Service Android
Posted Andy__Wu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Service Android相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
引言
Service 服务是 android 系统最常用的四大部件之一,Android 支持 Service 服务的原因主要目的有两个,一是简化后台任务的实现,二是实现在同一台设备当中跨进程的远程信息通信。
Service 服务主要分为 Local Service 本地服务与 Remote Service 远程服务两种,本地服务只支持同一进程内的应用程序进行访问,远程服务可通过AIDL(Android Interface Definition Language)技术支持跨进程访问。服务可以通过Context.startService()和Context.bindService()进行启动,一般Local Service本地服务可使用其中一种方法启动,但Remote Service远程服务只能使用Context.bindService()启动,而两种调用方式在使用场景与活动流程中都存在差异。还有通过多线程技术处理 Service 服务的延时操作等技术,下文将针对Android 系统的 Service 服务的一系列操作进行深入探讨。
目录
一、Android Service的概念与说明
1.1 Service 服务的定义
Android Service 是 Android 平台最常用的部件之一,其概念与 Windows Service 类似,熟悉Windows开发的朋友应该对此概念会有所了解。当 Android 系统需要对现有的程序数据进行监听,或者对现有 Actitvity 提供数据服务支撑时,就会使用到 Android Service 。例如:对用户地理位置的检测,对SD卡定时扫描,对当地气候的定期检测都会使用到 Service 服务,Service 一般都是运行于后台,不需要用户界面支撑。Service 服务不会自动创建线程,如果开发人员没有为Service服务添加异步操作,那Service服务将运行于主线程当中。
1.2 Service 服务的类型
1.2.1 按照 Service 的生命周期模型一共分为两种类型
第一类是直接通过Context.startService()启动,通过Context.stopService() 结束Service,其特点在于调用简单,方便控制。缺点在于一旦启动了 Service 服务,除了再次调用或结束服务外就再无法对服务内部状态进行操控,缺乏灵活性。
第二类是通过Context.bindService()启动,通过Context.unbindService() 结束,相对其特点在运用灵活,可以通过 IBinder 接口中获取 Service 的句柄,对 Service 状态进行检测。
从 Android 系统设计的架构上看,startService() 是用于启动本地服务,bindService() 更多是用于对远程服务进行绑定。当然,也可以结合两者进行混合式应用,先通过startService()启动服务,然后通过 bindService() 、unbindService()方法进行多次绑定,以获取 Service 服务在不同状态下的信息,最后通过stopService()方法结束Service运行,在下面文章里将举例一一说明。
1.2.2 按照 Service 的寄存方式分为两种类型
本地服务 (Local Service) 寄存于当前的进程当中,当前进程结束后 Service 也会随之结束,Service 可以随时与 Activity 等多个部件进行信息交换。Service服务不会自动启动线程,如果没有人工调用多线程方式进行启动,Service将寄存于主线程当中。
远程服务 (Remote Service ) 独立寄存于另一进程中, 通过 AIDL (Android Interface Definition Language)接口定义语言,实现Android设备上的两个进程间通信(IPC)。AIDL 的 IPC 机制是基于 RPC (Remote Proceduce Call) 远程过程调用协议建立的,用于约束两个进程间的通讯规则,供编译器生成代码。进程之间的通信信息,首先会被转换成AIDL协议消息,然后发送给对方,对方收到AIDL协议消息后再转换成相应的对象,其使用方法在下文将会详细说明。
二、Android Service 的生命周期
2.1 Service 服务的常用方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
| void onCreate() | 当Service被启动时被触发,无论使用Context.startServcie还是Context.bindService启动服务,在Service整个生命周期内只会被触发一次 |
| int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) | 当通过Context.startService启动服务时将触发此方法,但当使用 Context.bindService 方法时不会触发此方法,其中参数 intent 是 startCommand 的输入对象,参数 flags 代表 service 的启动方式,参数 startId 当前启动 service 的唯一标式符。返回值决定服务结束后的处理方式,下文将再作详细说明。 |
| void onStart(Intent intent,int startId) | 2.0旧版本的方法,已被Android抛弃,不推荐使用,默认在onStartCommand 执行中会调用此方法 |
| IBinder onBind(Intent intent) | 使用 Context.bindService 触发服务时将调用此方法,返回一个IBinder 对象,在远程服务时可用于对 Service 对象进行远程操控 |
| void onRebind(Intent intent) | 当使用startService启动Service,调用bindService启动Service,且 onUnbind 返回值为 true 时,下次再次调用 Context.bindService 将触发方法 |
| boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) | 调用 Context.unbindService 触发此方法,默认返回 false, 当返回值 true 后,再次调用 Context.bindService 时将触发 onRebind 方法 |
| void onDestory() | 分三种情况:1.以Context.startService启动service,调用Context.stopService结束时触发此方法;2.以Context.bindService启动service,以Context.unbindService结束时触发此方法;3.先以Context.startService 启动服务,再用Context.bindService绑定服务,结束时必须先调用Context.unbindService解绑再使用Context.stopService结束service才会触发此方法。 |
表2.1
- 细说onStartCommand 方法
由于手机的RAM、内部资源有限,所以很多Service都会因为资源不足而被Kill掉,这时候返回值就决定了Service被Kill后的处理方式,一般 int onStartCommand(intent,flags,startId)的返回值分为以下几种:
START_STICKY
如果service进程被kill掉,系统会尝试重新创建Service,如果在此期间没有任何启动命令被传递到Service,那么参数intent将为null。
START_NOT_STICKY
使用这个返回值时,如果在执行完onStartCommand()后,服务被异常kill掉,系统不会自动重启该服务。
START_REDELIVER_INTENT
使用这个返回值时,如果在执行完onStartCommand()后,服务被异常kill掉,系统会自动重启该服务,并将intent的值传入。
而输入参数flags正是代表此次onStartCommand()方法的启动方式,正常启动时,flags默认为0,被kill后重新启动,参数分为以下两种:
START_FLAG_RETRY
代表service被kill后重新启动,由于上次返回值为START_STICKY,所以参数 intent 为null
START_FLAG_REDELIVERY
代表service被kill后重新启动,由于上次返回值为START_REDELIVER_INTENT,所以带输入参数intent
2.2 Service 的运作流程
上文曾经提到 Service 的启动方法有Context.startService(intent),Context.bindService(intent,serviceConnection,int) 两种,下面详细介绍一下它们工作流程。
当系统调用Context.startService()方法时,先会触发Service的onCreate()方法,这一般用于对Service的运行条件作初始化处理,且在Service的生命周期内只会被触发一次。然后系统将触发Service的onStartCommand()方法,用户每次调用startService()方法,都会触发onStartCommand()方法。之后,Service 除非在资源不足的情况下被系统 kill 掉,否则Service不会自动结束,直至系统调用Context.stopService()方法时,Service 才会结束。在Service结束时将自动启动onDestory()方法对运转中的Service作最后处理。
注意:即使系统多次调用 startService()或 bindService()方法, onCreate() 方法只会在第一次调用时被触发。同理 onDestory () 方法也只会在服务完结时被触发,其原理可看第2.1节该方法的详细说明。
当系统调用Context.bindService()方法时,也会触发Service的onCreate()方法对Service对象的运行条件作初始化处理,然后触发Service 的 onBind ()方法对服务进行绑定,成功获取Service的句柄后,系统就会通过用户自定义的serviceConnection对象onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service)方法,对 Service 对象作出处理。最后当系统调用Context.unbindService()结束服务时,就会激发Service的onDestory()方法对运转中的 Service 作最后的处理。
注意:系统调用 Context.bindService()方法,完成 Service.onBind() 绑定后就会触发 serviceConnection对象的 onServiceConnected()方法,但只要系统未使用 Context.unbindService()方法对 service 服务进行解绑,即使多次调用 bindService(),系统也只会在第一次绑定时调用 onBind() 和 onServiceConnected方()法一次。这正是 startService()与 bindService()方法其中的区别,单从字面上理解 startService () 启动服务是可以多次执行,所以多次调用 startService()方法都会触发 onStartCommand()事件,而 bindService() 是绑定服务,所以只要服务已经被绑定,在未解绑时也不会多次执行onServiceConnected()绑定后的操作,这也是两者在使用场景上的区别所在。
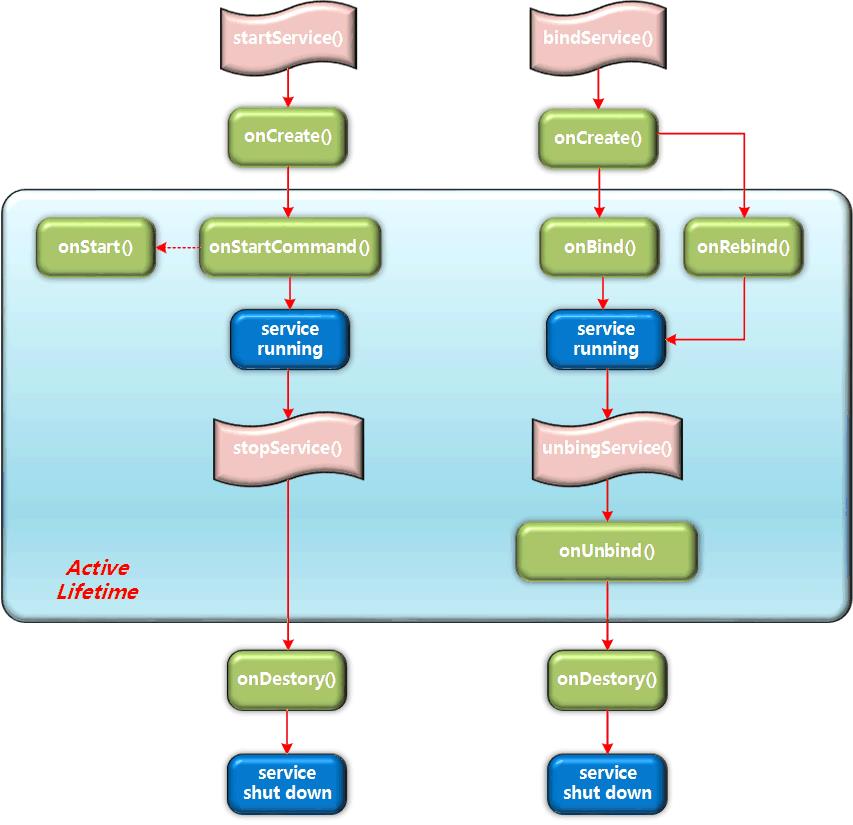
Service 生命周期 图2.2
Service 的运转流程就先介绍到这里,具体的使用方法将在下面的章节中详细介绍。
三、Local Service 应用原理与开发实例
3.1 通过 Context.startService 启动 Service 服务
首先建立MyService继承Service,实现onCreate()、onDestory()、onStartCommand()、onStart()等几个方法,使用日志记录其运作信息。在Activity中通过Intent绑定Service服务,通过Context.startService()启动服务,通过Context.stopService()结束服务。

1 public class MainActivity extends Activity 2 3 @Override 4 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) 5 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 6 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 7 8 9 public void btnStart_onclick(View view) 10 //通过Intent绑定MyService,加入输入参数 11 Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this,MyService.class); 12 intent.putExtra("Name", "Leslie"); 13 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, "----------onClick startService-----------"); 14 //启动MyService 15 startService(intent); 16 17 18 public void btnStop_onclick(View view) 19 Intent intent=new Intent(MainActivity.this,MyService.class); 20 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, "----------onClick stopService------------"); 21 //停止MyService 22 stopService(intent); 23 24 25 26 public class MyService extends Service 27 28 @Override 29 public void onCreate() 30 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE,"Service onCreate"); 31 super.onCreate(); 33 34 35 @Override 36 public void onDestroy() 37 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, "Service onDestroy"); 38 super.onDestroy(); 39 40 41 @Override 42 public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) 43 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE,"Service onStart"); 44 super.onStart(intent, startId); 45 46 47 @Override 48 public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) 49 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, "Service onStartCommand"); 50 String name=intent.getStringExtra("Name"); 51 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE,"His name is "+name); 52 return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); 53 54

AndroidManifest.xml 文件绑定

1 <activity 2 android:name=".MainActivity" 3 android:label="@string/title_activity_main" > 4 <intent-filter> 5 <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> 6 <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> 7 </intent-filter> 8 </activity> 9 <service 10 android:name="android.services.MyService" 11 android:enabled="true"> 12 </service>

Service 配置说明:
- android:name 服务类名,注意如果Service与Activity不在同一个包中,在android:name上必须写上Service的全路径
- android:label 服务的名字,如果为空,默认显示的服务名为类名
- android:icon 服务的图标
- android:permission 申明此服务的权限,这意味着只有提供了该权限的应用才能控制或连接此服务
- android:process 表示该服务是否运行在另外一个进程,如果设置了此项,那么将会在包名后面加上这段字符串表示另一进程的名字
- android:enabled 如果此项设置为 true,那么 Service 将会默认被系统启动,默认值为 false
- android:exported 表示该服务是否能够被其他应用程序所控制或连接,默认值为 false
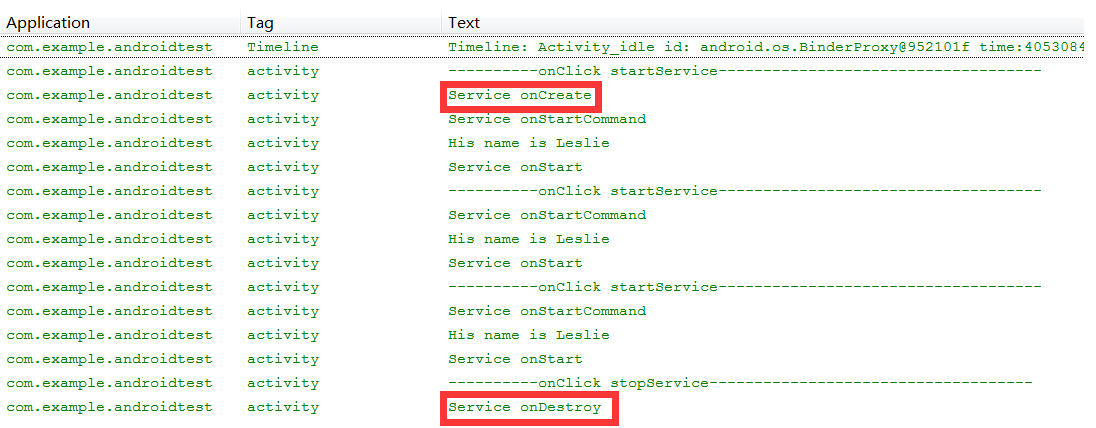
查看处理结果可清楚看到,多次调用startService()后,使用stopService()结束Service服务,onCreate()、onDestory()只会在Service启动和结束时被调用一次。只有Service中的onStartCommand()方法会被多次调用。而Android 2.0以下旧版的方法onStart()会在onStartCommand()调用过程中被激发。
3.2 通过Context.bindService启动Service服务
在介绍Context.bindService()前,先讲解一下与此相关的常用类 Binder、ServiceConnection,首先 IBinder 是 Binder 远程对象的基本接口,是为高性能而设计的轻量级远程调用机制的核心部分。这个接口定义了与远程对象交互的协议,但它不仅用于远程调用,也用于进程内调用。系统可以通过它以获取Service的句柄,在此先简单介绍它的基本用法,在下面关于Remote Service远程服务对象时再详细讲述IBinder的主体功能。ServiceConnection主要用于通过Binder绑定Service句柄后,对Service对象进行处理,它主要有两个方法void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service)和void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name)。在Context.bindService()完成绑定后,系统就会调用 onServiceConnected() 方法,用户可以通过 IBinder 参数获取Service句柄,对Service进行处理。而 onServiceDisconnected() 方法一般不会被调用,只有Service被绑定后,由于内存不足等问题被意外 kill 时才会被调用。下面举个例子说明一下bindService()的用法。

1 public class MainActivity extends Activity 2 private MyServiceConnection serviceConnection; 3 4 @Override 5 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) 6 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 7 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 8 9 serviceConnection=new MyServiceConnection(); 10 11 12 public void btnBind_onclick(View view) 13 //绑定 MyService 14 Intent intent=new Intent(this,MyService.class); 15 16 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, "----------onClick bindService-----------"); 17 //通过bindService(intent,serviceConnection,int)方式启动Service 18 bindService(intent,this.serviceConnection,Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); 19 20 21 public void btnUnbind_onclick(View view) 22 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, "----------onClick unbindService----------"); 23 unbindService(serviceConnection); 24 25 26 27 public class MyService extends Service 28 private MyBinder myBinder; 29 30 @Override 31 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) 32 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE,"Service onBind"); 33 return this.myBinder; 34 35 36 @Override 37 public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) 38 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE,"Service onUnbind"); 39 return super.onUnbind(intent); 40 41 42 @Override 43 public void onCreate() 44 super.onCreate(); 45 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE,"Service onCreate"); 46 myBinder=new MyBinder(); 47 48 49 @Override 50 public void onDestroy() 51 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, "Service onDestroy"); 52 super.onDestroy(); 53 54 55 public String getDate() 56 Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); 57 return calendar.getTime().toString(); 58 59 60 public class MyBinder extends Binder 61 public MyService getService() 62 return MyService.this; 63 64 65 66 67 public class MyServiceConnection implements ServiceConnection 68 69 @Override 70 public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) 71 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, "Service Connected"); 72 String data=null; 73 //通过IBinder获取Service句柄 74 MyService.MyBinder myBinder=(MyService.MyBinder)service; 75 MyService myService=myBinder.getService(); 76 data=myService.getDate(); 77 78 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE,data); 79 80 81 @Override 82 public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) 83 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, "Service Disconnected"); 84 85

在运行时多次点击按钮激发btnBind_onclick(View view)方法后再使用btnUnbind_onclick(View view)结束服务,请留意处理结果。当系统调用Context .bindService()后,Service将跟随onCreate()、onBind()、onUnbind()、onDestory()的流程走下去。在成功完成onBind()绑定后,就会激发ServiceConnection对象的onServiceConnected()方法,在此用户可对Service进行处理。记得第2.2节所提过的问题,即使多次调用Context.bindService()方法,只要没有调用unbindService()结束绑定,系统只会在第一次调用时激发Service.onBind()和onServiceConnected()方法,这点从运行结果中可得到证实。
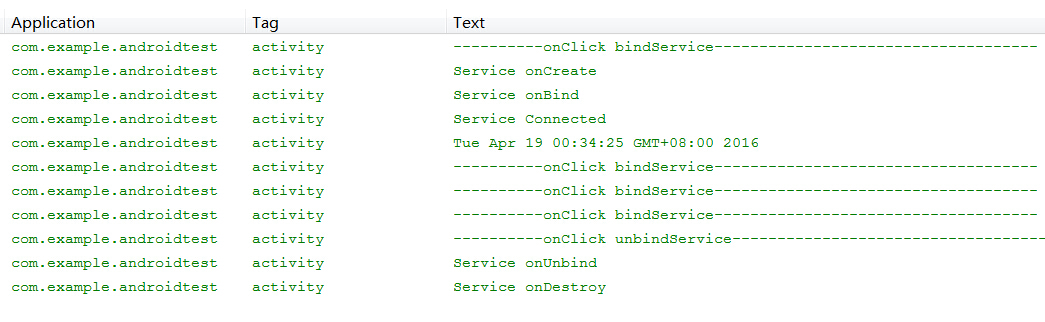
注意:调用 Context .bindService() 启动 Service 后 ,只能调用 unbindService() 一次,如重复多次调用此方法系统将会抛出错误异常。所以最简单的处理方式是设置一个静态变量 boolean connected,在调用 unbindService() 前先作出判断

1 public class MainActivity extends Activity 2 private MyServiceConnection serviceConnection; 3 private static boolean connected; 4 5 @Override 6 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) 7 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 8 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 9 10 serviceConnection=new MyServiceConnection(); 11 12 13 public void btnBind_onclick(View view) 14 connected=true; 15 //绑定 MyService 16 Intent intent=new Intent(this,MyService.class); 17 18 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, "----------onClick bindService-----------"); 19 //通过bindService(intent,serviceConnection,int)方式启动Service 20 bindService(intent,this.serviceConnection,Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); 21 22 23 public void btnUnbind_onclick(View view) 24 Log.i(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, "----------onClick unbindService----------"); 25 if(connected) 26 unbindService(serviceConnection);