,各个IC厂商各自有不同的结构,但核心思想是类似的,所以这里拿google的结构来分析。
重要的部分为红色标记的:
- active_slot:当前正在运行的slot
- slot_info:每个slot的信息(实际的产品实现不会这么简单)
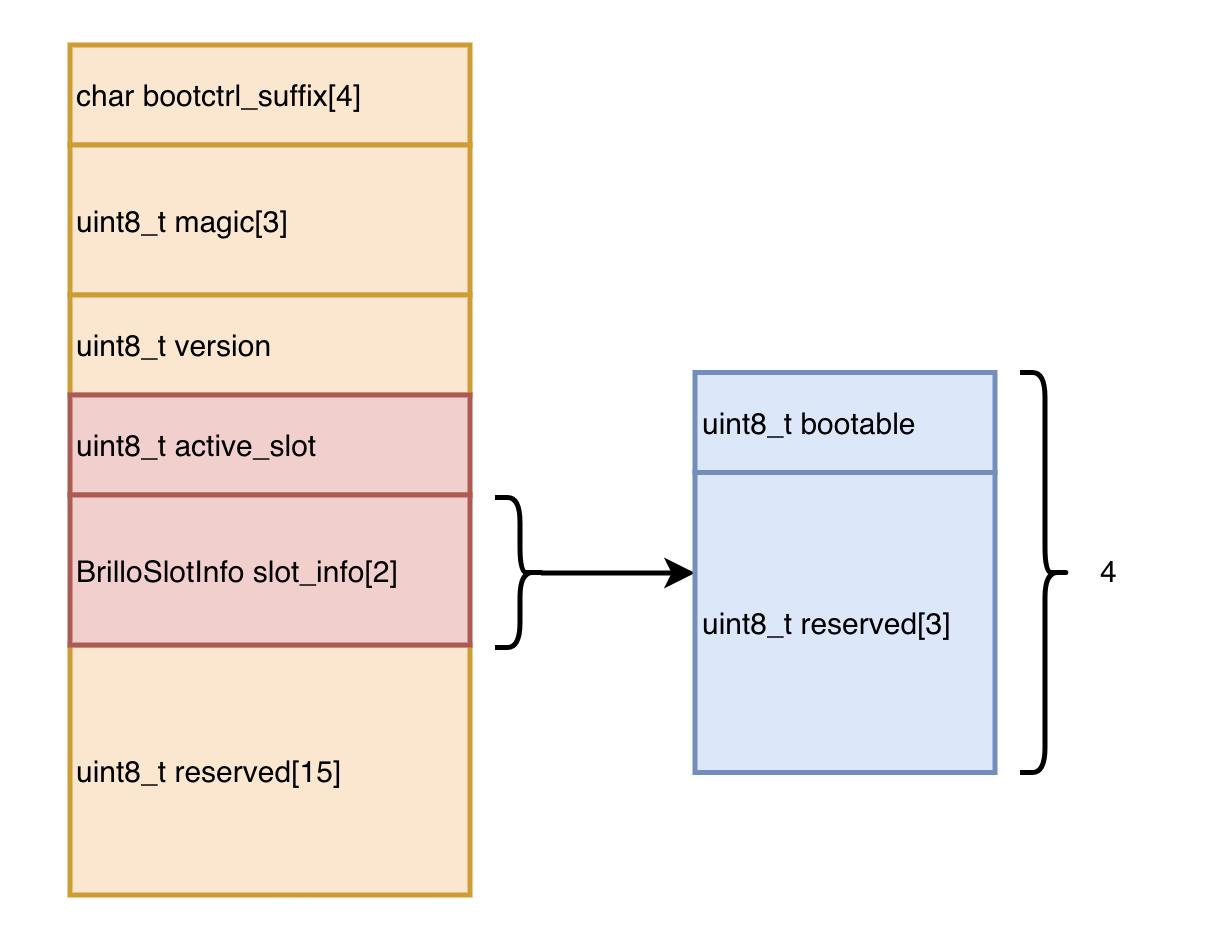
/system/extras/boot_control_copy/bootinfo.h
typedef struct BrilloSlotInfo
uint8_t bootable : 1;
uint8_t reserved[3];
BrilloSlotInfo;
typedef struct BrilloBootInfo
// Used by fs_mgr. Must be NUL terminated.
char bootctrl_suffix[4];
// Magic for identification - must be 'B', 'C', 'c' (short for
// "boot_control copy" implementation).
uint8_t magic[3];
// Version of BrilloBootInfo struct, must be 0 or larger.
uint8_t version;
// Currently active slot.
uint8_t active_slot;
// Information about each slot.
BrilloSlotInfo slot_info[2];
uint8_t reserved[15];
BrilloBootInfo;
根据这个结构,bootinfo.cpp实现了对BrilloBootInfo进行存取操作的接口,这里的操作比较简单,这里就不去研究了。
/system/extras/boot_control_copy/bootinfo.cpp
- 存取操作
bool boot_info_load(BrilloBootInfo *out_info)bool boot_info_save(BrilloBootInfo *info)
- 校验和复位操作
bool boot_info_validate(BrilloBootInfo* info)void boot_info_reset(BrilloBootInfo* info)
- 指定分区的打开操作
int boot_info_open_partition(const char *name, uint64_t *out_size, int flags)
bootctrl
再来看对应bootctrl HAL接口的function是如何实现的
module_getCurrentSlot
unsigned module_getCurrentSlot(boot_control_module_t *module)
struct stat statbuf;
dev_t system_a_dev, system_b_dev;
if (stat("/system", &statbuf) != 0)
fprintf(stderr, "WARNING: Error getting information about /system: %s\\n",
strerror(errno));
return 0;
if (!get_dev_t_for_partition("system_a", &system_a_dev) ||
!get_dev_t_for_partition("system_b", &system_b_dev))
return 0;
if (statbuf.st_dev == system_a_dev)
return 0;
else if (statbuf.st_dev == system_b_dev)
return 1;
else
fprintf(stderr, "WARNING: Error determining current slot "
"(/system dev_t of %d:%d does not match a=%d:%d or b=%d:%d)\\n",
major(statbuf.st_dev), minor(statbuf.st_dev),
major(system_a_dev), minor(system_a_dev),
major(system_b_dev), minor(system_b_dev));
return 0;
module_setActiveBootSlot
- 取出BrilloBootInfo的信息,并校验
- 设置active_slot为传入的slot
- 设置该slot为bootable
- 将对应分区的内容copy到boot中(这里是指partition有三份,boot/boot_a/boot_b,系统每次只从boot启动,这样是不符合A/B system的精神,如果boot启动失败,是不会去切换,那么A/B system的优势是没办法体现的)
int module_setActiveBootSlot(boot_control_module_t *module, unsigned slot)
BrilloBootInfo info;
int src_fd, dst_fd;
uint64_t src_size, dst_size;
char src_name[32];
if (slot >= 2)
return -EINVAL;
if (!boot_info_load(&info))
fprintf(stderr, "WARNING: Error loading boot-info. Resetting.\\n");
boot_info_reset(&info);
else
if (!boot_info_validate(&info))
fprintf(stderr, "WARNING: boot-info is invalid. Resetting.\\n");
boot_info_reset(&info);
info.active_slot = slot;
info.slot_info[slot].bootable = true;
snprintf(info.bootctrl_suffix,
sizeof(info.bootctrl_suffix),
"_%c", slot + 'a');
if (!boot_info_save(&info))
fprintf(stderr, "Error saving boot-info.\\n");
return -errno;
// Finally copy the contents of boot_X into boot.
snprintf(src_name, sizeof(src_name), "boot_%c", slot + 'a');
src_fd = boot_info_open_partition(src_name, &src_size, O_RDONLY);
if (src_fd == -1)
fprintf(stderr, "Error opening \\"%s\\" partition.\\n", src_name);
return -errno;
dst_fd = boot_info_open_partition("boot", &dst_size, O_RDWR);
if (dst_fd == -1)
fprintf(stderr, "Error opening \\"boot\\" partition.\\n");
close(src_fd);
return -errno;
if (src_size != dst_size)
fprintf(stderr,
"src (%" PRIu64 " bytes) and dst (%" PRIu64 " bytes) "
"have different sizes.\\n",
src_size, dst_size);
close(src_fd);
close(dst_fd);
return -EINVAL;
if (!copy_data(src_fd, dst_fd, src_size))
close(src_fd);
close(dst_fd);
return -errno;
if (fsync(dst_fd) != 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Error calling fsync on destination: %s\\n",
strerror(errno));
return -errno;
close(src_fd);
close(dst_fd);
return 0;
以上是关于Android A/B system - bootctrl的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章