MIT 18.01 单变量微积分总结
Posted Xurtle
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MIT 18.01 单变量微积分总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
引言
这篇文章是对 MIT Single Variable Calculus 这个课程的知识点总结。在这个课程中,我遇到一些问题涉及到先前高中学过的知识,同时也有一些比较难理解的或容易混淆的概念,因此我把找到的这些资料链接列在下面(这些资料弥补了我先前忘记的知识,并且加深了对课程内容的理解,非常有帮助):
What is a Function?
Even and Odd Functions
Function Transformations
Inverse function
In what sense is the derivative the “best” linear approximation?
Inflection points introduction
Continuous versus differentiable
How to Detrmine when Limits Don’t Exist
Prove that the derivative of an even differentiable function is odd, and the derivative of an odd is even
limit and continuity
下面是 continuous 的定义:
A function f is continuous at
x0 if limx→x0f(x)=f(x0)
如果一个函数在 x0 处是 continuous 的,那么从下面的定义中,我们可以得出以下3个属性:
- limx→x+0f(x)=limx→x−0f(x)
- f(x0) is defined
- limx→x+0f(x)=limx→x−0f(x)=f(x0)
下面中的链接是关于 limit 的一些属性,和证明这些属性为什么是正确的。
下面我们来证明一个定理,定理的内容如下:
If f is differentiable at
x0 , then f is continuous atx0
如果
f
is continuous at
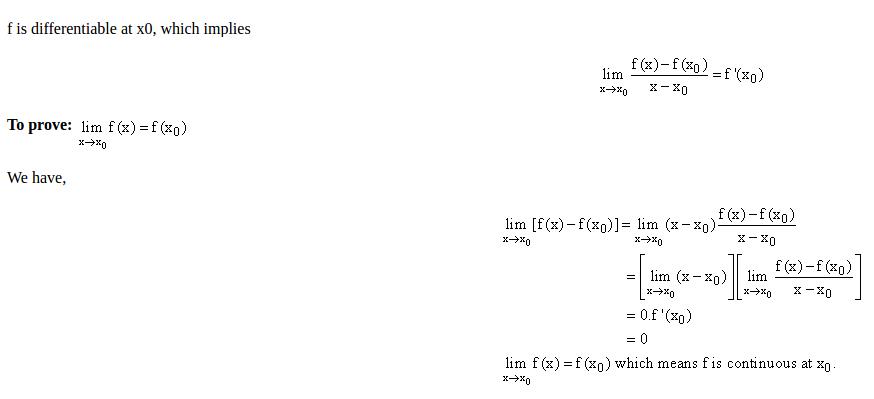
sin 与 cos 导数的证明
在这个 lecture 中,David Jerison 教授讲解了 sin 与 cos 函数导数的代数与几何证明,在具体证明之前,让我们首先求出2个极限的解,它们分别是:
limΔx→0.cosΔx−1Δx=0limΔx→0.sinΔxΔx=1
我们首先来证明第2个极限,下图是个单位圆,角度 θ is described in radians but NOT when it is measured in degrees.
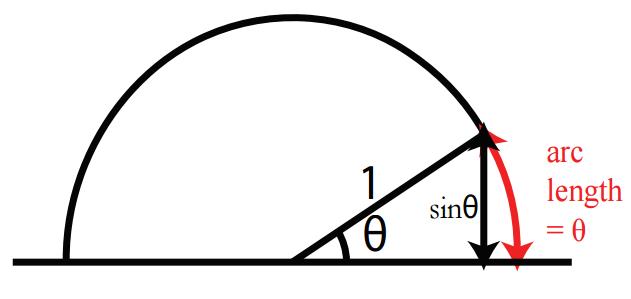
把第2个极限中的 Δx 用 θ 替换,我们可以看出当 θ 无限接近于0时, sinθ 与 arc length(即 θ )无限接近,因此我们可以总结出:
limx→0.sinxx=1
接下来让我们来求第1个极限,下图来自于单位圆的一部分,我们可以看出当 θ 无限接近于0时, 1−cosθ 无限接近接近于0,因此我们可以总结出:
limx→0.cosx−1x=0
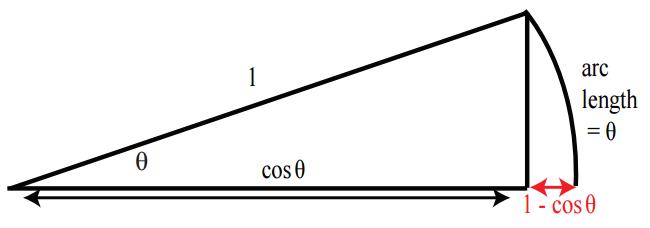
上面的几何证明过程中,有2个重点我需要解释一下:
1、在MIT的课堂上,我看到很多同学会问到:当 θ 无限接近于0时, 1−cosθ 无限接近接近于0,同时 arc length 不也接近于0吗?这里我们忽略了一个重点,就是