URL中嵌套用户名:密码的问题处理(base64加密的方式)
Posted alen_xie
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了URL中嵌套用户名:密码的问题处理(base64加密的方式)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在添加一个新功能时,发现需要URL中嵌套user name 和passwd时,发现通过普通的方式,获取不到资源,常会被服务器拒绝掉,反馈403信息。
通过分析这个url,发现服务器端使用了一个很简单的加密协议。分析发现,使用的是base64位加密,把user and passwd 通过base64加密成一串字符串,然后在request header 上添加上,然后再去请求。就可以获取到资源了。
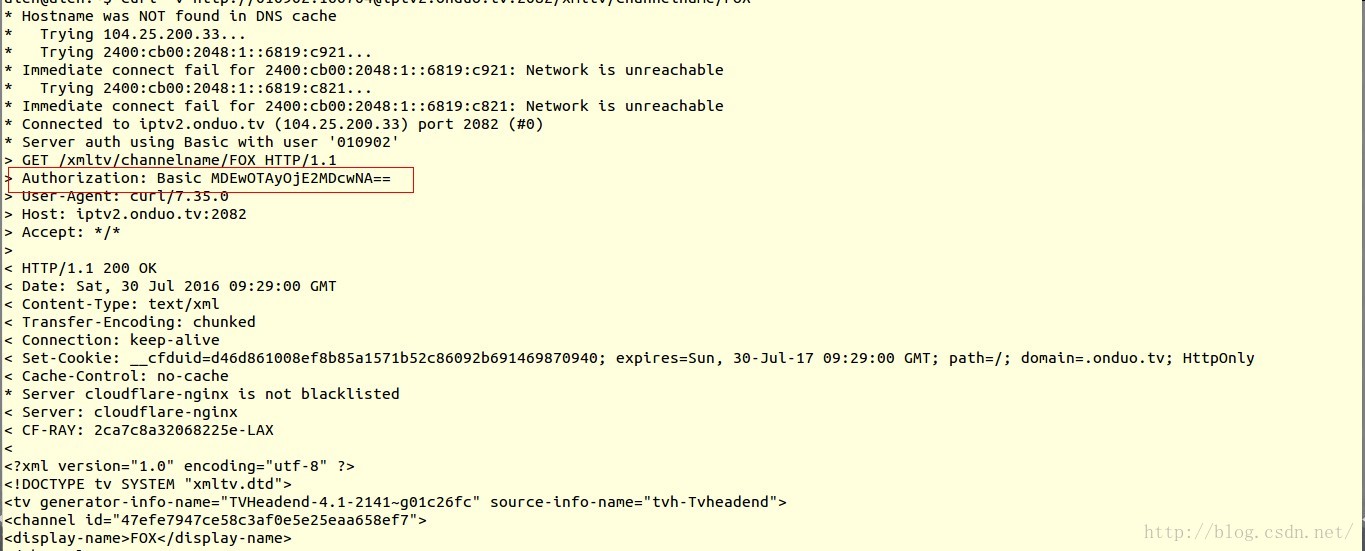
加密以及解密的code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
const char base64char[] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/";
char *http_base64_encode(unsigned char *bindata, char * base64, int binlength)
int i, j;
unsigned char current;
for (i = 0, j = 0; i < binlength; i += 3)
current = (bindata[i] >> 2);
current &= (unsigned char)0x3F;
base64[j++] = base64char[(int)current];
current = ((unsigned char)(bindata[i] << 4)) & ((unsigned char)0x30);
if (i + 1 >= binlength)
base64[j++] = base64char[(int)current];
base64[j++] = '=';
base64[j++] = '=';
break;
current |= ((unsigned char)(bindata[i + 1] >> 4)) & ((unsigned char)0x0F);
base64[j++] = base64char[(int)current];
current = ((unsigned char)(bindata[i + 1] << 2)) & ((unsigned char)0x3C);
if (i + 2 >= binlength)
base64[j++] = base64char[(int)current];
base64[j++] = '=';
break;
current |= ((unsigned char)(bindata[i + 2] >> 6)) & ((unsigned char)0x03);
base64[j++] = base64char[(int)current];
current = ((unsigned char)bindata[i + 2]) & ((unsigned char)0x3F);
base64[j++] = base64char[(int)current];
base64[j] = '\\0';
return base64;
int http_base64_decode(const char * base64, unsigned char * bindata)
int i, j;
unsigned char k;
unsigned char temp[4];
for (i = 0, j = 0; base64[i] != '\\0'; i += 4)
memset(temp, 0xFF, sizeof(temp));
for (k = 0; k < 64; k++)
if (base64char[k] == base64[i])
temp[0] = k;
for (k = 0; k < 64; k++)
if (base64char[k] == base64[i + 1])
temp[1] = k;
for (k = 0; k < 64; k++)
if (base64char[k] == base64[i + 2])
temp[2] = k;
for (k = 0; k < 64; k++)
if (base64char[k] == base64[i + 3])
temp[3] = k;
bindata[j++] = ((unsigned char)(((unsigned char)(temp[0] << 2)) & 0xFC)) | ((unsigned char)((unsigned char)(temp[1] >> 4) & 0x03));
if (base64[i + 2] == '=')
break;
bindata[j++] = ((unsigned char)(((unsigned char)(temp[1] << 4)) & 0xF0)) | ((unsigned char)((unsigned char)(temp[2] >> 2) & 0x0F));
if (base64[i + 3] == '=')
break;
bindata[j++] = ((unsigned char)(((unsigned char)(temp[2] << 6)) & 0xF0)) | ((unsigned char)(temp[3] & 0x3F));
return j;
snprintf(pcRequest, iRequestBuffSize, "GET /%s HTTP/1.1\\r\\n"
"Authorization: Basic %s\\r\\n"
"User-Agent: curl/7.35.0\\r\\n"
"Host: %s\\r\\nConnection: keep-alive\\r\\n"
"Accept: */*\\r\\n\\r\\n",
pcFile, acEncodeBuff, acHost);就可以获取到资源了.
改进版本:
偶然的机会,阅读了一个libghttp源码(有局限性,只支持http,适合入门学习),发现上面也使用了bash64的encode,发现它那个写的比上面的好很多,相对上者,比较清晰明了简介,虽然实现的效果是一样的,但是更倾向于下着,所以,分享一下,后期遇到这种问题可以直接拿来使用。
const char b64_alphabet[65] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
"0123456789+/=";
char *http_base64_encode(const char *text)
/* The tricky thing about this is doing the padding at the end,
* doing the bit manipulation requires a bit of concentration only */
char *buffer = NULL;
char *point = NULL;
int inlen = 0;
int outlen = 0;
/* check our args */
if (text == NULL)
return NULL;
/* Use 'buffer' to store the output. Work out how big it should be...
* This must be a multiple of 4 bytes */
inlen = strlen(text);
/* check our arg...avoid a pesky FPE */
if (inlen == 0)
buffer = malloc(sizeof(char));
buffer[0] = '\\0';
return buffer;
outlen = (inlen * 4) / 3;
if ((inlen % 3) > 0) /* got to pad */
outlen += 4 - (inlen % 3);
buffer = malloc(outlen + 1); /* +1 for the \\0 */
memset(buffer, 0, outlen + 1); /* initialize to zero */
/* now do the main stage of conversion, 3 bytes at a time,
* leave the trailing bytes (if there are any) for later */
for (point = buffer; inlen >= 3; inlen -= 3, text += 3)
*(point++) = b64_alphabet[*text >> 2];
*(point++) = b64_alphabet[(*text << 4 & 0x30) | *(text + 1) >> 4];
*(point++) = b64_alphabet[(*(text + 1) << 2 & 0x3c) | *(text + 2) >> 6];
*(point++) = b64_alphabet[*(text + 2) & 0x3f];
/* Now deal with the trailing bytes */
if (inlen)
/* We always have one trailing byte */
*(point++) = b64_alphabet[*text >> 2];
*(point++) = b64_alphabet[(*text << 4 & 0x30) | (inlen == 2 ? *(text + 1) >> 4 : 0)];
*(point++) = (inlen == 1 ? '=' : b64_alphabet[*(text + 1) << 2 & 0x3c]);
*(point++) = '=';
*point = '\\0';
return buffer;
分析wget源码时,看到base64的另一种加密方式,可以参考选择哪个方式
/* Encode the octets in DATA of length LENGTH to base64 format,
storing the result to DEST. The output will be zero-terminated,
and must point to a writable buffer of at least
1+BASE64_LENGTH(length) bytes. The function returns the length of
the resulting base64 data, not counting the terminating zero.
This implementation does not emit newlines after 76 characters of
base64 data. */
int base64_encode(const void *data, int length, char *dest)
/* Conversion table. */
static const char tbl[64] = 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U',
'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u',
'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '+', '/';
/* Access bytes in DATA as unsigned char, otherwise the shifts below
don't work for data with MSB set. */
const unsigned char *s = data;
/* Theoretical ANSI violation when length < 3. */
const unsigned char *end = (const unsigned char *)data + length - 2;
char *p = dest;
/* Transform the 3x8 bits to 4x6 bits, as required by base64. */
for (; s < end; s += 3)
*p++ = tbl[s[0] >> 2];
*p++ = tbl[((s[0] & 3) << 4) + (s[1] >> 4)];
*p++ = tbl[((s[1] & 0xf) << 2) + (s[2] >> 6)];
*p++ = tbl[s[2] & 0x3f];
/* Pad the result if necessary... */
switch (length % 3)
case 1:
*p++ = tbl[s[0] >> 2];
*p++ = tbl[(s[0] & 3) << 4];
*p++ = '=';
*p++ = '=';
break;
case 2:
*p++ = tbl[s[0] >> 2];
*p++ = tbl[((s[0] & 3) << 4) + (s[1] >> 4)];
*p++ = tbl[((s[1] & 0xf) << 2)];
*p++ = '=';
break;
/* ...and zero-terminate it. */
*p = '\\0';
return p - dest;
/* Store in C the next non-whitespace character from the string, or \\0
when end of string is reached. */
#define NEXT_CHAR(c, p) do \\
c = (unsigned char) *p++; \\
while (ISSPACE (c))
#define IS_ASCII(c) (((c) & 0x80) == 0)
/* Decode data from BASE64 (a null-terminated string) into memory
pointed to by DEST. DEST is assumed to be large enough to
accomodate the decoded data, which is guaranteed to be no more than
3/4*strlen(base64).
Since DEST is assumed to contain binary data, it is not
NUL-terminated. The function returns the length of the data
written to TO. -1 is returned in case of error caused by malformed
base64 input.
This function originates from Free Recode. */
int base64_decode(const char *base64, void *dest)
/* Table of base64 values for first 128 characters. Note that this
assumes ASCII (but so does Wget in other places). */
static const signed char base64_char_to_value[128] = -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, /* 0- 9 */
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, /* 10- 19 */
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, /* 20- 29 */
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, /* 30- 39 */
-1, -1, -1, 62, -1, -1, -1, 63, 52, 53, /* 40- 49 */
54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, -1, -1, /* 50- 59 */
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, /* 60- 69 */
5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, /* 70- 79 */
15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, /* 80- 89 */
25, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 26, 27, 28, /* 90- 99 */
29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, /* 100-109 */
39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, /* 110-119 */
49, 50, 51, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 /* 120-127 */
;
#define BASE64_CHAR_TO_VALUE(c) ((int) base64_char_to_value[c])
#define IS_BASE64(c) ((IS_ASCII (c) && BASE64_CHAR_TO_VALUE (c) >= 0) || c == '=')
const char *p = base64;
char *q = dest;
while (1)
unsigned char c;
unsigned long value;
/* Process first byte of a quadruplet. */
NEXT_CHAR(c, p);
if (!c)
break;
if (c == '=' || !IS_BASE64(c))
return -1; /* illegal char while decoding base64 */
value = BASE64_CHAR_TO_VALUE (c) << 18;
/* Process second byte of a quadruplet. */
NEXT_CHAR(c, p);
if (!c)
return -1; /* premature EOF while decoding base64 */
if (c == '=' || !IS_BASE64(c))
return -1; /* illegal char while decoding base64 */
value |= BASE64_CHAR_TO_VALUE (c) << 12;
*q++ = value >> 16;
/* Process third byte of a quadruplet. */
NEXT_CHAR(c, p);
if (!c)
return -1; /* premature EOF while decoding base64 */
if (!IS_BASE64(c))
return -1; /* illegal char while decoding base64 */
if (c == '=')
NEXT_CHAR(c, p);
if (!c)
return -1; /* premature EOF while decoding base64 */
if (c != '=')
return -1; /* padding `=' expected but not found */
continue;
value |= BASE64_CHAR_TO_VALUE (c) << 6;
*q++ = 0xff & value >> 8;
/* Process fourth byte of a quadruplet. */
NEXT_CHAR(c, p);
if (!c)
return -1; /* premature EOF while decoding base64 */
if (c == '=')
continue;
if (!IS_BASE64(c))
return -1; /* illegal char while decoding base64 */
value |= BASE64_CHAR_TO_VALUE(c);
*q++ = 0xff & value;
#undef IS_BASE64
#undef BASE64_CHAR_TO_VALUE
return q - (char *)dest;
以上是关于URL中嵌套用户名:密码的问题处理(base64加密的方式)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章